Related Research Articles

Top-of-the-World is a census-designated place (CDP) in Gila and Pinal counties in the U.S. state of Arizona. The population was 274 at the 2020 census, up from 231 at the 2010 census, and down from 330 at the 2000 census.
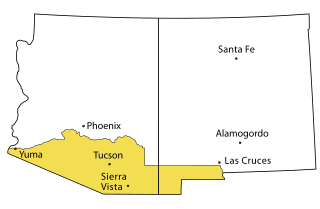
The Gadsden Purchase is a 29,640-square-mile (76,800 km2) region of present-day southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico that the United States acquired from Mexico by the Treaty of Mesilla, which took effect on June 8, 1854. The purchase included lands south of the Gila River and west of the Rio Grande where the U.S. wanted to build a transcontinental railroad along a deep southern route, which the Southern Pacific Railroad later completed in 1881–1883. The purchase also aimed to resolve other border issues.

The Territory of Nebraska was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 30, 1854, until March 1, 1867, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of Nebraska. The Nebraska Territory was created by the Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854. The territorial capital was Omaha. The territory encompassed areas of what is today Nebraska, Wyoming, South Dakota, North Dakota, Colorado, and Montana.
The Department of the Pacific or Pacific Department was a major command (Department) of the United States Army from 1853 to 1858. It replaced the Pacific Division, and was itself replaced by the Department of California and the Department of Oregon.

The Pacific coast theater of the American Civil War consists of major military operations in the United States on the Pacific Ocean and in the states and Territories west of the Continental Divide. The theater was encompassed by the Department of the Pacific that included the states of California, Oregon, and Nevada, the territories of Washington, Utah, and later Idaho.
The Department of the Missouri was a command echelon of the United States Army in the 19th century and a sub division of the Military Division of the Missouri that functioned through the Indian Wars.
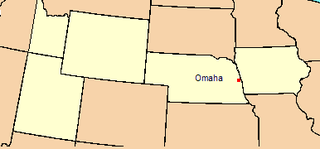
The Department of the Platte was a military administrative district established by the U.S. Army on March 5, 1866, with boundaries encompassing Iowa, Nebraska, Dakota Territory, Utah Territory and a small portion of Idaho. With headquarters in Omaha, the district commander oversaw the army's role initially along the Overland route to Salt Lake City, then later the construction route of the Union Pacific Railroad. The district also included the Montana road through eastern Wyoming. The district was discontinued when the Army's command was reorganized in 1898.

The Simon Kenton Council (#441) is a Boy Scouts of America council created in 1994 that serves members of the Cub Scouts, Scouts BSA, Venturing, Exploring and in-school programs in central and southern Ohio, and northern Kentucky. The council is divided into five districts with headquarters in Columbus, Ohio. Simon Kenton Council is named for frontiersman Simon Kenton.
Mohave City is a ghost town in Mohave County in the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Arizona. Settled in the 1860s, in what was then the Arizona Territory, it was founded as a river landing and trading center for area miners and soldiers, and was named for Mohave County.
The 1st Battalion of Native Cavalry, California Volunteers was a cavalry battalion in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Recruits were largely drawn from the Californio population, though its ranks included Yaqui and Mission Indians as well as immigrants from Mexico, Hispano America and Europe. In addition to its ethnic makeup, the Battalion is also considered unusual for being one of the few lancer units in the United States Army.

Fort Lapwai (1862–1884), was a federal fort in present-day Lapwai in north central Idaho, United States. On the Nez Perce Indian Reservation in Nez Perce County, it was originally called Camp Lapwai until 1863. East of Lewiston, it was located on the west bank of Lapwai Creek, three miles (5 km) above where it joins the Clearwater River at the state's first settlement, Lapwai Mission Station, built in 1836 by Henry Spalding. It is part of the multi-site Nez Perce National Historical Park. The word "Lapwai" means place of the butterflies, as the area had thousands in early summer in earlier years.
District of Arizona was a subordinate district of the Department of New Mexico territory created on August 30, 1862 and transferred to the Department of the Pacific in March 1865.

The Department of California was an administrative department of the United States Army. The Department was created in 1858, replacing the original Department of the Pacific, and it was ended by the reorganizations of the Henry L. Stimson Plan implemented in February 1913. As with the preceding organization, headquarters were in San Francisco. Its creation was authorized by General Orders, No. 10, of the War Department, Adjutant-General's Office, September 13, 1858.
The Presidio de Calabasas, also known as Fort Calabasas or Camp Calabasas, was a stone fortress built by Mexico in 1837 south of Tumacacori, Arizona. It was built on the land of the Grant of Manuel María Gándara, by Gándara to protect his lands near the Mission San Cayetano de Calabazas from the Apache. Civilians established a small farming settlement called Calabasas, in the area nearby the protection of the Presidio.

The Battle of Fort Buchanan was an Apache attack on the United States Army post of Old Fort Buchanan in southern Arizona Territory, which occurred on February 17, 1865. Though a skirmish, it ended with a significant Apache victory when they forced the small garrison of California Volunteers to retreat to the Santa Rita Mountains. Fort Buchanan was the only American military post conquered during the war against the Chiricahua.

Fort Crittenden, originally Camp Crittenden, was a United States Army post built in 1867 three miles from Sonoita, Arizona along Sonoita Creek. It was established for campaigning against the Apache and to protect American pioneers in the area.

At the outbreak of the American Civil War, Oregon raised the 1st Oregon Cavalry that was activated in 1862 and served until June 1865. During the Civil War, emigrants to the newfound gold fields in Idaho and Oregon continued to clash with the Paiute, Shoshone and Bannock tribes of Oregon, Idaho and Nevada until relations degenerated into the bloody 1864–1868 Snake War. The 1st Oregon Volunteer Infantry Regiment was formed in 1864 and its last company was mustered out of service in July 1867. Both units were used to guard travel routes and Indian reservations, escort emigrant wagon trains, and protect settlers from Indian raiders. Several infantry detachments also accompanied survey parties and built roads in central and southern Oregon.
Following the Gadsden Purchase, the United States Army sent Major Enoch Steen and four companies of the 1st U. S. Dragoons to occupy the former site of the Mexican Presidio de Calabasas. Major Steen arrived on November 27, 1856, and named his post Camp Moore. The dragoons put roofs on the old adobe structures and added a few new ones. Camp Moore was abandoned in March 1857 after another location in the San Rafael Valley was chosen for a permanent fort that was christened Fort Buchanan.
Camp Gaston, sometimes called Fort Gaston is a former U. S. Army camp, that was located 3 miles west of the old original course of the Colorado River south of modern Palo Verde, California in Imperial County, California, near Milpitas Wash Road. It was 80 miles (130 km) up river from Fort Yuma, and was active between 1859 and 1867.

Calabasas is a former populated place or ghost town, within the Census-designated place of Rio Rico, a suburb of Nogales in Santa Cruz County, Arizona.
References
- ↑ Robert Frazer, Robert W. Frazer, Forts of the West: Military Forts and Presidios and Posts Commonly Called Forts West of the Mississippi River to 1898, University of Oklahoma Press, 1975, p. 7
- ↑ North American Forts: Southern Arizona, Camp Cameron
- ↑ North American Forts: Southern Arizona, Camp Mason