Related Research Articles

Poliovirus, the causative agent of polio, is a serotype of the species Enterovirus C, in the family of Picornaviridae.

Picornaviruses are a group of related nonenveloped RNA viruses which infect vertebrates including fish, mammals, and birds. They are viruses that represent a large family of small, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses with a 30-nm icosahedral capsid. The viruses in this family can cause a range of diseases including the common cold, poliomyelitis, meningitis, hepatitis, and paralysis.
Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) is a member of the genus Caulimovirus, one of the six genera in the family Caulimoviridae, which are pararetroviruses that infect plants. Pararetroviruses replicate through reverse transcription just like retroviruses, but the viral particles contain DNA instead of RNA.

Plant viruses are viruses that affect plants. Like all other viruses, plant viruses are obligate intracellular parasites that do not have the molecular machinery to replicate without a host. Plant viruses can be pathogenic to higher plants.

Tombusviridae is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA plant viruses. There are three subfamilies, 17 genera, and 95 species in this family. The name is derived from Tomato bushy stunt virus (TBSV).
VPg is a protein that is covalently attached to the 5′ end of positive strand viral RNA and acts as a primer during RNA synthesis in a variety of virus families including Picornaviridae, Potyviridae and Caliciviridae. There are some studies showing that a possible VPg protein is also present in astroviridae, however, experimental evidence for this has not yet been provided and requires further study. The primer activity of VPg occurs when the protein becomes uridylated, providing a free hydroxyl that can be extended by the virally encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. For some virus families, VPg also has a role in translation initiation by acting like a 5' mRNA cap.
An internal ribosome entry site, abbreviated IRES, is an RNA element that allows for translation initiation in cap-independent manner, as part of the greater process of protein synthesis. In eukaryotic translation, initiation typically occurs at the 5' end of mRNA molecules, since 5' cap recognition is required for the assembly of the initiation complex. The location for IRES elements is often in the 5'UTR, but can also occur elsewhere in mRNAs.
Ribosome shunting is a mechanism of translation initiation in which ribosomes bypass, or "shunt over", parts of the 5' untranslated region to reach the start codon. However, a benefit of ribosomal shunting is that it can translate backwards allowing more information to be stored than usual in an mRNA molecule. Some viral RNAs have been shown to use ribosome shunting as a more efficient form of translation during certain stages of viral life cycle or when translation initiation factors are scarce. Some viruses known to use this mechanism include adenovirus, Sendai virus, human papillomavirus, duck hepatitis B pararetrovirus, rice tungro bacilliform viruses, and cauliflower mosaic virus. In these viruses the ribosome is directly translocated from the upstream initiation complex to the start codon (AUG) without the need to unwind RNA secondary structures.
Tombusvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Tombusviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 17 species in this genus. Symptoms associated with this genus include mosaic. The name of the genus comes from Tomato bushy stunt virus.

Alfalfa mosaic virus (AMV), also known as Lucerne mosaic virus or Potato calico virus, is a worldwide distributed phytopathogen that can lead to necrosis and yellow mosaics on a large variety of plant species, including commercially important crops. It is the only Alfamovirus of the family Bromoviridae. In 1931 Weimer J.L. was the first to report AMV in alfalfa. Transmission of the virus occurs mainly by some aphids, by seeds or by pollen to the seed.

The Alfalfa mosaic virus RNA 1 5′ UTR stem-loop represents a putative stem-loop structure found in the 5′ UTR in RNA 1 of alfalfa mosaic virus. RNA 1 is responsible for encoding the viral replicase protein P1. This family is required for negative strand RNA synthesis in the alfalfa mosaic virus and may also be involved in positive strand RNA synthesis.
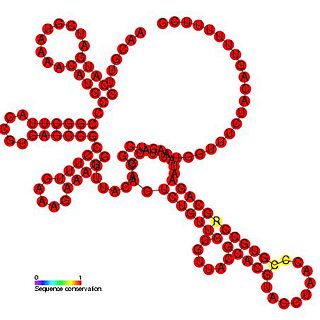
The Bamboo mosaic potexvirus (BaMV) cis-regulatory element represents a cloverleaf-like cis-regulatory element found in the 3' UTR of the bamboo mosaic virus. This family is thought to play an important role in the initiation of minus-strand RNA synthesis and may also be involved in the regulation of viral replication.

