Eswatini, is a country in Southern Africa lying between Mozambique and South Africa. The country is located at the geographic coordinates 26°30′S31°30′E. Eswatini has an area of 17,363 square kilometres, of which 160 are water. The major regions of the country are Lowveld, Midveld and Highveld.

Zimbabwe is a landlocked country in southern Africa lying wholly within the tropics. It straddles an extensive high inland plateau that drops northwards to the Zambezi valley where the border with Zambia is and similarly drops southwards to the Limpopo valley and the border with South Africa. The country has borders with Botswana 813 km, Mozambique 1,231 km, South Africa 225 km, Zambia 797 km and almost meets Namibia at its westernmost point.

A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in a type of cloud known as a cumulonimbus. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce heavy rain and sometimes snow, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms produce little precipitation or no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow through the layer of the troposphere that they occupy, vertical wind shear sometimes causes a deviation in their course at a right angle to the wind shear direction.
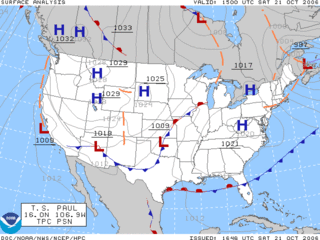
Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations.

A severe thunderstorm watch is a severe weather watch product issued by regional offices of weather forecasting agencies throughout the world when meteorological conditions are favorable for the development of severe thunderstorms as defined by regional criteria that may contain large hail, straight-line winds, lightning, intense hydrological phenomena and/or tornadoes. A severe thunderstorm watch does not necessarily mean that severe weather is actually occurring, only that conditions present a credible risk for thunderstorms producing severe weather phenomena to affect portions of the watch area. A watch must not be confused with a severe thunderstorm warning.

The Intertropical Convergence Zone, known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal equator though its specific position varies seasonally. When it lies near the geographic Equator, it is called the near-equatorial trough. Where the ITCZ is drawn into and merges with a monsoonial circulation, it is sometimes referred to as a monsoon trough, a usage that is more common in Australia and parts of Asia.

The climate of Virginia, a state on the east coast of the United States, is considered mild compared to more northern areas of the United States such as New England and the Midwest. Most of Virginia east of the Blue Ridge mountains, the southern part of the Shenandoah Valley, and the Roanoke Valley, has a humid subtropical climate. In the mountainous areas west of the Blue Ridge, the climate is warm-summer humid continental or oceanic climate. Severe weather, in the form of tornadoes, tropical cyclones, and winter storms, impacts the state on a regular basis. Central Virginia received significant snowfall of 20 inches in December 2009.

Lichinga is the capital city of Niassa Province of Mozambique. It lies on the Lichinga Plateau at an altitude of 1,360 metres (4,460 ft), east of Lake Niassa. The town was founded as Vila Cabral as a farming and military settlement. It is served by Lichinga Airport. The province borders Ruvuma Region in Tanzania.
Milwaukee has a humid continental climate, with four distinct seasons and wide variations in temperature and precipitation in short periods of time. The city's climate is also strongly influenced by nearby Lake Michigan, which creates two varying climates within the Milwaukee area. The Urban heat island effect also plays a role in the city's climate, insulating it from winter cold, but keeping it cooler in spring and summer.
Oklahoma City lies in a temperate humid subtropical climate, with frequent variations in weather daily and seasonally, except during the consistently hot and humid summer months. Consistent winds, usually from the south or south-southeast during the summer, help temper the hotter weather. Consistent northerly winds during the winter can intensify cold periods. Oklahoma City's climate transitions toward semi-arid further to the west, toward humid continental to the north, and toward humid subtropical to the east and southeast. The normal annual mean temperature is 61.4 °F (16.3 °C); the coolest year was 1895 with a mean of 57.9 °F (14.4 °C), while the warmest 2012 at 64.1 °F (17.8 °C). Precipitation averages 36.52 inches (928 mm) annually, falling on an average 84 days, with the warmer months receiving more; annual precipitation has historically ranged from 15.74 in (400 mm) in 1901 to 56.95 in (1,447 mm) in 2007. The sun shines about 69% of the time, with monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 60% in December to 80% in July.

The climate in Greece is predominantly Mediterranean. However, due to the country's geography, Greece has a wide range of micro-climates and local variations. The Greek mainland is extremely mountainous, making Greece one of the most mountainous countries in Europe. To the west of the Pindus mountain range, the climate is generally wetter and has some maritime features. The east of the Pindus mountain range is generally drier and windier in summer. The highest peak is Mount Olympus, 2,918 metres (9,573 ft). The northern areas of Greece have a transitional climate between the continental and the Mediterranean climate. There are mountainous areas that have an alpine climate.
The climate of Delhi is an overlap between monsoon-influenced humid subtropical and semi-arid, with high variation between summer and winter temperatures and precipitation. Delhi's version of a humid subtropical climate is markedly different from many other humid subtropical cities such as São Paulo, New Orleans and Brisbane in that the city features dust storms and wildfire haze due to its semi-arid climate.

