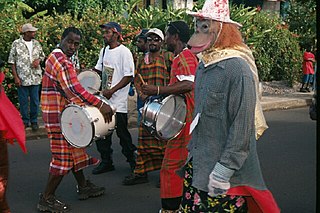Soca music is a genre of music defined by Lord Shorty, its inventor, as the "Soul of Calypso", which has influences of African and East Indian rhythms. It was originally spelled "sokah" by its inventor but through an error in a local newspaper when reporting on the new music it was erroneously spelled "soca"; Lord Shorty confirmed the error but chose to leave it that way to avoid confusion. It is a genre of music that originated in Trinidad and Tobago in the early 1970s and developed into a range of styles during the 1980s and after. Soca was initially developed by Lord Shorty in an effort to revive traditional calypso, the popularity of which had been flagging amongst younger generations in Trinidad due to the rise in popularity of reggae from Jamaica and soul and funk from the United States. Soca is an offshoot of calypso/kaiso, with influences from East Indian rhythms and hooks.
Calypso is a style of Caribbean music that originated in Trinidad and Tobago during the early to mid-19th century and spread to the rest of the Caribbean Antilles by the mid-20th century. Its rhythms can be traced back to West African Kaiso and the arrival of French planters and their slaves from the French Antilles in the 18th century.
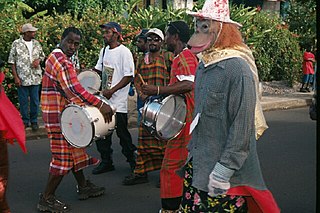
The music of Dominica includes a variety of genres including all the popular genres of the world. Popular music is widespread, with a number of native Dominican performers gaining national fame in imported genres such as calypso, reggae, soca, kompa, zouk and rock and roll. Dominica's own popular music industry has created a form called bouyon, which combines elements from several styles and has achieved a wide fanbase in Dominica. Groups include WCK, Native musicians in various forms, such as reggae, kadans (Ophelia Marie, and calypso, have also become stars at home and abroad.
The music of Sri Lanka has its roots in five primary influences: ancient folk rituals, Hindu religious traditions, Buddhist religious traditions, the legacy of European colonisation, and the commercial and historical influence of nearby Indian culture—specifically, Kollywood cinema and Bollywood cinema.
The music of the Lesser Antilles encompasses the music of this chain of small islands making up the eastern and southern portion of the West Indies. Lesser Antillean music is part of the broader category of Caribbean music; much of the folk and popular music is also a part of the Afro-American musical complex, being a mixture of African, European and indigenous American elements. The Lesser Antilles' musical cultures are largely based on the music of African slaves brought by European traders and colonizers. The African musical elements are a hybrid of instruments and styles from numerous West African tribes, while the European slaveholders added their own musics into the mix, as did immigrants from India. In many ways, the Lesser Antilles can be musically divided based on which nation colonized them.
Baila is a form of music, popular in Sri Lanka and among Goan Catholics in India. The genre originated centuries ago among the Portuguese Burghers and Sri Lankan Kaffirs. Baila songs are played during parties and weddings in Sri Lanka, Goa, and Mangalore accompanied by dancing.

Desmond Anaclitus Rajiva de Silva, popularly known as Desmond de Silva, was a Sri Lankan singer, background musician and entertainer. Often regarded as the "King of Baila", he is noted for his youthful voice that was said to have changed little over four decades of performing.
Desmond Kelly is a Ceylonese musician who has entertained in Sri Lanka and in Australia. He was born in Colombo in 1936.
The Sri Lankan Kaffirs are an ethnic group in Sri Lanka who are partially descended from 16th-century Portuguese traders and Bantu slaves who were brought by them to work as labourers and soldiers to fight against the Sinhala kings. They are very similar to the Zanj-descended populations in Iraq and Kuwait, and are known in Pakistan as Sheedis and in India as Siddis. The Kaffirs spoke a distinctive creole based on Portuguese, and the "Sri Lankan Kaffir language". Their cultural heritage includes the dance styles Kaffringna and Manja and their popular form of dance music Baila.
Kumar Navaratnam was a popular rock and roll singer in Colombo, Sri Lanka during the 1960s and 1970s.
Mahagamage Samson Fernando,, popularly as M. S. Fernando, was a Sri Lankan singer and musician. He is a major player in the development of Baila music and was widely popular among Sri Lankan audiences commonly referred to as the "Baila Chakkrawarthi".
Tamil cinema in Sri Lanka is not as developed as Sinhala cinema or its Indian counterpart, the Tamil cinema of Kodambakkam, Chennai, Tamil Nadu. This is especially due to the high production rates of the influential commercial Tamil films from Tamil Nadu, India and the long run ethnic civil war in Sri Lanka. Tamils contributed significantly to Sinhala cinema as well as Indian Tamil cinema, also known as Kollywood. Only a few Tamil language films were produced in the Northern Province of Sri Lanka. Earlier Tamil movies produced were all most destroyed or unrecovered due to civil war.
Uswatta Liyanage Ivor Sylvester Sunil Perera was a Sri Lankan vocalist, guitarist, songwriter and composer. Described as one of the most influential musicians in Sri Lankan music history, Perera was the leader and the lead vocalist of The Gypsies. He was associated with Sri Lanka's baila genre, and gained the nickname "Baila Chakravarthy".
Mariazelle Goonetilleke is a Sri Lankan singer and musician.

Thangaikkaaga is a 1971 Indian Tamil-language film, directed by D. Yoganand. The film stars Sivaji Ganesan, Vennira Aadai Nirmala and Lakshmi. It was released on 6 February 1971.
Kala Bhushana Thelge Wayaman Peiris, popularly known by stage name Dhanapala Udawatta, is a Sri Lankan singer. An indispensable singer on the outdoor stage, Udawaththa has been able to show his talents and sang several popular baila songs such as Ae Neela Warala, Ma Adaraneeya Mage Amma Wethatai, Man Italiye Thani Una, Nelum Wile Nelum Nelana and Ranga Nadeeka.
Madawela Hewage Paul Fernando, popularly as Paul Fernando, was a Sri Lankan musician and a Baila singer. Often referred to as the "Prince of Baila", Fernando became one of the most popular singers in Sri Lankan western music industry. Also, he is one of the leading artists dedicated to popularizing the art of Baila in Sri Lanka.