| Cascajal River | |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Country | Panama |
The Cascajal River is a river of Panama.
| Cascajal River | |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Country | Panama |
The Cascajal River is a river of Panama.

Canals are waterway channels, or artificial waterways, for water conveyance, or for servicing water transport vehicles. They carry free surface flow under atmospheric pressure, and can be thought of as artificial rivers.

Panama, officially the Republic of Panama, is a transcontinental country in Central America and South America, bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the south. The capital and largest city is Panama City, whose metropolitan area is home to nearly half the country's 4 million people.

Panama is a country located in Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, between Colombia and Costa Rica. Panama is located on the narrow and low Isthmus of Panama.
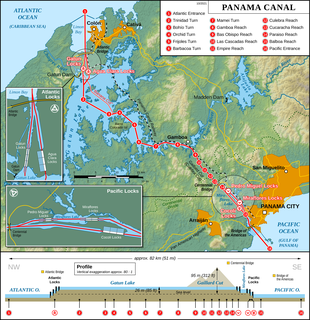
The Panama Canal is an artificial 82 km (51 mi) waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a conduit for maritime trade. One of the largest and most difficult engineering projects ever undertaken, the Panama Canal shortcut greatly reduces the time for ships to travel between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, enabling them to avoid the lengthy, hazardous Cape Horn route around the southernmost tip of South America via the Drake Passage or Strait of Magellan and the even less popular route through the Arctic Archipelago and the Bering Strait.

Panama City, also simply known as Panama, is the capital and largest city of Panama. It has an urban population of 880,691, with over 1.5 million in its metropolitan area. The city is located at the Pacific entrance of the Panama Canal, in the province of Panama. The city is the political and administrative center of the country, as well as a hub for banking and commerce.

A steamboat is a boat that is propelled primarily by steam power, typically driving propellers or paddlewheels. Steamboats sometimes use the prefix designation SS, S.S. or S/S or PS ; however, these designations are most often used for steamships.
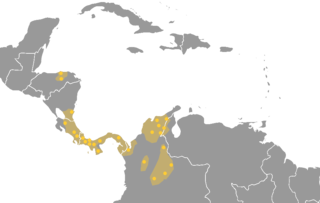
The Chibchan languages make up a language family indigenous to the Isthmo-Colombian Area, which extends from eastern Honduras to northern Colombia and includes populations of these countries as well as Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. The name is derived from the name of an extinct language called Chibcha or Muysccubun, once spoken by the people who lived on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense of which the city of Bogotá was the southern capital at the time of the Spanish Conquista. However, genetic and linguistic data now indicate that the original heart of Chibchan languages and Chibchan-speaking peoples might not have been in Colombia, but in the area of the Costa Rica-Panama border, where the greatest variety of Chibchan languages has been identified.

Colón is a city and seaport in Panama, beside the Caribbean Sea, lying near the Atlantic entrance to the Panama Canal. It is the capital of Panama's Colón Province and has traditionally been known as Panama's second city. Originally it was located entirely on Manzanillo Island, surrounded by Limon Bay, Manzanillo Bay, and the Folks River; however, since the disestablishment of the Panama Canal Zone, the city's limits have been redefined to include Fort Gulick, a former U.S. Army base, as well the former Panama Canal Zone towns of Cristobal, Margarita, and Coco Solo.

The Darién Gap is a break across the North and South American continents within Central America, consisting of a large watershed, forest, and mountains in the northern portion of Colombia's Chocó Department and Panama's Darién Province.

Darién is a province in Panama whose capital city is La Palma. With an area of 11,896.5 km2 (4,593.3 sq mi), it is located at the eastern end of the country and bordered to the north by the province of Panamá and the region of Kuna Yala. To the south, it is bordered by the Pacific Ocean and Colombia. To the east, it borders Colombia; to the west, it borders the Pacific Ocean and the province of Panama.

