
CSS McRae was a Confederate gunboat that saw service during the American Civil War. Displacing around 680 tons, she was armed with one 9-inch (229 mm) smoothbore and six 32-pounder (15 kg) smoothbore cannon.

The First Battle of Memphis was a naval battle fought on the Mississippi River immediately north of the city of Memphis, Tennessee on June 6, 1862, during the American Civil War. The engagement was witnessed by many of the citizens of Memphis. It resulted in a crushing defeat for the Confederate forces, and marked the virtual eradication of a Confederate naval presence on the river. Despite the lopsided outcome, the Union Army failed to grasp its strategic significance. Its primary historical importance is that it was the last time civilians with no prior military experience were permitted to command ships in combat. As such, it is a milestone in the development of professionalism in the United States Navy.

The Confederate States Marine Corps (CSMC), also referred to as the Confederate States Marines, was a branch of the Confederate Navy during the American Civil War. It was established by an act of the Provisional Congress of the Confederate States on March 16, 1861. The Corps' manpower was initially authorized at 46 officers and 944 enlisted men, and was increased on September 24, 1862, to 1,026 enlisted men. The organization of the Corps began at Montgomery, Alabama, and was completed at Richmond, Virginia, when the capital of the Confederate States was moved to that location. The headquarters and main training facilities remained in Richmond throughout the war, located at Camp Beall on Drewry's Bluff and at the Gosport Shipyard in Portsmouth, Virginia. The last Marine unit surrendered to the Union army on April 9, 1865, with the Confederacy itself capitulating a month later.

USS Sciota was a Unadilla-class gunboat built on behalf of the United States Navy for service during the Civil War. She was outfitted as a gunboat, with both a 20-pounder rifle for horizontal firing, and two howitzers for shore bombardment, and assigned to the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.

The second USS Memphis was a 7-gun screw steamer, built by William Denny and Brothers, Dumbarton, Scotland in 1861, which briefly served as a Confederate blockade runner before being captured and taken into the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was destroyed by fire in 1883.

Laurent Millaudon was a wooden side-wheel river steamboat launched at Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1856 operating in the New Orleans, Louisiana, area, and captained by W. S. Whann. At the beginning of the American Civil War she was taken into service by the Confederate Navy as CSS General Sterling Price. On 6 June 1862, she was sunk at the First Battle of Memphis. She was raised and repaired by the Union army, and on 16 June 1862 was moved into Union service as USS General Price and served until the end of the war.
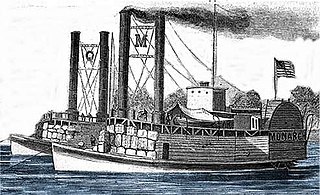
USS Monarch was a United States Army sidewheel ram that saw service in the American Civil War as part of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. She operated on the Mississippi River and Yazoo River during 1862 and 1863.

The battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip was the decisive battle for possession of New Orleans in the American Civil War. The two Confederate forts on the Mississippi River south of the city were attacked by a Union Navy fleet. As long as the forts could keep the Federal forces from moving on the city, it was safe, but if they fell or were bypassed, there were no fall-back positions to impede the Union advance.

USS General Bragg was a heavy (1,043-ton) steamer captured by Union Navy forces during the American Civil War. She was outfitted as a U.S. Navy gunboat and was assigned to enforce the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.

CSS General Earl Van Dorn was a cottonclad warship used by the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War. She was purchased for Confederate service in New Orleans, Louisiana, in early 1862 to serve with the River Defense Fleet. She was converted into a cottonclad warship by installing an iron-covered framework of timbers on her bow that served as a ram, and protecting her machinery with timber bulkheads packed with cotton. A sidewheel steamer, she was 182 feet (55 m) long and was armed with a single 32-pounder cannon on the bow.

CSS Colonel Lovell was a cotton-clad ram ship of the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War

Little Rebel was a cotton-clad ram that had been converted from a Mississippi River steamer to serve as the flagship of the Confederate River Defense Fleet in the American Civil War. Sent from New Orleans to defend against the Federal descent of the Mississippi, she was among the force that engaged vessels of the Union Army's Western Gunboat Flotilla at the Battle of Plum Point Bend on May 10, 1862. On June 6, she again was involved in an action with the Federal gunboats, this time at the First Battle of Memphis. In the battle, a shot from a Federal gun pierced her boiler, disabling her, and she was then pushed aground by the Federal ram USS Monarch and captured.
CSS New Orleans was a floating battery used by the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War. Converted from a floating drydock in 1861, she was commissioned on October 14, 1861. The vessel was unable to move under her own power and lacked facilities for her crew to live aboard, so CSS Red Rover was used to move the floating battery and house her crew. She was then sent upriver to assist in the Confederate defense of Columbus, Kentucky, arriving there in December. After the Confederates abandoned Columbus in March 1862, New Orleans was moved to Island No. 10 near New Madrid, Missouri. The Confederate defenders of Island No. 10 surrendered on April 8, and New Orleans was scuttled that day. Not fully sunk, the floating battery drifted downriver to the New Madrid area, where it was captured by Union forces. In Union hands, New Orleans was used as a floating drydock until the Confederates burned her in August or September 1863.

