
Food preservation includes processes that make food more resistant to microorganism growth and slow the oxidation of fats. This slows down the decomposition and rancidification process. Food preservation may also include processes that inhibit visual deterioration, such as the enzymatic browning reaction in apples after they are cut during food preparation. By preserving food, food waste can be reduced, which is an important way to decrease production costs and increase the efficiency of food systems, improve food security and nutrition and contribute towards environmental sustainability. For instance, it can reduce the environmental impact of food production.

Shellac is a resin secreted by the female lac bug on trees in the forests of India and Thailand. Chemically, it is mainly composed of aleuritic acid, jalaric acid, shellolic acid, and other natural waxes. It is processed and sold as dry flakes and dissolved in alcohol to make liquid shellac, which is used as a brush-on colorant, food glaze and wood finish. Shellac functions as a tough natural primer, sanding sealant, tannin-blocker, odour-blocker, stain, and high-gloss varnish. Shellac was once used in electrical applications as it possesses good insulation qualities and seals out moisture. Phonograph and 78 rpm gramophone records were made of shellac until they were replaced by vinyl long-playing records from 1948 onwards.

Taxidermy is the art of preserving an animal's body by mounting or stuffing, for the purpose of display or study. Animals are often, but not always, portrayed in a lifelike state. The word taxidermy describes the process of preserving the animal, but the word is also used to describe the end product, which are called taxidermy mounts or referred to simply as "taxidermy".

Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology, in cytology, and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues, cell populations, or organelles within individual cells.

Wood easily degrades without sufficient preservation. Apart from structural wood preservation measures, there are a number of different chemical preservatives and processes that can extend the life of wood, timber, and their associated products, including engineered wood. These generally increase the durability and resistance from being destroyed by insects or fungi.

Histopathology refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments.

A killing jar or killing bottle is a device used by entomologists to kill captured insects quickly and with minimum damage. The jar typically contains plaster of Paris on the bottom to absorb a killing fluid. The killing fluid evaporates into the air and gasses the insect. Typically only adult hard bodied insects are killed in a killing jar; other insects require different methods of killing.

Insect collecting refers to the collection of insects and other arthropods for scientific study or as a hobby. Most insects are small and the majority cannot be identified without the examination of minute morphological characters, so entomologists often make and maintain insect collections. Very large collections are conserved in natural history museums or universities where they are maintained and studied by specialists. Many college courses require students to form small collections. There are also amateur entomologists and collectors who keep collections.
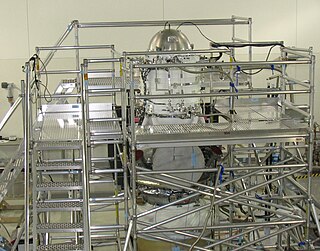
A cryostat is a device used to maintain low cryogenic temperatures of samples or devices mounted within the cryostat. Low temperatures may be maintained within a cryostat by using various refrigeration methods, most commonly using cryogenic fluid bath such as liquid helium. Hence it is usually assembled into a vessel, similar in construction to a vacuum flask or Dewar. Cryostats have numerous applications within science, engineering, and medicine.

Freeze drying, also known as lyophilization or cryodesiccation, is a low temperature dehydration process that involves freezing the product and lowering pressure, thereby removing the ice by sublimation. This is in contrast to dehydration by most conventional methods that evaporate water using heat.

The conservation and restoration of parchment constitutes the care and treatment of parchment materials which have cultural and historical significance. Typically undertaken by professional book and document conservators, this process can include preventive measures which protect against future deterioration as well as specific treatments to alleviate changes already caused by agents of deterioration.

Bird collections are curated repositories of scientific specimens consisting of birds and their parts. They are a research resource for ornithology, the science of birds, and for other scientific disciplines in which information about birds is useful. These collections are archives of avian diversity and serve the diverse needs of scientific researchers, artists, and educators. Collections may include a variety of preparation types emphasizing preservation of feathers, skeletons, soft tissues, or (increasingly) some combination thereof. Modern collections range in size from small teaching collections, such as one might find at a nature reserve visitor center or small college, to large research collections of the world's major natural history museums, the largest of which contain hundreds of thousands of specimens. Bird collections function much like libraries, with specimens arranged in drawers and cabinets in taxonomic order, curated by scientists who oversee the maintenance, use, and growth of collections and make them available for study through visits or loans.

Home canning or bottling, also known colloquially as putting up or processing, is the process of preserving foods, in particular, fruits, vegetables, and meats, by packing them into glass jars and then heating the jars to create a vacuum seal and kill the organisms that would create spoilage.
A bottle trap is a type of baited arboreal insect trap for collecting either prized or harmful frugivorous beetles, especially flower beetles, leaf chafers and longhorn beetles as well as wasps and other unwanted flying insects.

A zoological specimen is an animal or part of an animal preserved for scientific use. Various uses are: to verify the identity of a (species), to allow study, increase public knowledge of zoology. Zoological specimens are extremely diverse. Examples are bird and mammal study skins, mounted specimens, skeletal material, casts, pinned insects, dried material, animals preserved in liquid preservatives, and microscope slides. Natural history museums are repositories of zoological specimens
The conservation and restoration of herbaria includes the preventive care, repair, and restoration of herbarium specimens. Collections of dried plant specimens are collected from their native habitats, identified by experts, pressed, and mounted onto archival paper. Care is taken to make sure major morphological characteristics are visible. Herbaria documentation provides a record of botanical diversity.

The conservation and restoration of insect specimens is the process of caring for and preserving insects as a part of a collection. Conservation concerns begin at collection and continue through preparation, storage, examination, documentation, research and treatment when restoration is needed.
Microtechnique is an aggregate of methods used to prepare micro-objects for studying. It is currently being employed in many fields in life science. Two well-known branches of microtechnique are botanical (plant) microtechnique and zoological (animal) microtechnique.

Fossil preparation is a complex of tasks that can include excavating, revealing, conserving, and replicating the ancient remains and traces of organisms. It is an integral part of the science of paleontology, of museum exhibition, and the preservation of fossils held in the public trust. It involves a wide variety of techniques, from the mechanical to the chemical, depending upon the qualities of the specimen being prepared and the goals of the effort. Fossil preparation may be executed by scientists, students or collections personnel, but is often undertaken by professional fossil preparators.
