Gatun Lake is a large freshwater artificial lake to the south of Colón, Panama. It forms a major part of the Panama Canal, carrying ships for 33 km (21 mi) of their transit across the Isthmus of Panama.
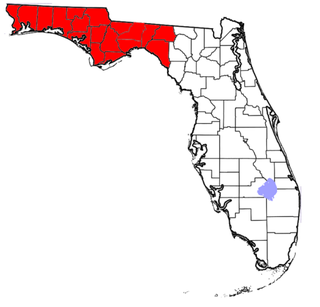
The Florida Panhandle is the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Florida; it is a strip of land roughly 200 miles (320 km) long and 50 to 100 miles wide, lying between Alabama on the north and the west, Georgia on the north, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. Its eastern boundary is arbitrarily defined. In terms of population, major communities include Tallahassee, Pensacola, and Navarre.

The Chagres River, in central Panama, is the largest river in the Panama Canal's watershed. The river is dammed twice, and the resulting reservoirs—Gatun Lake and Lake Alajuela—form an integral part of the canal and its water system. Although the river's natural course runs northwest to its mouth at the Caribbean Sea, its waters also flow, via the canal's locks, into the Gulf of Panama to the south. The Chagres thus has the unusual claim of drainage into two oceans.
The Embera–Wounaan are a semi-nomadic indigenous people in Panama living in Darién Province on the shores of the Chucunaque, Sambú, Tuira Rivers and its water ways. The Embera-Wounaan were formerly and widely known by the name Chocó, and they speak the Embera and Wounaan languages, part of the Choco language family.
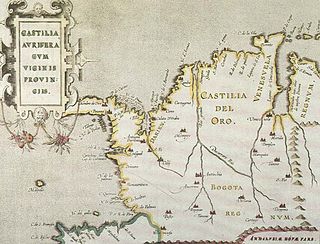
Castilla de Oro or del Oro was the name given by the Spanish settlers at the beginning of the 16th century to the Central American territories from the Gulf of Urabá, near today's Colombian-Panamanian border, to the Belén River. Beyond that river, the region was known as Veragua, and was disputed by the Spanish crown along with the Columbus family. The name "Castilla de Oro" was made official in May 1513 by King Ferdinand II of Aragon, then regent of the Crown of Castile.
The Chepo expedition was a pirate voyage led by Spanish renegades Juan Guartem, Eduardo Blomar and Bartolomé Charpes in the Spanish Main during 1679. Sailing up the Mandinga River, the expedition crossed the Isthmus of Panama into the Pacific where they raided shipping for several months as well as looting and then burning the town of Chepo, Panama. They were tried in absentia by the Viceroy of Bogotá and on his orders were burned in effigy at Santa Fe de Bogotá. However, the three continued committing piracy on both coasts of Central America and were never caught for their crimes. This was the second major expedition following the "Pacific Adventure" led by John Coxon that same year.
Rio Bravo is a former settlement in Kern County, California. It was located on the railroad 2 miles (3.2 km) north of Panama.

The Emberálisten (help·info), also known in the historical literature as the Chocó or Katío Indians are an indigenous people of Panama and Colombia. In the Emberá language, the word ẽberá can be used to mean person, man, or indigenous person, depending on the context in which it is used. There are approximately 33,000 people living in Panama and 50,000 in Colombia who identify as Emberá.

The fortifications on the Caribbean Side of Panama: Portobelo-San Lorenzo are military constructions, built by the Spanish Empire during the 17th and 18th centuries on the Caribbean coastline of Colón Province in Panama. The ruins are located on the coast of the province of Colón. In view of their cultural importance, the sites have been inscribed by UNESCO in 1980 as a World Heritage Site under Criteria (i) and (iv), with the description, "Magnificent examples of 17th- and 18th-century military architecture, these Panamanian forts on the Caribbean coast form part of the defence system built by the Spanish Crown to protect transatlantic trade."

The Panama Papers are 2.6TB of data or 11.5 million leaked documents that detail financial and attorney–client information for more than 214,488 offshore entities leaked beginning on 3 April 2016. The documents, some dating back to the 1970s, were created by, and taken from, former Panamanian law firm and corporate service provider Mossack Fonseca.