The climate of the United States varies due to changes in latitude, and a range of geographic features, including mountains and deserts. Generally, on the mainland, the climate of the U.S. becomes warmer the further south one travels, and drier the further west, until one reaches the West Coast.

North Carolina's climate varies from the Atlantic coast in the east to the Appalachian Mountain range in the west. The mountains often act as a "shield", blocking low temperatures and storms from the Midwest from entering the Piedmont of North Carolina.
On the evening of September 2, 1984 several tornadoes hit southwestern Ontario from Windsor to London. This was the biggest severe weather event of the year for the province. During the morning hours, the surface map revealed a rather potent low pressure system over northern Michigan, moving to the northeast.

The North American monsoon, variously known as the Southwest monsoon, the Mexican monsoon, the New Mexican monsoon, or the Arizona monsoon is a pattern of pronounced increase in thunderstorms and rainfall over large areas of the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico, typically occurring between June and mid-September. During the monsoon, thunderstorms are fueled by daytime heating and build up during the late afternoon and early evening. Typically, these storms dissipate by late night, and the next day starts out fair, with the cycle repeating daily. The monsoon typically loses its energy by mid-September when much drier conditions are reestablished over the region. Geographically, the North American monsoon precipitation region is centered over the Sierra Madre Occidental in the Mexican states of Sinaloa, Durango, Sonora and Chihuahua.

Estonia lies in the northern part of the temperate climate zone and in the transition zone between maritime and continental climate. Because Estonia is continuously warmed by maritime air influenced by the heat content of the northern Atlantic Ocean, it has a milder climate despite its northern latitude. The Baltic Sea causes differences between the climate of coastal and inland areas. Estonia has four seasons of near-equal length. Average temperatures range from 17.8 °C (64.0 °F) on the Baltic islands to 18.4 °C (65.1 °F) inland in July, the warmest month, and from −1.4 °C (29.5 °F) on the Baltic islands to −5.3 °C (22.5 °F) inland in February, the coldest month.

Dubai has a hot desert climate. Dubai has 4 seasons – winter, spring, fall, and summer. Summer in Dubai begins around the last week of April and ends around the first week of October. This period is characterized by extremely hot weather, hot winds and high humidity. Due to the city's close proximity to the sea, the temperatures in Dubai are slightly milder in summer in comparison to other Gulf cities such as Kuwait City and Riyadh. However, this means the city has high humidity which can make the weather extremely unpleasant in summer. Rainfall is scarce during the summer months, but the windy conditions ensure there are frequent dust storms. Temperatures regularly climb above 38 °C (100 °F) during this period and fall to around 26 °C (79 °F) overnight. Winter in Dubai begins around the last week of October and lasts until the beginning of April. The winter season has the most pleasant weather, making it ideal for outdoor activities. Most of the precipitation takes place during this season. Strong thunderstorms are not uncommon to the city during this period, this is accompanied by strong north-westerly winds and lower temperatures. The Average daytime high during the winter season is around 22 °C (72 °F) with overnight lows of 12 °C (54 °F). Rainfall has been increasing over the past few decades in the city accumulating to more than 130 mm (5.12 in) per year.
The climate of Seoul features a humid continental climate with dry winter, called "Dwa" in the Köppen climate classification. Seoul is classed as having a temperate climate with four distinct seasons, but temperature differences between the hottest part of summer and the depths of winter are extreme. In summer the influence of the North Pacific high-pressure system brings hot, humid weather with temperatures soaring as high as 35 °C (95 °F) on occasion. In winter the city is topographically influenced by expanding Siberian High-pressure zones and prevailing west winds, temperatures dropping almost as low as -20 °C (-4 °F) in severe cold waves. The bitterly cold days tend to come in three-day cycles regulated by rising and falling pressure systems. The most pleasant seasons for most people in the city are spring and autumn, when azure skies and comfortable temperatures are typical. Most of Seoul's precipitation falls in the summer monsoon period between June and September, as a part of East Asian monsoon season.
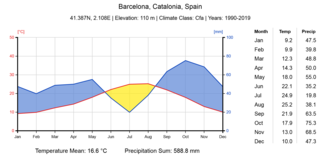
Barcelona has a maritime Mediterranean climate Csa according to Köppen-Geiger classification, a warm-temperate subtropical climate according to Troll-Paffen climate classification, and a subtropical climate according to Siegmund/Frankenberg climate classification.