
The Research Triangle Regional Public Transportation Authority, known as GoTriangle, provides regional bus service to the Research Triangle region of North Carolina in Wake, Durham, and Orange counties. The GoTriangle name was adopted in 2015 as part of the consolidated GoTransit branding scheme for the Triangle. In 2023, the system had a ridership of 1,735,700, or about 6,300 per weekday as of the fourth quarter of 2023.

Halifax Regional Council is the governing body of Halifax, known as the Halifax Regional Municipality (HRM). Halifax is governed by a mayor-council system, where councillors are elected from sixteen geographic districts though a first-past-the-post system and the mayor is elected via a municipality-wide first-past-the-post vote. Halifax Regional Council was formed in 1996 and consisted of twenty-three councillors and one mayor. It was reduced in size to sixteen councillors and the mayor in 2012. The council meets at Halifax City Hall.

The San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency is an agency created by consolidation of the San Francisco Municipal Railway (Muni), the Department of Parking and Traffic (DPT), and the Taxicab Commission. The agency oversees public transport, taxis, bicycle infrastructure, pedestrian infrastructure, and paratransit for the City and County of San Francisco.

A Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO) is a federally mandated and federally funded transportation policy-making organization in the United States that is made up of representatives from local government and governmental transportation authorities. They were created to ensure regional cooperation in transportation planning. MPOs were introduced by the Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1962, which required the formation of an MPO for any urbanized area (UZA) with a population greater than 50,000. Federal funding for transportation projects and programs are channeled through this planning process. Congress created MPOs in order to ensure that existing and future expenditures of governmental funds for transportation projects and programs are based on a continuing, cooperative, and comprehensive ("3-C") planning process. Statewide and metropolitan transportation planning processes are governed by federal law. Transparency through public access to participation in the planning process and electronic publication of plans now is required by federal law. As of 2015, there are 408 MPOs in the United States.
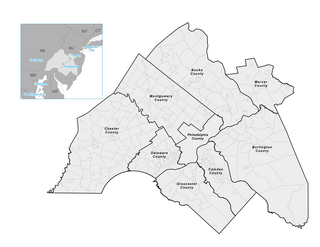
The Delaware Valley Regional Planning Commission (DVRPC) is the metropolitan planning organization for the Delaware Valley. Created in 1965 by an interstate compact, DVRPC is responsible for transportation and regional planning in the greater Philadelphia area.

