
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) is an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security, initially created under President Jimmy Carter by Presidential Reorganization Plan No. 3 of 1978 and implemented by two Executive Orders on April 1, 1979. The agency's primary purpose is to coordinate the response to a disaster that has occurred in the United States and that overwhelms the resources of local and state authorities. The governor of the state in which the disaster occurs must declare a state of emergency and formally request from the President that FEMA and the federal government respond to the disaster. The only exception to the state's gubernatorial declaration requirement occurs when an emergency or disaster takes place on federal property or to a federal asset—for example, the 1995 bombing of the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, or the Space Shuttle Columbia in the 2003 return-flight disaster.
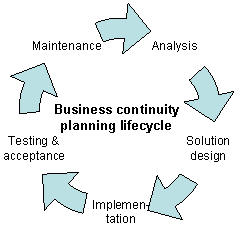
Business continuity planning is the process of creating systems of prevention and recovery to deal with potential threats to a company. In addition to prevention, the goal is to enable ongoing operations before and during execution of disaster recovery.
Earthquake preparedness is a set of measures taken at the individual, organisational and societal level to minimise the effects of an earthquake. Preparedness measures can range from securing heavy objects, structural modifications and storing supplies, to having insurance, an emergency kit, and evacuation plans.
Crisis management is the process by which an organization deals with a disruptive and unexpected event that threatens to harm the organization or its stakeholders. The study of crisis management originated with large-scale industrial and environmental disasters in the 1980s. It is considered to be the most important process in public relations.

Emergency management is the organization and management of the resources and responsibilities for dealing with all humanitarian aspects of emergencies. The aim is to reduce the harmful effects of all hazards, including disasters.

The Robert T. Stafford Disaster Relief and Emergency Assistance Act is a 1988 United States federal law designed to bring an orderly and systematic means of federal natural disaster assistance for state and local governments in carrying out their responsibilities to aid citizens. Congress' intention was to encourage states and localities to develop comprehensive disaster preparedness plans, prepare for better intergovernmental coordination in the face of a disaster, encourage the use of insurance coverage, and provide federal assistance programs for losses due to a disaster.

Hazus is a geographic information system-based natural hazard analysis tool developed and freely distributed by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA).
Preparedness refers to a very concrete research-based set of actions that are taken as precautionary measures in the face of potential disasters. These actions can include both physical preparations and trainings for emergency action. Preparedness is an important quality in achieving goals and in avoiding and mitigating negative outcomes. There are different types of preparedness, such as public health preparedness and local emergency preparedness or snow preparedness, but probably the most developed type is "Disaster Preparedness", defined by the UN as involving "forecasting and taking precautionary measures before an imminent threat when warnings are possible". This includes not only natural disasters, but all kinds of severe damage caused in a relatively short period, including warfare. Preparedness is a major phase of emergency management, and is particularly valued in areas of competition such as sport and military science.
The Massachusetts Emergency Management Agency (MEMA) is a Commonwealth of Massachusetts agency. The Massachusetts Emergency Management Agency is the Agency that coordinates federal, state, local, and private resources throughout the Commonwealth during times of disasters and emergencies.
Emergency Management BC (EMBC) used to be known as the Provincial Emergency Program and is a division of the Ministry of Public Safety and Solicitor General of British Columbia, Canada. EMBC works with local governments and other provincial and federal agencies year round, providing coordination and support before, during and after emergencies. EMBC is administered under the Emergency Program Act.
Citizen Corps is a program under the Department of Homeland Security that provides training for the population of the United States to assist in the recovery after a disaster or terrorist attack. Each local Citizen Corps Council partners with organizations, volunteers and businesses to organize responders, volunteers and professional first responders for an efficient response so efforts are not wasted by being duplicated. By training in Incident Command, volunteers know whom to report to and how the incident is organized. This prevents sites from being inundated by untrained and unprepared people milling about and getting in the way. Citizen Corps also works in conjunction with the Corporation for National and Community Service in promoting national service opportunities for promoting homeland security needs.

Disaster risk reduction (DRR) is a systematic approach to identifying, assessing and reducing the risks of disaster. It aims to reduce socio-economic vulnerabilities to disaster as well as dealing with the environmental and other hazards that trigger them. Here it has been strongly influenced by the mass of research on vulnerability that has appeared in print since the mid-1970s. It is the responsibility of development and relief agencies alike. It should be an integral part of the way such organizations do their work, not an add-on or one-off action. Disaster risk reduction is very wide-ranging: Its scope is much broader and deeper than conventional emergency management. There is potential for Disaster risk reduction initiatives in just about every sector of development and humanitarian work.

On December 19, 2006, the Pandemic and All-Hazards Preparedness Act (PAHPA), Public Law No. 109-417, was signed into law by President George W. Bush. First introduced in the House by Rep. Mike Rogers (R-MI) and Rep. Anna Eshoo (D-CA), PAHPA had broad implications for the United States Department of Health and Human Services's (HHS) preparedness and response activities. Among other things, the act amended the Public Health Service Act to establish within the department a new Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR); provided new authorities for a number of programs, including the advanced development and acquisitions of medical countermeasures; and called for the establishment of a quadrennial National Health Security Strategy.
The California Governor's Office of Emergency Services (CalOES) is a California cabinet-level agency responsible for overseeing and coordinating emergency preparedness, response, recovery and homeland security activities within the state. The agency was created by AB 38 (2008), superseding both the Office of Emergency Services (OES) and Office of Homeland Security (OHS).

Ready Georgia is a statewide emergency preparedness campaign in the U.S. state of Georgia instituted by the Georgia Emergency Management Agency (GEMA) and Governor Sonny Perdue in conjunction with the national Ready America campaign sponsored by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). Ready Georgia is supported by The Ad Council, local volunteer organizations, and corporate partnerships.
The Stephenson Disaster Management Institute at Louisiana State University is located in the Stephenson National Center for Security Research and Training at LSU.

The Safe America Foundation is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization working nationally and headquartered in Marietta, GA. The organization was founded in 1994 and partners with corporate, government, public and private sector organizations and non-profit organization to improve the awareness of safety and preparedness in the United States. The Safe America Foundation operates an Emergency Preparedness program and Driver Education program.

The Universal Logistics Standard is a strategic framework for managing disaster response among local, state, regional and federal disaster response personnel. Its intended use is as a foundation on which local, state and federal emergency management stakeholders can build a comprehensive disaster logistics program. The Universal Logistics Standard was developed by the Regional Logistics Program under the oversight of the NY-NJ-CT-PA Regional Catastrophic Planning Team, which is funded as part of the US Department of Homeland Security's Regional Catastrophic Preparedness Grant Program to support all-hazard planning and coordination of response for catastrophic events.

The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) was created in December 1999 to ensure the implementation of the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction.

The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) was established on 16 November 2018 when President Donald Trump signed into law the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency Act of 2018. CISA is a standalone United States federal agency, an operational component under Department of Homeland Security (DHS) oversight. Its activities are a continuation of the National Protection and Programs Directorate (NPPD).










