Related Research Articles

Anishinaabe traditional beliefs cover the traditional belief system of the Anishinaabeg peoples, consisting of the Algonquin/Nipissing, Ojibwa/Chippewa/Saulteaux/Mississaugas, Odawa, Potawatomi and Oji-Cree, located primarily in the Great Lakes region of North America.
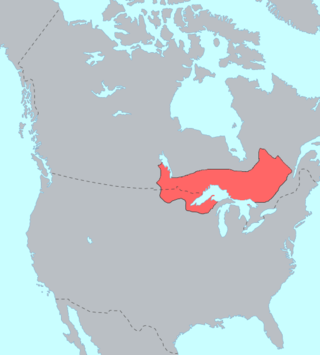
The Ojibwe are an Anishinaabe people whose homeland covers much of the Great Lakes region and the northern plains, extending into the subarctic and throughout the northeastern woodlands. Ojibweg, being Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands and of the subarctic, are known by several names, including Ojibway or Chippewa. As a large ethnic group, several distinct nations also consider themselves Ojibwe, including the Saulteaux, Nipissings, and Oji-Cree.
Indigenous music of Canada encompasses a wide variety of musical genres created by Aboriginal Canadians. Before European settlers came to what is now Canada, the region was occupied by many First Nations, including the West Coast Salish and Haida, the centrally located Iroquois, Blackfoot and Huron, the Dene to the North, and the Innu and Mi'kmaq in the East and the Cree in the North. Each of the indigenous communities had their own unique musical traditions. Chanting – singing is widely popular and most use a variety of musical instruments.

The Anishinaabe are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe, Odawa, Potawatomi, Mississaugas, Nipissing, and Algonquin peoples. The Anishinaabe speak Anishinaabemowin, or Anishinaabe languages that belong to the Algonquian language family.

The Métis are an Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces. They have a shared history and culture, deriving from specific mixed European and Indigenous ancestry, which became distinct through ethnogenesis by the mid-18th century, during the early years of the North American fur trade.
Saugeen First Nation is an Ojibway First Nation band located along the Saugeen River and Bruce Peninsula in Ontario, Canada. The band states that their legal name is the "Chippewas of Saugeen". Organized in the mid-1970s, Saugeen First Nation is the primary "political successor apparent" to the Chippewas of Saugeen Ojibway Territory; the other First Nation that is a part of Chippewas of Saugeen Ojibway Territory is Cape Croker. The Ojibway are of the Algonquian languages family. The First Nation consist of four reserves: Chief's Point 28, Saugeen 29, Saugeen Hunting Grounds 60A, and Saugeen and Cape Croker Fishing Islands 1.

George Copway was a Mississaugas Ojibwa writer, ethnographer, Methodist missionary, lecturer, and advocate of indigenous peoples. His Ojibwa name was Kah-Ge-Ga-Gah-Bowh, meaning "He Who Stands Forever". In 1847 he published a memoir about his life and time as a missionary. This work made him Canada's first literary celebrity in the United States. In 1851 he published The Traditional History and Characteristic Sketches of The Ojibway Nation, the first published history of the Ojibwa in English.
Drew Hayden Taylor is an Indigenous Canadian playwright, author and journalist.

Joseph Boyden is a Canadian novelist and short story writer. He is best known for writing about First Nations culture. Three Day Road, a novel about two Cree soldiers serving in the Canadian military during World War I, was inspired by Ojibwa Francis Pegahmagabow, the legendary First World War sniper. Joseph Boyden's second novel, Through Black Spruce, follows the story of Will, son of one of the characters in Three Day Road. The third novel in the Bird family trilogy was published in 2013 as The Orenda.

A wiigwaasabak is a birch bark scroll, on which the Ojibwa (Anishinaabe) people of North America wrote with a written language composed of complex geometrical patterns and shapes.

Garden River First Nation, also known as Ketegaunseebee, is an Ojibwa band located at Garden River 14 near Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Canada.

Basil H. Johnston was an Anishinaabe (Ojibwa) and Canadian writer, storyteller, language teacher and scholar.

Christi Marlene Belcourt is a Canadian visual artist and author. She is best known for her acrylic paintings which depict floral patterns inspired by Métis and First Nations historical beadwork art. Belcourt's work often focuses on questions around identity, culture, place and divisions within communities.
Jean Baptiste "John" Arcand, is a Canadian fiddler, composer, teacher, and luthier. Arcand has been composing and performing since childhood, having learned the traditional Métis tunes from his father Victor and his grandfather Jean-Baptiste. John Arcand has said, "I knew from childhood I would be a fiddler." "I love the constant challenge because you cannot ever master the fiddle." He is known for the impeccable sense of timing in his music, a skill that is necessary when guiding dancers.
Bonnie Devine is a Serpent River Ojibwa installation artist, performance artist, sculptor, curator, and writer from Serpent River First Nation, who lives and works in Toronto, Ontario. She is currently an associate professor at OCAD University and the founding chair of its Indigenous Visual Cultural Program.
Métis fiddle is the style that the Métis of Canada and Métis in the northern United States have developed to play the violin, solo and in folk ensembles. It is marked by the percussive use of the bow and percussive accompaniment. The Métis people are a poly-ethnic post-contact Indigenous peoples. Fiddles were "introduced in this area by Scottish and French-Canadian fur traders in the early 1800s", where the Metis community adopted the instrument into their culture.
Leo Yerxa is a Canadian visual artist, medallist, and writer. As an illustrator of children's picture books he won the Governor General's Award in 2006. He lived in Ottawa, Ontario, then. He died on September 1, 2017.

Richard Wagamese was an Ojibwe Canadian author and journalist from the Wabaseemoong Independent Nations in Northwestern Ontario. He was best known for his novel Indian Horse (2012), which won the Burt Award for First Nations, Métis and Inuit Literature in 2013, and was a competing title in the 2013 edition of Canada Reads.
Lawrence "Teddy Boy" Houle (1938–2020) was Métis fiddler from Ebb and Flow, Manitoba. He started to play at an early age, reportedly teaching himself to play "Red River Valley" on one string. Houle went on to become an influential fiddler and vocalist, recording a number of albums and maintaining an active performance schedule.
References
- 1 2 Cecil Youngfox Archived 2018-03-30 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 29 Mar 2018
- ↑ Cecil Youngfox - Ojibway Artist (1942- 1987) Archived 2018-03-29 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 29 Mar 2018
- ↑ Cecil Youngfox Archived 2018-03-30 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 29 Mar 2018
- ↑ Cecil Youngfox Winter Dancers Archived 2018-03-29 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 29 Mar 2018