
William Kennedy Laurie Dickson was a British-American inventor who devised an early motion picture camera under the employment of Thomas Edison.

Blacksmith Scene is an 1893 American short black-and-white silent film directed by William K.L. Dickson, the Scottish-French inventor who, while under the employ of Thomas Edison, developed one of the first fully functional motion picture cameras. It is historically significant as the first Kinetoscope film shown in public exhibition on May 9, 1893, and is the earliest known example of actors performing a role in a film. It was also the first U.S. motion picture film ever copyrighted that same year. 102 years later, in 1995, Blacksmithing Scene was selected for preservation in the United States National Film Registry by the Library of Congress as being "culturally, historically, or aesthetically significant". It is the second-oldest film included in the Registry, after Newark Athlete (1891).
The following is an overview of the events of 1895 in film, including a list of films released and notable births.
The following is an overview of the events of 1894 in film, including a list of films released and notable births.

The Kinetoscope is an early motion picture exhibition device, designed for films to be viewed by one person at a time through a peephole viewer window. The Kinetoscope was not a movie projector, but it introduced the basic approach that would become the standard for all cinematic projection before the advent of video: it created the illusion of movement by conveying a strip of perforated film bearing sequential images over a light source with a high-speed shutter. First described in conceptual terms by U.S. inventor Thomas Edison in 1888, it was largely developed by his employee William Kennedy Laurie Dickson between 1889 and 1892. Dickson and his team at the Edison lab in New Jersey also devised the Kinetograph, an innovative motion picture camera with rapid intermittent, or stop-and-go, film movement, to photograph movies for in-house experiments and, eventually, commercial Kinetoscope presentations.

Frederick Paul Ott, skilled machinist, was a key employee of Thomas Edison's laboratories from the 1870s until Edison's death in 1931. His likeness appears in two of the earliest surviving motion pictures – the well-known Edison Kinetoscopic Record of a Sneeze and the little-seen Fred Ott Holding a Bird – both from 1894.

The Dickson Experimental Sound Film is a film made by William Dickson in late 1894 or early 1895. It is the first known film with live-recorded sound and appears to be the first motion picture made for the Kinetophone, the proto-sound-film system developed by Dickson and Thomas Edison. The film was produced at the "Black Maria", Edison's New Jersey film studio. There is no evidence that it was ever exhibited in its original format.

Edwin Stanton Porter was an American film pioneer, most famous as a producer, director, studio manager and cinematographer with the Edison Manufacturing Company and the Famous Players Film Company. Of over 250 films created by Porter, his most important include What Happened on Twenty-third Street, New York City (1901), Jack and the Beanstalk (1902), Life of an American Fireman (1903), The Great Train Robbery (1903), The European Rest Cure (1904), The Kleptomaniac (1905), Life of a Cowboy (1906), Rescued from an Eagle's Nest (1908), and The Prisoner of Zenda (1913).
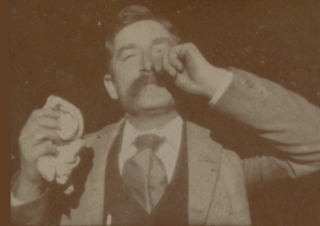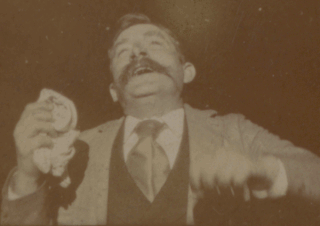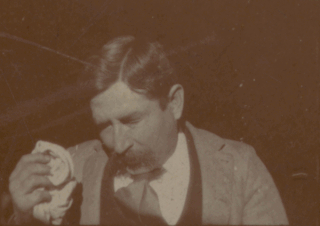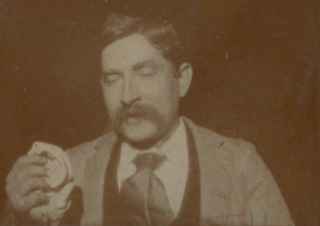
Fred Ott's Sneeze is an 1894 short, black-and-white silent film shot by William K.L. Dickson and featuring Fred Ott. According to the Library of Congress, it is the second oldest surviving U.S. motion picture to be copyrighted, although it is now in the public domain.

The Black Maria was Thomas Edison's film production studio in West Orange, New Jersey. It was the world's first film studio.

Actuality film is a non-fiction film genre that uses footage of real events, places, and things, a predecessor to documentary film. Unlike documentaries, actuality films are not structured into a larger narrative or coherent whole. During the era of early cinema, actualities—usually lasting no more than a minute or two and usually assembled together into a program by an exhibitor—were just as popular and prominent as their fictional counterparts. The line between "fact" and "fiction" was not as prominent in early cinema as it would become once documentaries became the predominant non-fiction filmmaking form. Actuality as a film genre is related to still photography.

Herman Casler was an American inventor and co-founder of the partnership called the K.M.C.D. Syndicate, along with W.K-L. Dickson, Elias Koopman, and Henry N "Harry" Marvin, which eventually was incorporated into the American Mutoscope Company in December 1895.
The decade of the 1890s in film involved some significant events.

Carmen Dauset Moreno, better known simply as Carmencita (1868–1910), was a Spanish-style dancer in American pre-vaudeville variety and music hall ballet.

Corbett and Courtney Before the Kinetograph is an 1894 American short black-and-white silent film produced by William K.L. Dickson and starring James J. Corbett. It was only the second boxing match to be filmed, following The Leonard-Cushing Fight which had been filmed by Dickson on June 14, 1894.

Luis Martinetti, Contortionist is an 1894 American short film produced by the Edison Manufacturing Company. The film, which runs 12.5 seconds, consists of a contortionist act performed by Luis Martinetti of the Martinetti Brothers trapeze act. Martinetti wears tiger-striped tights and performs contortionist poses on a pair of trapeze rings.

Men Boxing is an 1891 American short silent film, produced and directed by William K. L. Dickson and William Heise for the Edison Manufacturing Company, featuring two Edison employees with boxing gloves, pretending to spar in a boxing ring. The 12 feet of film was shot between May and June 1891 at the Edison Laboratory Photographic Building in West Orange, New Jersey, on the Edison-Dickson-Heise experimental horizontal-feed kinetograph camera and viewer, through a round aperture on 3/4 inch (19mm) wide film with a single edge row of sprocket perforations, as an experimental demonstration and was never publicly shown. A print has been preserved in the US Library of Congress film archive as part of the Gordon Hendricks collection.

The Leonard–Cushing Fight is an 1894 American short black-and-white silent film produced by William K.L. Dickson, starring Mike Leonard and Jack Cushing. Leonard and Cushing participate in a six-round boxing match under special conditions that allow for it to be filmed and displayed on a Kinetograph. The film was shot on an uncertain date between May 24 and June 14, 1894, in a specially configurated ring in Edison's Black Maria film studio in West Orange, New Jersey. Premiered on August 4, 1894 in Manhattan, the movie is the first sports film ever released. As of 2023, no full print of the film is known to have survived, making it a partially lost film. A 23-second fragment is available at the Library of Congress.