The Big Move is the regional transportation plan (RTP) published by Metrolinx for the Greater Toronto and Hamilton Area (GTHA) in Ontario, Canada. It makes specific recommendations for transit projects, resulting from seven "green papers" and two "white papers" released for public discussion. A draft RTP was released alongside draft investment strategy in September 2008. After a series of stakeholder consultations and public meetings, the final RTP was approved and published by Metrolinx on 28 November 2008.
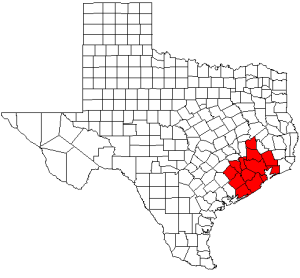
The Houston-Galveston Area Council (H-GAC) is the region-wide voluntary association of local governments in the 13-county Gulf Coast Planning Region of Texas. The organization works with local government officials to solve problems across the area. H-GAC was founded in 1966.
The Lexington Area Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO) has been involved with transportation planning in Lexington, Kentucky, USA, and its immediate area since being established in 1974. It is responsible, in cooperation with the Kentucky Transportation Cabinet, for planning and coordinating all aspects of transportation planning on behalf of local governments within its region, which includes the Lexington-Fayette Urban County Government and Jessamine County.
The Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT) oversees roads, public transit, aeronautics, and transportation licensing and registration in the US state of Massachusetts. It was created on November 1, 2009, by the 186th Session of the Massachusetts General Court upon enactment of the 2009 Transportation Reform Act.
The North Carolina Capital Area Metropolitan Planning Organization (NC CAMPO) is the federally required Metropolitan Planning Organization responsible for the continuous and comprehensive transportation planning process in Wake County and parts of Franklin County, Granville County, Harnett County and Johnston County Counties. NC CAMPO is responsible for carrying out an annual work program that includes updating the Metropolitan Transportation Improvement Program (a seven-year project programming schedule) and the Long-Range Transportation Plan (a minimum twenty-year forecast of projects and programs).
The Regional Transportation Plan (RTP) in the United States is a long-term blueprint of a region's transportation system. Usually RTPs are conducted every five years and are plans for thirty years into the future, with the participation of dozens of transportation and infrastructure specialists. The plan identifies and analyzes transportation needs of the metropolitan region and creates a framework for project priorities.
The Hampton Roads Transportation Accountability Commission (HRTAC) is a political subdivision of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States that has the responsibility for funding several major traffic projects in the Hampton Roads area. It was created by the Virginia General Assembly in 2014 to maintain and administer the Hampton Roads Transportation Fund, a trust fund established by the Virginia General Assembly through a 0.7% increase in the state sales and use tax and a 2.1% increase in the fuel tax region-wide. The organization previously existed as the Hampton Roads Transportation Authority (HRTA) but was disbanded in 2008 after the Virginia Supreme Court invalidated its authority to raise and levy taxes.
The Chicago Metropolitan Agency for Planning (CMAP) is a metropolitan planning organization (MPO) responsible for comprehensive regional transportation planning in Cook, DuPage, Kane, Kendall, Lake, McHenry and Will counties in northeastern Illinois. The agency developed and now guides implementation of ON TO 2050, a new long-range plan to help the seven counties and 284 communities of northeastern Illinois implement strategies that address transportation, housing, economic development, open space, the environment, and other quality-of-life issues.
The Puget Sound Regional Council (PSRC) is a metropolitan planning organization that develops policies and makes decisions about transportation planning, economic development, and growth management throughout the four-county Seattle metropolitan area surrounding Puget Sound. It is a forum for cities, towns, counties, transit agencies, port districts, Native American tribes, and state agencies to address regional issues.

The Tampa Bay Area Regional Transit Authority, or TBARTA, was a regional transportation agency of the U.S. state of Florida which was created on July 1, 2007. The transportation agency ceased all operations on December 30, 2023, after the governing board voted unanimously to disband. The purpose of the agency was "to plan, develop, finance, construct, own, purchase, operate, maintain, relocate, equip, repair, and manage multimodal systems in Hernando, Hillsborough, Manatee, Pasco, and Pinellas Counties." The agency coordinated its efforts with the Florida Department of Transportation to improve transportation in the Tampa Bay Area.

Victor Valley Transit Authority (VVTA), the second largest transit operator in San Bernardino County, is a transit agency providing bus service in the Victor Valley, California area. In 2023, the system had a ridership of 1,476,600.
The North Jersey Transportation Planning Authority (NJTPA) is the federally authorized metropolitan planning organization (MPO) for the 13-county northern New Jersey region, one of three MPOs in the state. NJTPA's annual budget is more than $2 billion for transportation improvement projects. The Authority also participates in inter-agency cooperation and receives public input into funding decisions. The NJTPA sponsors and conducts studies, assists county planning agencies and monitors compliance with national air quality goals. The Authority provides federal funding to support the planning work of its 15 subregions. The funds are matched by a local contribution. As vital partners in regional planning work, the subregions help bring a local perspective to all aspects of NJTPA's work to improve the northern New Jersey transportation network.
The Sustainable Communities and Climate Protection Act of 2008, also known as Senate Bill 375 or SB 375, is a State of California law targeting greenhouse gas emissions from passenger vehicles. The Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006 sets goals for the reduction of statewide greenhouse gas emissions. Passenger vehicles are the single largest source of greenhouse gas emissions statewide, accounting for 30% of total emissions. SB 375 therefore provides key support to achieve the goals of AB 32.
Urban freight distribution is the system and process by which goods are collected, transported, and distributed within urban environments. The urban freight system can include seaports, airports, manufacturing facilities, and warehouse/distribution centers that are connected by a network of railroads, rail yards, pipelines, highways, and roadways that enable goods to get to their destinations.
A transportation improvement program (TIP) is a United States federally mandated requirement for all metropolitan planning organizations (MPOs). The TIP, also known as a short-range plan, lists all transportation projects in an MPO's metropolitan planning area that seek federal transportation funding within at least a four-year horizon.