
In military organizations, a colour guard is a detachment of soldiers assigned to the protection of regimental colours and the national flag. This duty is highly prestigious, and the military colour is generally carried by a young officer (ensign), while experienced non-commissioned officers are assigned to the protection of the national flag. These non-commissioned officers, accompanied in several countries by warrant officers, can be ceremonially armed with either sabres or rifles to protect the colour. Colour guards are generally dismounted, but there are also mounted colour guard formations as well.
A company is a military unit, typically consisting of 100–250 soldiers and usually commanded by a major or a captain. Most companies are formed of three to seven platoons, although the exact number may vary by country, unit type, and structure.

Military ranks are a system of hierarchical relationships, within armed forces, police, intelligence agencies or other institutions organized along military lines. The military rank system defines dominance, authority, and responsibility in a military hierarchy. It incorporates the principles of exercising power and authority into the military chain of command—the succession of commanders superior to subordinates through which command is exercised. The military chain of command constructs an important component for organized collective action.
Sergeant major is a senior non-commissioned rank or appointment in many militaries around the world.

During the American Civil War, the United States Army, the land force that fought to preserve the collective Union of the states, was often referred to as the Union Army, the Grand Army of the Republic, the Federal Army, or the Northern Army. It proved essential to the restoration and preservation of the United States as a working, viable republic.

The several branches of the United States Armed Forces are represented by flags. Within the U.S. military, various flags fly on various occasions, and on various ships, bases, camps, and military academies.

The flag of the United States Marine Corps is the flag used to represent the U.S. Marine Corps, as well as its subsidiary units and formations.

Adjutant is a military appointment given to an officer who assists the commanding officer with unit administration, mostly the management of human resources in an army unit. The term adjudant is used in French-speaking armed forces as a non-commissioned officer rank similar to a staff sergeant or warrant officer but is not equivalent to the role or appointment of an adjutant.
The chart below shows the current enlisted rank insignia of the United States Army, with seniority, and pay grade, increasing from right to left. The enlisted ranks of corporal (E-4) and higher are considered non-commissioned officers (NCOs). The rank of specialist is also in pay grade E-4, but does not hold non-commissioned officer status; it is common that a soldier may never hold the rank of corporal, and instead be promoted from specialist to sergeant, attaining junior NCO status at that time.

Christian Abraham Fleetwood, was an African American non-commissioned officer in the United States Army, a commissioned officer in the D.C. National Guard, an editor, a musician, and a government official. He received the Medal of Honor for his actions during the American Civil War. He wrote "The Negro As a Soldier" for the Negro Congress at the Cotton States and International Exposition in Atlanta, Georgia held in November 1895.
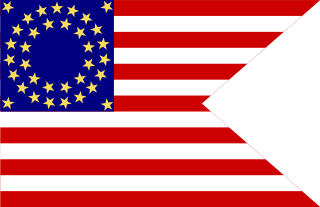
In the United States Armed Forces, a guidon is a military standard or flag that company/battery/troop or platoon-sized detachments carry to signify their unit designation and branch/corps affiliation or the title of the individual who carries it. A basic guidon can be rectangular, but sometimes has a triangular portion removed from the fly.

A distinctive unit insignia (DUI) is a metallic heraldic badge or device worn by soldiers in the United States Army. The DUI design is derived from the coat of arms authorized for a unit. DUIs may also be called "distinctive insignia" (DI) or, imprecisely, a "crest" or a "unit crest" by soldiers or collectors. The U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry is responsible for the design, development and authorization of all DUIs.

U.S. Army Berlin (USAB) was a command of the United States Army created in December 1961 at the height of the Berlin Wall crisis. USAB was a combined command with the Headquarters, U.S. Command Berlin (USCOB). This combined organization was sometimes called the "Berlin Command". USCOB/USAB was a separate command from the U.S. Army Europe (USAREUR) which had previously been in command of American troops in West Berlin.

The United States Air Force Honor Guard is the official ceremonial unit of the United States Air Force and is assigned to Joint Base Anacostia-Bolling, Washington D.C.

Andrew Jackson Smith served as a soldier in the Union Army during the American Civil War and received America's highest military decoration, the Congressional Medal of Honor, for his action in the Battle of Honey Hill.

A change of command is a military tradition that represents a formal transfer of authority and responsibility for a unit from one commanding or flag officer to another. The passing of colors, standards, or ensigns from an outgoing commander to an incoming one ensures that the unit and its soldiers is never without official leadership, a continuation of trust, and also signifies an allegiance of soldiers to their unit's commander.

Voltaire Paine Twombly was a Union veteran of the American Civil War and a recipient of the Medal of Honor. He received the Medal of Honor for his actions during the Battle of Fort Donelson on February 15, 1862, when he picked up and carried his regiment's national colors after three other members of his regiment were killed or incapacitated by Confederate fire while attempting to secure the flag. Twombly also participated in a number of other engagements in the Civil War, including the Siege of Corinth and Sherman's March to the Sea.

The Presentation of Colours is a military ceremony that marks an anniversary or significant event in the history of a particular regiment or similar military unit. This involves the presentation of a new version of the regimental colour to a regiment or equivalent formation in their respective armed forces service branch. This is a traditional ceremony that was pioneered by the British Armed Forces, and is today used in most Commonwealth countries.
A regiment is a military unit that has been in use by the United States Army since its inception. Derived from the concept originating in European armies, a regiment was historically commanded by a colonel, and consisted of ten companies, for a total of approximately 1,000 soldiers. Confusingly, the terms "regiment" and "battalion" were used interchangeably at this time; it was not until later that a battalion was defined as a sub-unit of a regiment. The regiment fulfilled both administrative and tactical functions and was the principal maneuver unit of the US Army until being superseded in the 20th century by the division.

Harvey May Munsell was an American soldier who fought with the Union Army in the American Civil War. Munsell received his country's highest award for bravery during combat, the Medal of Honor, for actions taken over the course of 13 engagements from July 1–3, 1863 during the Battle of Gettysburg.


















