Related Research Articles

The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about 85,133,000 km2 (32,870,000 sq mi). It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for separating the New World of the Americas from the Old World of Afro-Eurasia.

The Arabian Sea is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and on the southeast by the Laccadive Sea and the Maldives, on the southwest by Somalia. Its total area is 3,862,000 km2 (1,491,000 sq mi) and its maximum depth is 5,395 meters. The Gulf of Aden in the west connects the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea through the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb, and the Gulf of Oman is in the northwest, connecting it to the Persian Gulf.

The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about 2,500,000 km2 (970,000 sq mi), representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only 14 km (9 mi) wide.
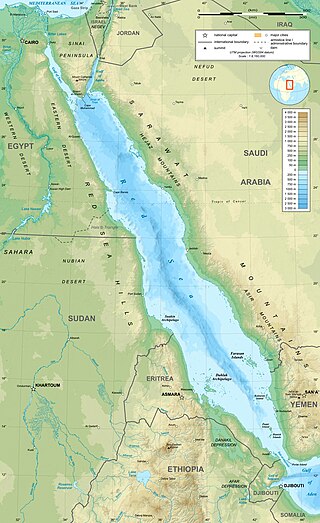
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez—leading to the Suez Canal. It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley.

Betuwe, also known in English as Batavia, is a historical and geographical region in the Netherlands, forming large fertile islands in the river delta formed by the waters of the Rhine and Meuse rivers. During the Roman Empire, it was an important frontier region and source of imperial soldiers. Its name is possibly pre-Roman.

Geographical exploration, sometimes considered the default meaning for the more general term exploration, refers to the practice of discovering remote lands and regions of the planet Earth. It is studied by geographers and historians.
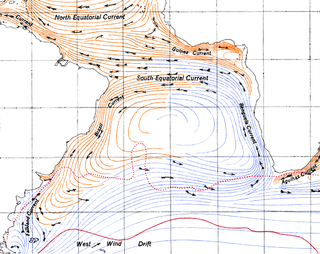
The Benguela Current is the broad, northward flowing ocean current that forms the eastern portion of the South Atlantic Ocean gyre. The current extends from roughly Cape Point in the south, to the position of the Angola-Benguela Front in the north, at around 16°S. The current is driven by the prevailing south easterly trade winds. Inshore of the Benguela Current proper, the south easterly winds drive coastal upwelling, forming the Benguela Upwelling System. The cold, nutrient rich waters that upwell from around 200–300 m (656–984 ft) depth in turn fuel high rates of phytoplankton growth, and sustain the productive Benguela ecosystem.
Rhapta was an emporion said to be on the coast of Southeast Africa, first described in the 1st century CE. Its location has not been firmly identified, although there are a number of plausible candidate sites. The ancient Periplus of the Erythraean Sea described Rhapta as "the last emporion of Azania", two days' travel south of the Menouthias islands. The Periplus also states that the city and port were ruled by South Arabian vassals of the Himyarite kingdom, particularly a certain "Mapharitic chieftain."

The Ptolemy world map is a map of the world known to Greco-Roman societies in the 2nd century. It is based on the description contained in Ptolemy's book Geography, written c. 150. Based on an inscription in several of the earliest surviving manuscripts, it is traditionally credited to Agathodaemon of Alexandria.

Palk Bay is a semi-enclosed shallow water body between the southeast coast of India and Sri Lanka, with a water depth maximum of 13 m. Palk Bay is located between 8° 50′ and 10° North latitudes and 78° 50′ and 80° 30′ East longitudes. The width of the bay ranges from 57 to 107 km and the length is around 150 km. It is one of the major sinks for sediments along with the Gulf of Mannar. Sediments discharged by rivers and transported by the surf currents as littoral drift settle in this sink. Few scientists have tried to understand the wave characteristics within the Palk Bay.
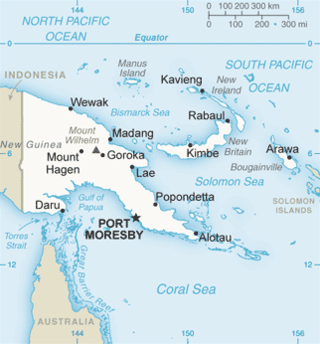
The Solomon Sea is a sea located within the Pacific Ocean. It lies between Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands. Many major battles were fought there during World War II.

The Cassiterides are an ancient geographical name used to refer to a group of islands whose precise location is unknown, but which was believed to be situated somewhere near the west coast of Europe.

The Libyan Sea is the portion of the Mediterranean Sea north of the African coast of ancient Libya, i.e. Cyrenaica, and Marmarica . The region of the Libyan Sea located south of Crete is also known as the South Cretan Sea.

The Gulf of Mexico is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southwest and south by the Mexican states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatán, and Quintana Roo; and on the southeast by Cuba. The coastal areas along the Southern U.S. states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, which border the gulf on the north, are occasionally referred to as the "Third Coast" of the United States, but more often as, "the Gulf Coast".
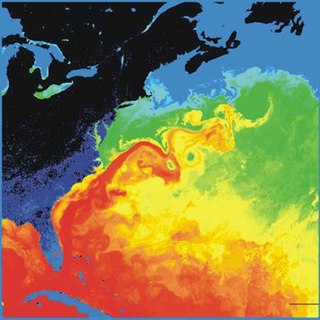
The Gulf Stream is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude and moves toward Northwest Europe as the North Atlantic Current. The process of western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northward-accelerating current off the east coast of North America. Around 40°0′N30°0′W, it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa.

Somov Sea was a proposed name for part of the Southern Ocean.
The Marsaci or Marsacii were a tribe in Roman imperial times, who lived within the area of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, under Roman domination.
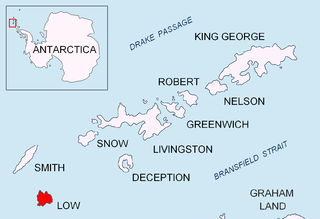
Presnakov Island is the 390 m long in southeast-northwest direction and 100 m wide rocky island lying off the west coast of Low Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.

Afala Island is the rocky island off the north coast of Nelson Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica extending 360 m in west-southwest to east-northeast direction and 310 m in south–north direction.

Kondor Island is the 320 m long in west–east direction and 140 m wide rocky island lying off the north coast of Nelson Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.
References
- ↑ Braund, David (1996), Ruling Roman Britain : kings, queens, governors and emperors from Julius Caesar to Agricola, pg. 150, London: Routledge, ISBN 0-415-00804-2