This family represents the internal ribosome entry site (IRES) of the hepatitis A virus. HAV IRES is a 450 nucleotide long sequence located in the 735 nt long 5’ UTR of Hepatitis A viral RNA genome. IRES elements allow cap and end-independent translation of mRNA in the host cell. The IRES achieves this by mediating the internal initiation of translation by recruiting a ribosomal 40S pre-initiation complex directly to the initiation codon and eliminates the requirement for eukaryotic initiation factor, eIF4F.
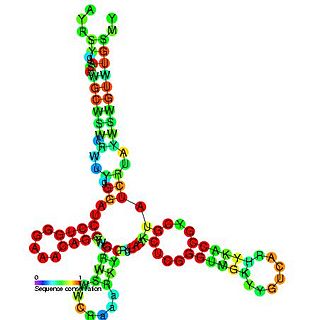
The Barley yellow dwarf virus-like cap-independent translation element (BTE) is an RNA element found in the 3' UTR of some luteoviruses. This element mediates translation of genomic RNA and subgenomic RNA1 (sgRNA1).

The Upstream pseudoknot (UPSK) domain is an RNA element found in the turnip yellow mosaic virus, beet virus Q, barley stripe mosaic virus and tobacco mosaic virus, which is thought to be needed for efficient transcription. Disruption of the pseudoknot structure gives rise to a 50% drop in transcription efficiency. This element acts in conjunction with the Tymovirus/Pomovirus tRNA-like 3' UTR element to enhance translation.

Ilarvirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Bromoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 22 species in this genus.

Red clover necrotic mosaic virus (RCNMV) contains several structural elements present within the 3′ and 5′ untranslated regions (UTR) of the genome that enhance translation. In eukaryotes transcription is a prerequisite for translation. During transcription the pre-mRNA transcript is processes where a 5′ cap is attached onto mRNA and this 5′ cap allows for ribosome assembly onto the mRNA as it acts as a binding site for the eukaryotic initiation factor eIF4F. Once eIF4F is bound to the mRNA this protein complex interacts with the poly(A) binding protein which is present within the 3′ UTR and results in mRNA circularization. This multiprotein-mRNA complex then recruits the ribosome subunits and scans the mRNA until it reaches the start codon. Transcription of viral genomes differs from eukaryotes as viral genomes produce mRNA transcripts that lack a 5’ cap site. Despite lacking a cap site viral genes contain a structural element within the 5’ UTR known as an internal ribosome entry site (IRES). IRES is a structural element that recruits the 40s ribosome subunit to the mRNA within close proximity of the start codon.

Barley yellow dwarf virus 5' UTR is a non-coding RNA element containing structural elements required for translation of the viral genome.

Positive-strand RNA viruses are a group of related viruses that have positive-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translated into viral proteins by the host cell's ribosomes. Positive-strand RNA viruses encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) which is used during replication of the genome to synthesize a negative-sense antigenome that is then used as a template to create a new positive-sense viral genome.

Flavivirus 5' UTR are untranslated regions in the genome of viruses in the genus Flavivirus.
References
- 1 2 Miller, WA; Wang, Z; Treder, K (Dec 2007). "The amazing diversity of cap-independent translation elements in the 3'-untranslated regions of plant viral RNAs". Biochemical Society Transactions. 35 (Pt 6): 1629–1633. doi:10.1042/BST0351629. PMC 3081161 . PMID 18031280.
- 1 2 Nicholson, BL; White, KA (Nov 2011). "3' Cap-independent translation enhancers of positive-strand RNA plant viruses". Current Opinion in Virology. 1 (5): 373–380. doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.002. PMID 22440838.
- ↑ An, M; Iwakawa, HO; Mine, A; Kaido, M; Mise, K; Okuno, T (Sep 15, 2010). "A Y-shaped RNA structure in the 3' untranslated region together with the trans-activator and core promoter of Red clover necrotic mosaic virus RNA2 is required for its negative-strand RNA synthesis" (PDF). Virology. 405 (1): 100–109. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.05.022 . PMID 20561661.