
The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace, since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were first produced in 1961, and the type remains one of the most popular sounding rockets. They have been repeatedly used by the Canadian Space Agency and NASA.

Aries is an American sounding rocket and target rocket, developed by Space Vector Corporation from retired LGM-30 Minuteman I intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) stages for use by the United States Air Force and NASA. Taken over by Orbital Sciences Corporation, Aries, as the Target Test Vehicle, remains in use.

Salto di Quirra is a restricted weapons testing range and rocket launching site near Perdasdefogu on Sardinia.
It is the largest military range in Italy, composed of 12000 hectares of land owned by the Italian Ministry of Defence and one of the largest in operation within the European Union. Birth defects and cancer in the area have been blamed on weaponry used at the site.

The Nike Apache, also known as Argo B-13, was a two-stage sounding rocket developed by Aerolab, later Atlantic Research, for use by the United States Air Force and NASA. It became the standard NASA sounding rocket and was launched over 600 times between 1961 and 1978.

Jason was an American sounding rocket with 5 stages. The Jason was launched 22 times in 1958. The Jason could carry a payload of 125 pounds to an altitude of 500 mi. The launch thrust was 82,100 pounds-force, the launch mass 7,340 lb, the diameter 58 centimeters and the length 17.5 meters.
Cajun Dart is the designation of an American sounding rocket. The Cajun Dart was used 87 times between 1964 and 1970. The Cajun rocket motor was developed from Deacon.
Nike Iroquois is the designation of a two-stage American sounding rocket. The Nike Iroquois was launched 213 times between 1964 and 1978. The maximum flight height of the Nike Iroquois amounts to 290 km (950,000 ft), the takeoff thrust 48,800 lbf (217 kN), the takeoff weight 700 kg and the length 8.00 m.
The Nike-Cajun was a two-stage sounding rocket built by combining a Nike base stage with a Cajun upper stage. The Nike-Cajun was known as a CAN for Cajun And Nike. The Cajun was developed from the Deacon rocket. It retained the external size, shape and configuration of the Deacon but had 36 percent greater impulse than the Deacon due to improved propellant. It was launched 714 times between 1956 and 1976 and was the most frequently used sounding rocket of the western world. The Nike Cajun had a launch weight of 698 kg (1538 lb), a payload of 23 kg (51 lb), a launch thrust of 246 kN (55,300 lbf) and a maximum altitude of 120 km (394,000 ft). It had a diameter of 42 cm and a length of 7.70 m. The maximum speed of the Nike-Cajun was 6,760 km/h (4,200 mph).

Arcas was the designation of an American sounding rocket, developed by the Atlantic Research Corp., Alexandria, Va.

ASP, (Atmospheric Sounding Projectile is the designation of an American sounding rocket family. ASP-I was used to sample nuclear explosions and resultant clouds The ASP was the fastest single stage sounding rocket when developed. The Asp was manufactured by Cooper Development Corporation, California. The solid propellant motor was made by Grand Central Rocket company.

The first orbital flight of an artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, was launched in October 1957, by the Soviet Union. In November, the second orbital flight took place. The Soviet Union launched the first animal to orbit the Earth, a dog, Laika, who died in orbit a few hours after launch.
Rehbar is a series of sounding rocket launched into the upper atmosphere by Pakistan's Space and Upper Atmosphere Research Commission (SUPARCO). Rehbar-I was the first rocket launched by SUPARCO, on 7 June 1962. Rehbar-I was a two-staged solid fuel rocket.

This is a list of spaceflight related events which occurred in 1956.

In 1955, both the United States and the Soviet Union (USSR) announced plans for launching the world's first satellites during the International Geophysical Year (IGY) of 1957–58. Project Vanguard, proposed by the US Navy, won out over the US Army's Project Orbiter as the satellite and rocket design to be flown in the IGY. Development of Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles, the Atlas by the US and the R-7 by the USSR, accelerated, entering the design and construction phase.

The Wallops Flight Facility Visitor Center is located in Building J-17, Wallops Island, Virginia, United States along Route 175. It contains exhibits highlighting past missions conducted at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility. The visitor center also provides information about current activities at Wallops Flight Facility, such as the sounding rocket, balloon and aircraft program. The outside grounds has a rocket garden consisting of rockets and aircraft used for space and aeronautical research, including a full-scale four-stage reentry vehicle used to study the Earth's atmosphere. In addition, the visitor center has educational programs on Earth and space science. It is also a viewing area for rocket launches.

The XMQR-13A Ballistic Missile Target System (BMTS) was an unguided target rocket developed by the United States Army during the 1960s, intended for use in the development of missile defense systems. Utilising off-the-shelf parts in four different configurations, the BMTS was utilised in a series of launches in the late 1960s supporting tests of several missile systems.
Terasca, or Terrier-ASROC-Cajun, was an American three-stage sounding rocket developed and launched by the United States Navy. Derived from a combination of the Terrier, ASROC and Cajun rockets, three launches were attempted during 1959, but only one was successful.
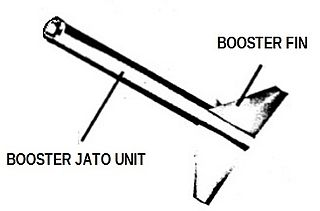
The Nike stage or Nike booster, a solid fuel rocket motor, was created by Hercules Aerospace for the Nike Ajax (M5) Nike Hercules (M5E1). It was developed for use as the first stage of the Nike Ajax and Nike Hercules missiles as part of Project Nike.

The Exos, originally designated RM-86 and later PWN-4, was a sounding rocket developed by the University of Michigan and NACA for use by the United States Air Force.















