Catnip , Nepeta cataria, is a species in the family Lamiaceae (mint).
Catnip may also refer to:
- Nepeta , cat mint or catnip, the plant genus
- Nepetalactone, the cat attractant in the catnip plant
- Methcathinone, a drug sometimes called "catnip"
Catnip , Nepeta cataria, is a species in the family Lamiaceae (mint).
Catnip may also refer to:

Nepeta is a genus of flowering plants in the family Lamiaceae. The genus name is reportedly in reference to Nepete, an ancient Etruscan city. There are about 250 species.

Valerian is a perennial flowering plant native to Europe and Asia. In the summer when the mature plant may have a height of 1.5 metres, it bears sweetly scented pink or white flowers that attract many fly species, especially hoverflies of the genus Eristalis. It is consumed as food by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species, including the grey pug.
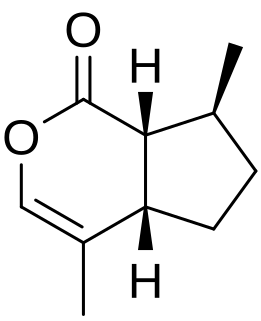
Nepetalactone is a name for multiple iridoid analog stereoisomers. Nepetalactones are produced by Nepeta cataria (catnip) and many other plants belonging to the genus Nepeta, in which they protect these plants from herbivorous insects by functioning as insect repellents. They are also produced by many aphids, in which they are sex pheromones. Nepetalactones are cat attractants, and cause the behavioral effects that catnip induces in domestic cats. However, they affect visibly only about two thirds of adult cats. They produce similar behavioral effects in many other felids, especially in lions and jaguars. In 1941, the research group of Samuel M. McElvain was the first to determine the structures of nepetalactones and several related compounds.
Catmint usually refers to:

Pulegone is a naturally occurring organic compound obtained from the essential oils of a variety of plants such as Nepeta cataria (catnip), Mentha piperita, and pennyroyal. It is classified as a monoterpene.

Schizonepeta is a genus of herbs. It should not be confused with the true catnips of the genus Nepeta known for their euphoria-inducing effect on domestic cats.

Nepeta × faassenii, a flowering plant also known as catmint and Faassen's catnip, is a primary hybrid of garden origin. The parent species are Nepeta racemosa and Nepeta nepetella.

Nepeta cataria, commonly known as catnip, catswort, catwort, and catmint, is a species of the genus Nepeta in the family Lamiaceae, native to southern and eastern Europe, the Middle East, Central Asia, and parts of China. It is widely naturalized in northern Europe, New Zealand, and North America. The common name catmint can also refer to the genus as a whole.

Actinidia polygama is a species of kiwifruit in the Actinidiaceae family. It grows in the mountainous areas of Korea, Japan and China at elevations between 500 and 1,900 metres.

Amblyptilia acanthadactyla, also known as the beautiful plume, is a moth of the family Pterophoroidea found in across the Palearctic including Europe. The species was first described by the German entomologist, Jacob Hübner in 1813.

Lonicera tatarica is a species of honeysuckle known by the common name Tatarian honeysuckle. It is native to Siberia and other parts of eastern Asia Lonicera tatarica is also known to grow in the Himalayas, however it is better known in North America as a widespread introduced species and noxious weed. Honeysuckles are native to temperate zones of both hemispheres. This plant, one of several exotic bush honeysuckles present in North America, was introduced as an ornamental plant in 1752. It is known across the continent west to Alaska and California, where it easily grows in disturbed habitat.

Clinopodium nepeta, known as lesser calamint, is a perennial herb of the mint family.
Nepeta discolor is a low-growing species of catnip that is commonly found in the alpine (Himalayas) and temperate regions of Xizang (Tibet) in China; Garhwal division, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu, Uttar Pradesh in India; Afghanistan; Pakistan; and Nepal. The species is named after the color of the leaves. It was described in 1833.

Nepeta racemosa, the dwarf catnip or raceme catnip, syn. N. mussiniii, is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae, native to the Caucasus, Turkey and northern Iran. Growing to 30 cm (12 in) tall by 45 cm (18 in) wide, it is a herbaceous perennial with aromatic leaves and violet or lilac-blue flowers in summer.

Nepeta nepetella, common name lesser cat-mint, is a low-growing species of catnip belonging to the family Lamiaceae. It is native to France, Spain, Italy, Algeria, and Morocco.
Nepeta is a genus of plant.

Nepeta grandiflora is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae, native to the Caucasus. Growing to 75 cm (30 in) tall by 30 cm (12 in), it is a clump-forming, erect deciduous herbaceous perennial with aromatic, slightly hairy, grey-green leaves, and spikes of purple/blue flowers in early summer. Species of Nepeta are called catnip or catmint, with reference to their reported effect on some domestic cats. The plants seem to induce a euphoria in the animals, causing them to roll in the foliage and exhibit signs of intoxication.

Nepeta curviflora, commonly known as Syrian catnip, is a herbaceous flowering plant native to the Middle East. It was first described in 1844.

Nepeta govaniana is a species of herbaceous flowering plant of the genus Nepeta. It was described in 1834. A common name for the species, Himalayan catnip, may also refer to Nepeta clarkei.

Nepeta subsessilis, the short-stalked catmint, is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae, from Japan. Growing to 100 cm (39 in) tall by 50 cm (20 in) broad, it is an erect herbaceous perennial with fresh, aromatic green leaves and soft blue flowers in summer and autumn. It is more compact and erect, with larger flowers, than other members of Nepeta. It may alo have a similar effect on cats.