Cellach húa Rúanada, Irish poet, died 1079.
Cellachy held the post of Chief Ollam of Ireland and died in 1079. His obit is given in the Annals of the Four Masters as follows- "M1079.4 Ceallach Ua Ruanadha, chief poet of Ireland in his time, died."
His obituary is given in the Annals of Ulster as follows- "U1079.1 Cellach ua Ruanada, chief ollav of Ireland, rested in peace."
His obituary is given in the Chronicon Scotorum as follows- "Annal CS1079 Kalends. Cellach ua Ruanadha, ollamh of Ireland, dies."
An Irish clavis or metrical tract has been preserved in the Book of Leinster as well as in the eighteenth-century manuscript Trinity College H 1 15, where it was copied from a fourteenth-century exemplar that seems now to be lost. Rudolf Thurneysen incorporated this poem in his Mittelirische Verslehren as Verslehre IV. In the Book of Leinster it was ascribed to a certain Cellach .h. Ruan, who may be identical with Cellach hua Ruanada.

Year 1079 (MLXXIX) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar.
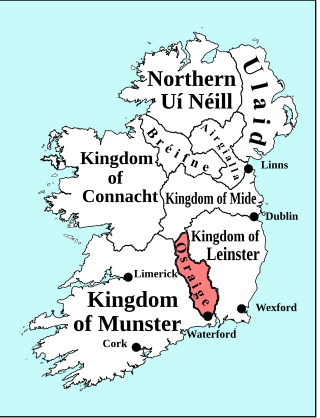
The kings of Osraige reigned over the medieval Irish kingdom of Osraige from the first or second century AD until the late twelfth century. Osraige was a semi-provincial kingdom in south-east Ireland which disappeared following the Norman Invasion of Ireland. A number of important royal Ossorian genealogies are preserved, particularly MS Rawlinson B502, which traces the medieval Mac Giolla Phádraig dynasty back through Óengus Osrithe, who supposedly flourished in the first or second century. and one in the Book of Leinster. Recent analysis of ninth and tenth century regnal succession in Osraige has suggested that in peaceful times, kingship passed primarily from eldest to youngest brother, before crossing generations and passing to sons and nephews.
Toirdhealbhach ua Briain, anglicised Turlough O'Brien, was King of Munster and effectively High King of Ireland. A grandson of Brian Bóruma, Toirdelbach was the son of Tadc mac Briain who was killed in 1023 by his half-brother Donnchad mac Briain.
Flann mac Lonáin was an Irish poet.
Cellach of Armagh or Celsus or Celestinus (1080–1129) was Archbishop of Armagh and an important contributor to the reform of the Irish church in the twelfth century. He is venerated in the Roman Catholic Church as Saint Cellach. Though a member of the laicised ecclesiastical dynasty of Clann Sínaig, he took holy vows and gained priestly ordination. This put an end to the anomalous state of affairs, in effect since 966, whereby the supreme head of the Irish Church had been a layman. Following the Synod of Ráith Bressail, in which a diocesan structure for Ireland was established, he became the first metropolitan primate of all Ireland.
Cellach is an Irish name. It might refer to:
Loingsech mac Óengusso was an Irish king who was High King of Ireland. Loingsech was a member of the northern Cenél Conaill branch of the Uí Néill. Although his father Óengus had not been High King, his grandfather Domnall mac Áedo had been.
Donngal mac Laidcnén was a king of the Uí Cheinnselaig of South Leinster. He belonged to the Sil Chormaic sept of this branch of the Laigin and specifically to a branch which took over leadership of the Uí Dróna -the baronies of Idrone in modern County Carlow. His last paternal ancestor to hold the throne was his great great grandfather Crundmáel Erbuilc He ruled from 758 to 761.
Cellach mac Fáelchair or Cellach Raigni was a King of Osraige in modern County Kilkenny. He was the son of Fáelchar Ua Máele Ódrain, a previous king.
Bran ua Máele Dúin was a king of the Uí Cheinnselaig of South Leinster. He was of the Sil Máeluidir sept of this branch of the Laigin, who were found in the later baronies of Shelmalier on the lower reaches of the Slaney River in southern modern County Wexford. The date of Bran's accession is unknown but the Book of Leinster king list gives him a reign of three years which would correspond to 709–712.
Cellach Tosach mac Donngaile was a king of the Uí Cheinnselaig of South Leinster. He belonged to the Sil Chormaic sept of this branch of the Laigin and specifically to a branch which took over leadership of the Uí Dróna -the baronies of Idrone in modern County Carlow. He was the son of Donngal mac Laidcnén and succeeded his uncle Cairpre mac Laidcnén. He ruled from 793 to 809.
Fland Dá Chongal or Flann Ua Congaile was a king of the Uí Failge, a Laigin people of County Offaly.
Cináed mac Flainn was the king of the Uí Failge, a Laigin people of County Offaly. He was one of the many sons of Fland Dá Chongal, a previous king. He ruled from 757 to 770. He was the second of Fland's sons by Érenach, daughter of Murchad Midi of Uisnech to hold the throne.
Events from the 8th century in Ireland.
Events from the 11th century in Ireland.
The Ollamh Érenn or Chief Ollam of Ireland was a professional title of Gaelic Ireland.
Cú Collchaille Ua Baígilláin was an Irish poet.
Ceaunfaeladh ua Cuill was an Irish poet who held the post of Chief Ollam of Ireland. He belonged to the family of O’Cuill who were hereditary poets in Munster. Only the Annals of Inisfallen term him Chief Ollam of Ireland. The other annals just describe him as Chief Poet of Munster but it was possible to hold both roles. A poem of his still exists in 160 verses beginning “Teach suain na horchra an aird tiar”, about the death of Eoghan, the grand-nephew of King Brian Boru, who was killed in the battle of Ossory in 1027.
Gormflaith ingen Flann Sinna was an Irish Queen of Tara, Munster, and Leinster.