
The Commodore 1581 is a 3½-inch double-sided double-density floppy disk drive that was released by Commodore Business Machines (CBM) in 1987, primarily for its C64 and C128 home/personal computers. The drive stores 800 kilobytes using an MFM encoding but formats different from the MS-DOS, Amiga, and Mac Plus formats. With special software it's possible to read C1581 disks on an x86 PC system, and likewise, read MS-DOS and other formats of disks in the C1581, provided that the PC or other floppy handles the "720 kB" size format. This capability was most frequently used to read MS-DOS disks. The drive was released in the summer of 1987 and quickly became popular with bulletin board system (BBS) operators and other users.

The Commodore 1571 is Commodore's high-end 5¼" floppy disk drive. With its double-sided drive mechanism, it has the ability to use double-sided, double-density (DS/DD) floppy disks natively. This is in contrast to its predecessors, the 1541 and 1570, which can fully read and write such disks only if the user manually flipped them over to access the second side. Because flipping the disk also reverses the direction of rotation, the two methods are not interchangeable; disks which had their back side created in a 1541 by flipping them over would have to be flipped in the 1571 too, and the back side of disks written in a 1571 using the native support for two-sided operation could not be read in a 1541.
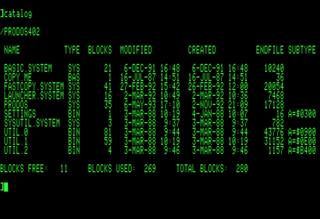
ProDOS is the name of two similar operating systems for the Apple II series of personal computers. The original ProDOS, renamed ProDOS 8 in version 1.2, is the last official operating system usable by all 8-bit Apple II series computers, and was distributed from 1983 to 1993. The other, ProDOS 16, was a stop-gap solution for the 16-bit Apple IIGS that was replaced by GS/OS within two years.
On the Amiga, the Old File System was the filesystem for AmigaOS before the Amiga Fast File System. Even though it used 512-byte blocks, it reserved the first small portion of each block for metadata, leaving an actual data block capacity of 488 bytes per block. It wasn't very suitable for anything except floppy disks, and it was soon replaced.

Commodore DOS, also known as CBM DOS, is the disk operating system used with Commodore's 8-bit computers. Unlike most other DOSes, which are loaded from disk into the computer's own RAM and executed there, CBM DOS is executed internally in the drive: the DOS resides in ROM chips inside the drive, and is run there by one or more dedicated MOS 6502 family CPUs. Thus, data transfer between Commodore 8-bit computers and their disk drives more closely resembles a local area network connection than typical disk/host transfers.
Wheels is a defunct operating system for the Commodore 64 and Commodore 128 home computers partially based on and an upgrade from GEOS. Wheels gave new abilities to the C64 and 128: the ability to open several, movable, resizable windows on the desktop and limited graphical web browsing At the core of the Wheels OS was the new Dashboard and Toolbox. The Dashboard was the name for the new desktop environment which made using the C64/128 similar to using modern Mac or Windows operating systems with icons and a menu bar. The Toolbox was the replacement for the GEOS Configure app.

The Commodore 4040 is the replacement for the previous models 2040 (USA) and 3040 (Europe). It's a dual-drive 5¼" floppy disk subsystem for Commodore International computers. It uses a wide-case form, and uses the parallel IEEE-488 interface common to Commodore PET/CBM computers.

The Commodore 8050, Commodore 8250, and Commodore SFD-1001 are 5¼-inch floppy disk drives manufactured by Commodore International, primarily for its 8-bit CBM and PET series of computers. The drives offered improved storage capacities over previous Commodore drive models.

The RAMLink was one of several RAM expansion products made by Creative Micro Designs (CMD) for Commodore's C64/128 home computers. The RAMLink was intended as a third-party alternative, successor and optionally companion to Commodore's own 17xx-series REU RAM expansion cartridges.
INT 13h is shorthand for BIOS interrupt call 13hex, the 20th interrupt vector in an x86-based computer system. The BIOS typically sets up a real mode interrupt handler at this vector that provides sector-based hard disk and floppy disk read and write services using cylinder-head-sector (CHS) addressing.

This article is about the various external peripherals of the Commodore 64 home computer. Due to the backwards compatibility of the Commodore 128, most peripherals will work on that system, as well. There's some compatibility with the VIC-20 and PET too.

A fast loader is a software program for a home computer, such as the Commodore 64 or ZX Spectrum, that accelerates the speed of file loading from floppy disk or compact cassette.

In computer disk storage, a sector is a subdivision of a track on a magnetic disk or optical disc. Each sector stores a fixed amount of user-accessible data, traditionally 512 bytes for hard disk drives (HDDs) and 2048 bytes for CD-ROMs and DVD-ROMs. Newer HDDs use 4096-byte (4 KiB) sectors, which are known as the Advanced Format (AF).
IDEDOS is a ROM-based disk operating system written in 6502/65816 assembly language for the Commodore 64, 128 and SuperCPU. Its main purpose is to control ATA(PI) devices connected to an IDE64 cartridge and present them like normal Commodore drives. Additionally it supports networked drives (PCLink) and has a built-in machine code monitor and file manager.
A master boot record (MBR) is a special type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept of MBRs was publicly introduced in 1983 with PC DOS 2.0.

The floppy disk is a data storage and transfer device which was ubiquitous from the mid-1970s well into the 2000s. Besides the 3½-inch and 5¼-inch formats used in IBM PC compatible systems, or the 8-inch format that preceded them, many proprietary floppy disk formats were developed, either using a different disk design or special layout and encoding methods for the data held on the disk.
In computer file systems, a block availability map (BAM) is a data structure used to track disk blocks that are considered free. It is used along with a directory to manage files on a disk.
The Commodore D9090 Hard Disk was the only family of hard drives that Commodore made for both the home and business market. The electronics are identical in the D9090 and the D9060 unit; the only difference is the size of the installed hard drive, with a jumper set to distinguish between 4 or 6 disk heads. Originally intended for the metal-cased PET series of computers, they were also usable with the Commodore 64 and later models with an adapter.
















