| Look up Carla in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Carla is a feminine given name.
Contents
Carla may also refer to:
| Look up Carla in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Carla is a feminine given name.
Carla may also refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Carla. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
The Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS), formerly the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale (SSHS), classifies hurricanes – Western Hemisphere tropical cyclones – that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms – into five categories distinguished by the intensities of their sustained winds.

The 1961 Atlantic hurricane season featured a large number of major hurricanes, with two reaching Category 5 intensity. The season officially began on June 15, and lasted until November 15. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. It was an above average season in terms of tropical storms with a total of 12 named storms. The first system, Hurricane Anna, developed in the eastern Caribbean Sea near the Windward Islands on July 20. It brought minor damage to the islands, as well as wind and flood impacts to Central America after striking Belize as a hurricane. Anna caused one death and about $300,000 (1961 USD) in damage. Activity went dormant for nearly a month and a half, until Hurricane Betsy developed on September 2. Betsy peaked as a Category 4 hurricane, but remained at sea and caused no impact.
The name Alex has been used for a total of 11 tropical cyclones worldwide: Four in the Atlantic Ocean, four in the West Pacific Ocean and three in the South Indian Ocean.

Hurricane Carla ranks as the most intense U.S. tropical cyclone landfall on the Hurricane Severity Index. The third named storm of the 1961 Atlantic hurricane season, Carla developed from an area of squally weather in the southwestern Caribbean Sea on September 3. Initially a tropical depression, it strengthened slowly while heading northwestward, and by September 5, the system was upgraded to Tropical Storm Carla. About 24 hours later, Carla was upgraded to a hurricane. Shortly thereafter, the storm curved northward while approaching the Yucatán Channel. Late on September 7, Carla entered the Gulf of Mexico while passing just northeast of the Yucatán Peninsula. By early on the following day, the storm became a major hurricane after reaching Category 3 intensity. Resuming its northwestward course, Carla continued intensification and on September 11, it was upgraded to a Category 4 hurricane. Later that day, Carla weakened slightly, but was still a large and intense hurricane when the storm made landfall near Port O'Connor, Texas. It weakened quickly inland and was reduced to a tropical storm on September 12. Heading generally northward, Carla transitioned into an extratropical cyclone on September 13, while centered over southern Oklahoma. Rapidly moving northeastward, Carla's remnants reached the Labrador Sea, Canada and dissipated on September 17, 1961.

Hurricane John, also known as Typhoon John, was both the longest-lasting and the farthest-traveling tropical cyclone ever observed. John formed during the 1994 Pacific hurricane season, which had above-average activity due to the El Niño of 1994–95, and peaked as a Category 5 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson scale, the highest categorization for hurricanes.
The name Gordon has been used for five tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean since 1988, when it replaced the name Gilbert on the list of hurricane names.
Tropical Storm Maria, Hurricane Maria or Typhoon Maria may refer to:
Tropical Storm Ophelia may refer to:
The appearances of tropical cyclones in popular culture spans many genres of media and encompasses many different plot uses.
Tropical Storm Alice may refer to:
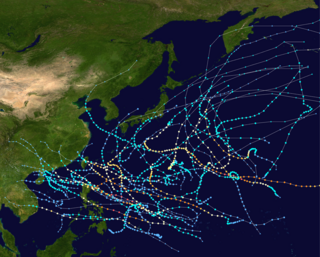
The 1967 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1967, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1955 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1955, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
Tropical cyclones are ranked on one of five tropical cyclone intensity scales, according to their maximum sustained winds and which tropical cyclone basin(s) they are located in. Only a few scales of classifications are used officially by the meteorological agencies monitoring the tropical cyclones, but some alternative scales also exist, such as accumulated cyclone energy, the Power Dissipation Index, the Integrated Kinetic Energy Index, and the Hurricane Severity Index.
The name Abby has been used as a name for tropical cyclones in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
The name Agnes has been used for a total of sixteen tropical cyclones worldwide: one in the Atlantic Ocean, thirteen in the Western Pacific Ocean, one in the Southwest Indian Ocean, and one in the Southwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1959 Pacific hurricane season featured the first Category 5 hurricane ever recorded in the Central Pacific basin.

Super Typhoon Fred, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Susang, was a powerful and destructive tropical cyclone that made landfall in southern China during the 1994 Pacific typhoon season. It was the worst storm to hit Zhejiang in 160 years.

This timeline documents all of the events of the 2013 Pacific typhoon season. Most of the tropical cyclones formed between May and November. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator between 100°E and the International Date Line. Tropical storms that form in the entire Western Pacific basin are assigned a name by the Japan Meteorological Agency. Tropical depressions that form in this basin are given a number with a "W" suffix by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center. In addition, the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assigns names to tropical cyclones that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility. These names, however, are not in common use outside of the Philippines.