Castle Hill may refer to:
Fort William may refer to:

Birdoswald Roman Fort was known as Banna in Roman times, reflecting the geography of the site on a triangular spur of land bounded by cliffs to the south and east commanding a broad meander of the River Irthing in Cumbria below.
Maiden Castle or the Maiden's Castle may refer to:

Pevensey Castle is a medieval castle and former Roman Saxon Shore fort at Pevensey in the English county of East Sussex. The site is a scheduled monument in the care of English Heritage and is open to visitors. Built around 290 AD and known to the Romans as Anderitum, the fort appears to have been the base for a fleet called the Classis Anderidaensis. The reasons for its construction are unclear; long thought to have been part of a Roman defensive system to guard the British and Gallic coasts against Saxon pirates, it has more recently been suggested that Anderitum and the other Saxon Shore forts were built by a usurper in an ultimately unsuccessful attempt to prevent Rome from reimposing its control over Britain.

The River Lowther is a small river which flows through limestone rock in Cumbria, England. It is a tributary of the River Eamont which in turn is a tributary of the River Eden which flows into the Solway Firth near Carlisle. The Lowther begins with the confluence of the Keld Gill and the Keld Dub near the village of Keld. It flows north-west until it passes between Bampton and Bampton Grange, before turning north until it flows into the River Eamont close to Penrith.

The Staffordshire Moorlands Pan, sometimes known as the Ilam Pan, is a 2nd-century AD enamelled bronze trulla with an inscription naming four of the forts of Hadrian's Wall. Its decoration uses coloured vitreous enamel, in antiquity a speciality of Celtic art, in ornamental forms that provide a very rare link between Iron Age and Early Medieval "Celtic" art.

There are 37 scheduled monuments in Greater Manchester, a metropolitan county in North West England. In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a "nationally important" archaeological site or historic building that has been given protection against unauthorised change by being placed on a list by the Secretary of State for Digital Culture, Media and Sport; Historic England recommends sites for scheduling to the Secretary of State. Scheduled monuments are defined in the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Areas Act 1979 and the National Heritage Act 1983. There are nearly 20,000 entries on the schedule, which is maintained by Historic England as part of the National Heritage List for England; more than one site can be included in a single entry. While a scheduled monument can also be recognised as a listed building, Historic England's aim is to set the most appropriate form of protection in place for the building or site. Applications to deschedule a site are administered Historic England, who will carry out an assessment and make a recommendation to the Secretary of State.
Castlesteads is an Iron Age promontory fort, situated on the east bank of the River Irwell on a natural promontory in Bury, Greater Manchester. It is listed as a Scheduled Ancient Monument. Excavated pottery indicates the site was occupied between 200BC and 250AD.

Walton is a village and civil parish in the far north of Cumbria, England. It is located 10 miles (16 km) from Carlisle and is about 2 miles (3 km) north of Brampton, on the north bank of the River Irthing. Nearby villages include Newtown, Banks and Lanercost.
Cohors quarta Gallorum equitata was a Roman auxiliary cohort containing both infantry and cavalry contingents.
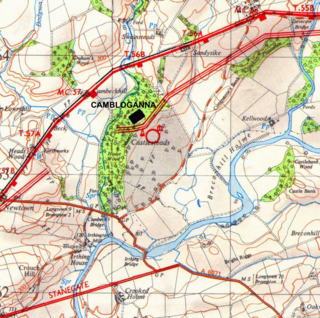
Camboglanna was a Roman fort. It was the twelfth fort on Hadrian's Wall counting from the east, between Banna (Birdoswald) almost 7 miles (11 km) to the east and Uxelodunum (Stanwix), 9 miles to the west. It was on a high bluff commanding the Cambeck Valley. It guarded an important approach to the Wall and also watched the east bank of the Cambeck against raiders from the Bewcastle area. The site was drastically levelled in 1791 when the gardens of Castlesteads House were laid over it. The name "Camboglanna" is believed to mean "Crook Bank", or "Bent Valley" because it overlooks a bend in the river Irthing; the name is Brythonic, made of cambo- "curved, bent, crooked" and glanna "steep bank, stream/river side, valley with a stream".
The Rudge Cup is a small enamelled bronze cup found in 1725 at Rudge, near Froxfield, in Wiltshire, England. The cup was found down a well on the site of a Roman villa. It is important in that it lists five of the forts on the western section of Hadrian's Wall, thus aiding scholars in identifying the forts correctly. The information on the cup has been compared with the two major sources of information regarding forts on the Wall, the Notitia Dignitatum and the Ravenna Cosmography.
Mellor hill fort is a prehistoric site in North West England dating from the British Iron Age – about 800 BC to 100 AD. Situated on a hill in Mellor, Greater Manchester, on the western edge of the Peak District, the hill fort overlooks the Cheshire Plain. Although the settlement was founded during the Iron Age, evidence exists of activity on the site as far back as 8,000 BC; during the Bronze Age the hill may have been an area where funerary practices were performed. Artefacts such as a Bronze Age amber necklace indicate the site was high status and that its residents took part in long-distance trade. The settlement was occupied into the Roman period. After the site was abandoned, probably in the 4th century, it was forgotten until its rediscovery in the 1990s.

Milecastle 56 (Walton) was a milecastle on Hadrian's Wall (grid reference NY522643).

Milecastle 57 (Cambeckhill) was a milecastle on Hadrian's Wall (grid reference NY50816368).
Susanna Maria Appleby was a British antiquarian who is principally known for excavating a Roman bath house north east of Camboglanna, Castlesteads Roman Fort, near Hadrian's Wall in 1741.

Castle Folds or Castlesteads was a Romano-British walled settlement on Great Asby Scar – an area of limestone pavement in the parish of Asby, Cumbria, England. In medieval times, it was used as a shieling – a temporary summer shelter. It is now in ruins but is protected as a scheduled monument.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.