CSS General M. Jeff Thompson was a warship which served in the River Defense Fleet of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War. Purchased in January 1862, the vessel was operated by the Confederate States Army and named after M. Jeff Thompson, an officer in the Missouri State Guard. She was equipped with a ram and armored as a cottonclad. General M. Jeff Thompson participated in the Battle of Plum Point Bend in May 1862, before being sunk on June 6 in the First Battle of Memphis. Her wreck remained on the floor of the Mississippi River until it was removed by a snagboat in July 1867; it had caused a shipwreck about six months earlier when another vessel struck it.

The Battle of the Head of Passes was a bloodless naval battle of the American Civil War. It was a naval raid made by the Confederate river defense fleet, also known as the “mosquito fleet” in the local media, on ships of the Union blockade squadron anchored at the Head of Passes. The mosquito fleet deployed three fire rafts, which were ignited and followed the ironclad ram CSS Manassas into the action. The attack occurred after moonset in the early hours of October 12, 1861, and routed the Union fleet, which fled in disorder down the Southwest pass of the delta. After sunrise Commodore George N. Hollins, running low on ammunition and fuel, ordered the mosquito fleet to withdraw upriver.

CSS Ivy was a sidewheel steamer and privateer purchased by Commodore Lawrence Rousseau for service with the Confederate States Navy, and chosen by Commodore George Hollins for his Mosquito Fleet. The Mosquito Fleet was a group of riverboats converted to gunboats, and used to defend the Mississippi River in the area of New Orleans during the American Civil War.

CSS Pickens was a Cushing-class schooner revenue cutter that saw service in the navies of the United States and Confederate States of America. Built as Robert McClelland in Somerset, Massachusetts, in 1853, she served along the coasts of Louisiana and Texas before transferring her crew and officers to USRC Washington in 1859 and heading to New York for repairs. In 1860, Robert McClelland reported to South West Pass, Mississippi, and was permanently assigned to New Orleans, Louisiana, later that year. After the 1861 secession of Louisiana, her commander turned her over to the state. She entered Confederate service on February 18 and was renamed Pickens. Pickens played a minor role in the Battle of the Head of Passes before being burned to prevent its capture on April 25, 1862, after Union Navy forces entered New Orleans.
CSS Tuscarora was a sidewheel steamer that briefly served as a gunboat in the Confederate States Navy at the beginning of the American Civil War. She was about 100 feet (30 m) long, displaced 400 short tons, and was manned by a 25-man crew. The vessel was purchased in 1861 from the Southern Steamship Company by Confederate authorities in New Orleans, Louisiana. Armed with two cannons, Tuscarora was engaged in the Battle of the Head of Passes on October 12, 1861. Ordered up the Mississippi River to Columbus, Kentucky, in November, she was destroyed on November 23, 1861, when a fire of unknown origin started in her boilers and spread to the ship's munitions.
CSS Pamlico was a sidewheel steamer that served in the Confederate States Navy during the early stages of the American Civil War. Originally a passenger vessel on Lake Pontchartrain, she was purchased by Confederate authorities on July 10, 1861, and converted into a gunboat. She participated in two minor naval actions in the vicinities of Horn Island and Ship Island in December, before taking part in two more small battles defending the Pass Christian area in March and April 1862. In late April, Union Navy ships passed the defenses of New Orleans, Louisiana. After ferrying Confederate troops out of the city, Pamlico was burned by her crew on Lake Pontchartrain on April 25 to prevent capture.
CSS Pontchartrain was a gunboat that served in the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War. Built in 1859 for passenger and cotton trade, she was purchased by the Confederates in October 1862. After seeing action against Union land positions during the campaigns for New Madrid, Missouri, and Island Number Ten, she was transferred to serve on the Arkansas River and the White River. In June 1862, two of her cannons were taken to a land fortification at St. Charles, Arkansas, where part of her crew saw action in the Battle of St. Charles while manning the guns. Her other cannons were then offloaded at Fort Hindman, where more of her crew were captured while fighting on land at the Battle of Arkansas Post in January 1863. Pontchartrain herself remained inactive at Little Rock, Arkansas, and was burned to prevent capture in September 1863 when the Confederates evacuated the city.















