Related Research Articles

Reinforced concrete (RC), also called reinforced cement concrete (RCC) and ferroconcrete, is a composite material in which concrete's relatively low tensile strength and ductility are compensated for by the inclusion of reinforcement having higher tensile strength or ductility. The reinforcement is usually, though not necessarily, steel bars (rebar) and is usually embedded passively in the concrete before the concrete sets. However, post-tensioning is also employed as a technique to reinforce the concrete. In terms of volume used annually, it is one of the most common engineering materials. In corrosion engineering terms, when designed correctly, the alkalinity of the concrete protects the steel rebar from corrosion.

A composite material is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions.

Building material is material used for construction. Many naturally occurring substances, such as clay, rocks, sand, wood, and even twigs and leaves, have been used to construct buildings. Apart from naturally occurring materials, many man-made products are in use, some more and some less synthetic. The manufacturing of building materials is an established industry in many countries and the use of these materials is typically segmented into specific specialty trades, such as carpentry, insulation, plumbing, and roofing work. They provide the make-up of habitats and structures including homes.

A railroad tie, crosstie, railway tie or railway sleeper is a rectangular support for the rails in railroad tracks. Generally laid perpendicular to the rails, ties transfer loads to the track ballast and subgrade, hold the rails upright and keep them spaced to the correct gauge.
Basalt fibers are produced from basalt rocks by melting them and converting the melt into fibers. Basalts are rocks of igneous origin. The main energy consumption for the preparation of basalt raw materials to produce of fibers is made in natural conditions. Basalt continuous, staple and super-thin fibers are produced and used. Basalt continuous fibers (BCF) are used for the production of reinforcing materials and composite products, fabrics and non-woven materials. Basalt staple fibers - for the production of thermal insulation materials. Basalt superthin fibers (BSTF) - for the production of high quality heat and sound insulating and fireproof materials.

Cardington is a village and civil parish in the Borough of Bedford in Bedfordshire, England.

Delamination is a mode of failure where a material fractures into layers. A variety of materials including laminate composites and concrete can fail by delamination. Processing can create layers in materials such as steel formed by rolling and plastics and metals from 3D printing which can fail from layer separation. Also, surface coatings such as paints and films can delaminate from the coated substrate.

A metal foam is a cellular structure consisting of a solid metal with gas-filled pores comprising a large portion of the volume. The pores can be sealed or interconnected. The defining characteristic of metal foams is a high porosity: typically only 5–25% of the volume is the base metal. The strength of the material is due to the square–cube law.

The Eurocodes are the ten European standards specifying how structural design should be conducted within the European Union (EU). These were developed by the European Committee for Standardization upon the request of the European Commission.

Fireproofing is rendering something resistant to fire, or incombustible; or material for use in making anything fire-proof. It is a passive fire protection measure. "Fireproof" or "fireproofing" can be used as a noun, verb or adjective; it may be hyphenated ("fire-proof").

Structural steel is a category of steel used for making construction materials in a variety of shapes. Many structural steel shapes take the form of an elongated beam having a profile of a specific cross section. Structural steel shapes, sizes, chemical composition, mechanical properties such as strengths, storage practices, etc., are regulated by standards in most industrialized countries.

Anchor bolts are used to connect structural and non-structural elements to concrete. The connection can be made by a variety of different components: anchor bolts, steel plates, or stiffeners. Anchor bolts transfer different types of load: tension forces and shear forces.
Fiber-reinforced concrete or fibre-reinforced concrete (FRC) is concrete containing fibrous material which increases its structural integrity. It contains short discrete fibers that are uniformly distributed and randomly oriented. Fibers include steel fibers, glass fibers, synthetic fibers and natural fibers – each of which lend varying properties to the concrete. In addition, the character of fiber-reinforced concrete changes with varying concretes, fiber materials, geometries, distribution, orientation, and densities.
The Edinburgh Fire Research Centre is the research group at The Institute of Infrastructure and Environment, University of Edinburgh conducting research in fire, structures and environment.
Composite construction is a generic term to describe any building construction involving multiple dissimilar materials. Composite construction is often used in building aircraft, watercraft, and building construction. There are several reasons to use composite materials including increased strength, aesthetics, and environmental sustainability.

Progressive collapse is the process where a primary structural element fails, resulting in the failure of adjoining structural elements, which in turn causes further structural failure.
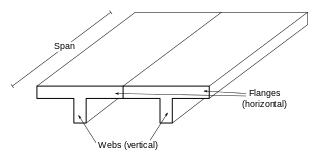
A T-beam, used in construction, is a load-bearing structure of reinforced concrete, wood or metal, with a T-shaped cross section. The top of the T-shaped cross section serves as a flange or compression member in resisting compressive stresses. The web of the beam below the compression flange serves to resist shear stress. When used for highway bridges the beam incorporates reinforcing bars in the bottom of the beam to resist the tensile stresses which occur during bending.

Structural engineering depends on the knowledge of materials and their properties, in order to understand how different materials resist and support loads.
In the Eurocode series of European standards (EN) related to construction, Eurocode 4: Design of composite steel and concrete structures describes how to design of composite structures, using the limit state design philosophy. It was approved by the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) on 4 November 2004. Eurocode 4 is divided in two parts EN 1994-1 and EN 1994-2.
Colin F. Bailey is a researcher in structural engineering, who became the President and Principal of Queen Mary University of London in September 2017. Prior to that, Bailey was Deputy President and Deputy Vice-Chancellor at the University of Manchester. He is a Fellow of the Royal Academy of Engineering, the Institution of Civil Engineers, the Institution of Structural Engineers and a member of the Institution of Fire Engineers.