| Look up Canis in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Canis is a genus which includes dogs, wolves and jackals.
Contents
Canis may also refer to:
| Look up Canis in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Canis is a genus which includes dogs, wolves and jackals.
Canis may also refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Canis. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
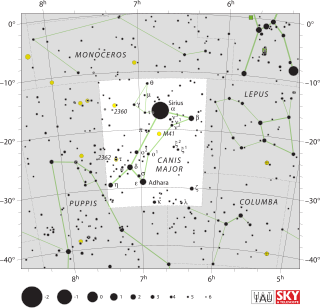
Canis Major is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for "greater dog" in contrast to Canis Minor, the "lesser dog"; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter through the sky. The Milky Way passes through Canis Major and several open clusters lie within its borders, most notably M41.

Canis Minor is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for "lesser dog", in contrast to Canis Major, the "greater dog"; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.

Canidae is a biological family of dog-like carnivorans. A member of this family is called a canid. There are three subfamilies found within the canid family, which are the extinct Borophaginae and Hesperocyoninae, and the extant Caninae. The Caninae are known as canines, which includes domestic dogs, wolves, foxes and other extant and extinct species.

A Flamsteed designation is a combination of a number and constellation name that uniquely identifies most naked eye stars in the modern constellations visible from southern England. They are named for John Flamsteed who first used them while compiling his Historia Coelestis Britannica.
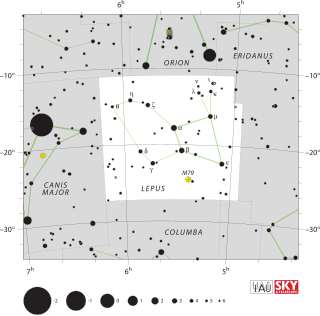
Lepus is a constellation lying just south of the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for hare. It is located below—immediately south—of Orion, and is sometimes represented as a hare being chased by Orion or, alternatively, by Orion's hunting dogs.

Canis is a genus of the Caninae containing multiple extant species, such as wolves, dogs, coyotes and jackals. Species of this genus are distinguished by their moderate to large size, their massive, well-developed skulls and dentition, long legs, and comparatively short ears and tails.

Messier 79 is a globular cluster in the constellation Lepus. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1780 and is at a distance of about 42,000 light years away from Earth and 60,000 light years away from the Galactic Center.

NGC 2362 is an open cluster in the constellation Canis Major. It was discovered by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654. Its brightest star is Tau Canis Majoris, and therefore it is sometimes called the Tau Canis Majoris Cluster. NGC 2362 has a distance of 1.48 kpc and is a relatively young 4–5 million years in age. It is a massive open cluster, with more than 500 solar masses. The cluster is in relation with the giant nebula Sh2-310, that lies at the same distance.
The Canis Major Overdensity or Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy is a disputed dwarf irregular galaxy in the Local Group, located in the same part of the sky as the constellation Canis Major.
Canid hybrids are the result of interbreeding between different species of the "true dog" tribe Canini, specifically in the Canina subtribe of wolf-like canids. They often occur in the wild, in particular between domestic or feral dogs and wild native canids.
A dog is a mammal.

The dog is a member of the genus Canis (canines), which forms part of the wolf-like canids, and is the most widely abundant terrestrial carnivore. The dog and the extant gray wolf are sister taxa as modern wolves are not closely related to the wolves that were first domesticated, which implies that the direct ancestor of the dog is extinct. The dog was the first species to be domesticated, and has been selectively bred over millennia for various behaviors, sensory capabilities, and physical attributes.

Toxocara canis is a worldwide-distributed helminth parasite of dogs and other canids. The name is derived from the Greek word "toxon," meaning bow or quiver, and the Latin word "caro," meaning flesh. They live in the small intestine of the definitive host. In adult dogs, the infection is usually asymptomatic but may be characterized by diarrhea. By contrast, massive infection with Toxocara canis can be fatal in puppies, causing diarrhea, vomiting, an enlarged abdomen, flatulence, and poor growth rate.

Dog types are broad categories of domestic dogs based on form, function or style of work, lineage, or appearance. Some may be locally adapted dog types that may have the visual characteristics of a modern purebred dog. In contrast, modern dog breeds strictly adhere to long established breed standards, that began with documented foundation breeding stock sharing a common set of inheritable characteristics, developed by long established, reputable kennel clubs that recognize the dog as a purebred.
The Inuit have traditional names for many constellations, asterisms and stars. A number of these constellations overlap with, or can be found within, more commonly known western constellations:

Canis lupus dingo is a taxonomic rank that includes both the dingo that is native to Australia and the rare New Guinea singing dog that is native to the New Guinea Highlands. It also includes some extinct dogs that were once found in coastal Papua New Guinea and the island of Java in the Indonesian Archipelago. It is a subspecies of Canis lupus. The genetic evidence indicates that the dingo clade originated from East Asian domestic dogs and was introduced through the Malay Archipelago into Australia, with a common ancestry between the Australian dingo and the New Guinea singing dog.
According to traditional Chinese uranography, the modern constellation Canis Major is located within the southern quadrant of the sky, which is symbolized as the Vermilion Bird of the South.
Sharvara (शर्वर) is an ancient Hindu mythological dog belonging to Yama. It is one of the two dogs that guard the netherworld. Sharvara is identified with the constellation Canis Major, the other dog with Canis Minor, together they guard the gates of the netherworld, known as pitriloka or vaivasvataloka, which is the domain of Yama.

NGC 2354 is an open cluster in the constellation Canis Major. It lies 2 degrees southwest from NGC 2362 and northeast of Delta Canis Majoris. About 15 member stars are visible through binoculars.
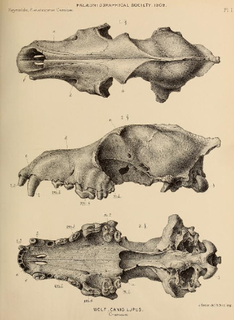
The evolution of the wolf occurred over a geologic time scale of at least 300 thousand years. The grey wolf Canis lupus is a highly adaptable species that is able to exist in a range of environments and which possesses a wide distribution across the Holarctic. Studies of modern grey wolves have identified distinct sub-populations that live in close proximity to each other. This variation in sub-populations is closely linked to differences in habitat – precipitation, temperature, vegetation, and prey specialization – which affect cranio-dental plasticity.