Related Research Articles

Edith Louisa Cavell was a British nurse. She is celebrated for treating wounded soldiers from both sides without discrimination during the First World War and for helping some 200 Allied soldiers escape from German-occupied Belgium. Cavell was arrested, court-martialled under German military law and sentenced to death by firing squad. Despite international pressure for mercy, the German Government refused to commute her sentence and she was shot. The execution received worldwide condemnation and extensive press coverage.

The Royal London Hospital is a large teaching hospital in Whitechapel in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It is part of Barts Health NHS Trust. It provides district general hospital services for the City of London and Tower Hamlets and specialist tertiary care services for patients from across London and elsewhere. The current hospital building has 1248 beds and 34 wards. It opened in February 2012.

Whittington Hospital is a district general and teaching hospital of UCL Medical School and Middlesex University School of Health and Social Sciences. Located in Upper Holloway, it is managed by Whittington Health NHS Trust, operating as Whittington Health, an integrated care organisation providing hospital and community health services in the north London boroughs of Islington and Haringey. Its Jenner Building, a former smallpox hospital, is a Grade II listed building.

The Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) is the regulator for nursing and midwifery professions in the UK. The NMC maintains a register of all nurses, midwives and specialist community public health nurses and nursing associates eligible to practise within the UK. It sets and reviews standards for their education, training, conduct and performance. The NMC also investigates allegations of impaired fitness to practise.

Saint Mary's Hospital is a hospital in Manchester, England. It is part of Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust. Founded in 1790, St Mary's provides a range of inter-related services specifically for women and children. In 1986, St Mary's Sexual Assault Referral Centre was the first sexual assault referral centre (SARC) to open in the UK.
The Seafarers Hospital Society, formerly the Seamen's Hospital Society, is a charity for people currently or previously employed by the British Merchant Navy and fishing fleets, and their families. It was established in 1821.
Nursing in the United Kingdom is the largest health care profession in the country. It has evolved from assisting doctors to encompass a variety of professional roles. Over 700,000 nurses practice, working in settings such as hospitals, health centres, nursing homes, hospices, communities, military, prisons, and academia. Most are employed by the National Health Service (NHS).

The Frontier Nursing Service (FNS) provides healthcare services to rural, underserved populations since 1925, and educates nurse-midwives since 1939.

Queen Charlotte's and Chelsea Hospital is one of the oldest maternity hospitals in Europe, founded in 1739 in London. Until October 2000, it occupied a site at 339–351 Goldhawk Road, Hammersmith, but is now located between East Acton and White City, adjacent to the Hammersmith Hospital. It is managed by the Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust.

The Queen's Nursing Institute (QNI) is a charity that works to improve the nursing care of people in their own homes in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland. It does not operate in Scotland, where the Queen's Nursing Institute Scotland performs a similar function. The QNI is also affiliated to the Queen's Institute of District Nursing in Ireland. The QNI is a member of the International Council of Nurses.
The Edith Cavell Hospital was an acute hospital serving the city of Peterborough and north Cambridgeshire, east Northamptonshire and Rutland in the United Kingdom. Situated on a greenfield site at Westwood, Peterborough, it was decommissioned in late 2010 and demolished in early 2011.

Eva Charlotte Ellis Luckes was matron of the London Hospital from 1880 to 1919.
Nursing in Japan did not develop as an occupation until the end of the nineteenth century. Initially introduced only in Tokyo in the late 1860s, small schools utilizing Western models were being opened by the late 1880s. In response to disaster relief, the Japanese Red Cross became an integral part of nursing development. By 1915, nurse registration had been established and public health nurses began working throughout the country. Nursing universities were established in the twentieth century and regulations were passed to develop standards for training and public health.

St Leonard's Hospital is a hospital in Hoxton, London.
The history of nursing in the United Kingdom relates to the development of the profession since the 1850s. The history of nursing itself dates back to ancient history, when the sick were cared for in temples and places of worship. In the early Christian era, nursing in the United Kingdom was undertaken by certain women in the Christian Church, their services being extended to patients in their homes. These women had no real training by today's standards, but experience taught them valuable skills, especially in the use of herbs and folk drugs, and some gained fame as the physicians of their era. Remnants of the religious nature of nurses remains in Britain today, especially with the retention of the job title "Sister" for a senior female nurse.
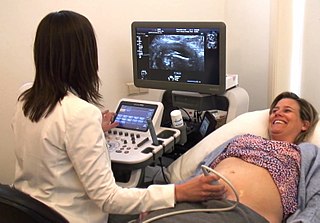
A midwife is a health professional who cares for mothers and newborns around childbirth, a specialization known as midwifery.

Highgate Hospital was a name used to refer to the infirmary building which opened in 1869 on the St Pancras side of Dartmouth Park Hill in Highgate, London.

The Maidstone typhoid epidemic, was the largest typhoid epidemic the UK had experienced.

The Edith Cavell Memorial is an outdoor memorial to Edith Cavell located in Kings Domain, Melbourne, Australia. It consists of a marble bust on a granite pedestal; the bust was sculpted by Margaret Baskerville. The memorial was unveiled in November 1926.
References
- ↑ Kenny, Craig (6 October 2014). "Working nurses facing hardship". www.independentnurse.co.uk. Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- ↑ "Cavell Nurses Trust". Royal College of Nursing. 7 April 2014. Archived from the original on 11 September 2016. Retrieved 8 May 2016.
- ↑ Scott Cavell, F.M. (14 October 1916). "Miss Edith Cavell and homes of rest for nurses" (PDF). The Lancet . 188 (4859): 693. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)27628-4.
- ↑ "Nursing Echoes". British Journal of Nursing : 396. 11 November 1916. Archived from the original on 11 September 2016. Retrieved 3 May 2016.
- ↑ "Edith Cavell Homes". British Journal of Nursing: 32. 13 July 1918. Archived from the original on 11 September 2016.
- ↑ "History". Cavell Nurses' Trust. Archived from the original on 9 August 2016. Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- ↑ Plumtpre, George (12 October 2015). "Who was Edith Cavell? A heroine's legacy of compassion to nurses". The Telegraph . Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- ↑ "Edith Cavell Home of Rest, Richmond". British Journal of Nursing. 25 January 1919. Archived from the original on 11 September 2016.
- ↑ "Search Archives and Manuscripts:Nation's Fund for Nurses". Wellcome Library . Retrieved 3 May 2016.
- ↑ Youde, Kate (2 October 2012). "NurseAid changes name to Cavell Nurses' Trust". Third Sector . Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- ↑ "Edith Cavell Fund For Nurses". Charity Commission for England and Wales . Retrieved 2 May 2016.