Related Research Articles

Alagoas is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil and is situated in the eastern part of the Northeast Region. It borders: Pernambuco ; Sergipe (S); Bahia (SW); and the Atlantic Ocean (E). Its capital is the city of Maceió. It has 1.6% of the Brazilian population and produces 0.8% of the Brazilian GDP. It is made up of 102 municipalities and its most populous cities are Maceió, Arapiraca, Palmeira dos Índios, Rio Largo, Penedo, União dos Palmares, São Miguel dos Campos, Santana do Ipanema, Delmiro Gouveia, Coruripe, Marechal Deodoro, and Campo Alegre.

Camaragibe is a city in northeastern Brazil, in the State of Pernambuco. It lies near Recife at 8.00° South, 35.04° West.

The São Francisco River is a large river in Brazil. With a length of 2,914 kilometres (1,811 mi), it is the longest river that runs entirely in Brazilian territory, and the fourth longest in South America and overall in Brazil. It used to be known as the Opara by the indigenous people before colonisation, and is today also known as "Velho Chico".

Maceió, formerly sometimes Anglicised as Maceio, is the capital and the largest city of the coastal state of Alagoas, Brazil. The name "Maceió" is an Indigenous term for a spring. Most maceiós flow to the sea, but some get trapped and form lakes.

Aurélio Buarque de Holanda Ferreira was a Brazilian lexicographer, philologist, translator, and writer, best known for editing the Novo Dicionário da Língua Portuguesa, a major dictionary of the Portuguese language.

Maragogi is a municipality in the Brazilian state of Alagoas, 125 km north of the capital city of Maceió. It has 33,032 inhabitants, a city situated on the northern coast of Alagoas state, Brazil, being the easternmost city of that state.
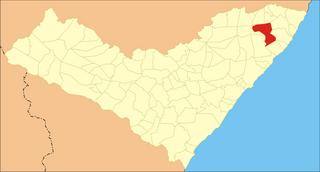
Matriz de Camaragibe is a municipality located in the Brazilian state of Alagoas.
Passo de Camaragibe is a municipality located in the northern coast of the Brazilian state of Alagoas. Its population is 15,258 (2020) and its area is 187 km².
The Mundaú River is a river in northeastern Brazil. The Mundaú originates in the Borborema Plateau of Pernambuco state, and flows southeast through Pernambuco and Alagoas states to empty into the Mundaú Lagoon at Maceió, Alagoas' capital. Mundaú Lagoon is an estuary, connected to the Atlantic Ocean and Manguaba Lagoon to the south by a network of channels.

The Moxotó River is a tributary of the São Francisco River in northeastern Brazil. The Moxotó originates on the Borborema Plateau in Pernambuco state, and flows southwest to join the São Francisco. The lower portion of the river forms the border between Pernambuco state to the west and Alagoas state to the east.
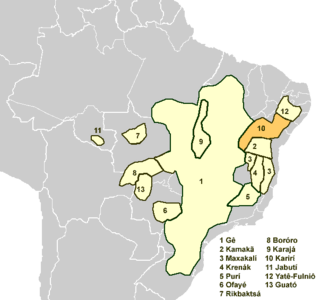
The Karirí languages, generally considered dialects of a single language, were a group of languages formerly spoken by the Kiriri people of Brazil. It was spoken until the middle of the 20th century; the 4,000 ethnic Kiriri are now monolingual Portuguese speakers, though a few know common phrases and names of medicinal plants.

Beberibe River is a river located in Pernambuco, Brazil. The river rises in the city of Camaragibe from the confluence of the rivers Araçá and Pacas, and is 23.7 km long. Its drainage basin measures 81 square kilometers and includes the following cities: Recife, Olinda and Camaragibe. Today, the main tributaries are the Euclides channel, Malaria channel and Vasco da Gama channel all located in Recife metropolitan area. The Beberibe meets the Capibaribe River near to the end of Aurora street to flow into the Atlantic Ocean. The name Beberibe means where the sugar cane grows. Also, in Recife Beberibe could be a neighborhood with the eponymous name.

Paudalho is a city in northeastern Brazil, in the State of Pernambuco.
Global Village Telecom (GVT) was a Brazilian telecommunications company that offers services on landline telephone, broadband for both consumer and business, Pay TV and voice over IP. GVT has been in the market since the end of 2000. GVT today operates under the Vivo brand.

The 2010 Northeastern Brazil rains caused widespread flooding in the second half of June 2010. The flooding mainly hit Alagoas and Pernambuco, where entire villages were carried away, killing dozens and causing hundreds to disappear.

The Pará-class monitors were a group of six wooden-hulled ironclad monitors named after Brazilian provinces and built in Brazil for the Imperial Brazilian Navy during the Paraguayan War in the late 1860s. The first three ships finished, Pará, Alagoas and Rio Grande, participated in the Passage of Humaitá in February 1868. Afterwards the remaining ships joined the first three and they all provided fire support for the army for the rest of the war. The ships were split between the newly formed Upper Uruguay and Mato Grosso Flotillas after the war. Alagoas was transferred to Rio de Janeiro in the 1890s and participated in the Fleet Revolt of 1893–94.

The Brazilian monitor Alagoas was the third ship of the Pará-class river monitors built for the Imperial Brazilian Navy during the Paraguayan War in the late 1860s. Alagoas participated in the Passage of Humaitá on 19 February 1868 and provided fire support for the army for the rest of the war. The ship was assigned to the Upper Uruguay flotilla after the war. Alagoas was transferred to Rio de Janeiro in the 1890s and participated in the Navy Revolt of 1893–94. The ship was scrapped in 1900.
Xocó is a dead and poorly attested language or languages of Brazil that is not known to be related to other languages. It is known from three populations: Xokó (Chocó) in Sergipe, Kariri-Xocó in Alagoas, and Xukuru-Kariri in Alagoas. It is not clear if these were one language or three. It is only known from a few dozen words from one Kariri-Xoco elder and three Xukuru-Kariri elders in 1961.

Sport Club Bom Jesus was a Brazilian football club based in Matriz de Camaragibe, Alagoas. The team last participated in the Campeonato Alagoano in the 2006 season.