
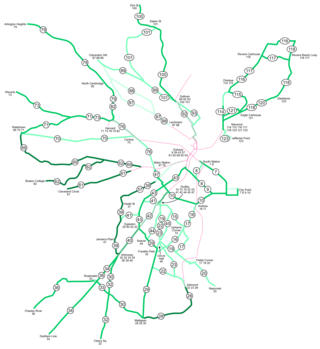
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority is the public agency responsible for operating most public transportation services in Greater Boston, Massachusetts. The MBTA transit network includes the MBTA subway with three metro lines, two light rail lines, and a five-line bus rapid transit system ; MBTA bus local and express service; the twelve-line MBTA Commuter Rail system, and several ferry routes. In 2023, the system had a ridership of 239,981,700, or about 796,300 per weekday as of the second quarter of 2024, of which the rapid transit lines averaged 265,900 and the light rail lines 95,900, making it the fourth-busiest rapid transit system and the third-busiest light rail system in the United States. As of the second quarter of 2024, average weekday ridership of the commuter rail system was 107,500, making it the fifth-busiest commuter rail system in the U.S.

The Red Line is a rapid transit line operated by the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) as part of the MBTA subway system. The line runs south and east underground from Alewife station in North Cambridge through Somerville and Cambridge, surfacing to cross the Longfellow Bridge then returning to tunnels under Downtown Boston. It continues underground through South Boston, splitting into two branches on the surface at JFK/UMass station. The Ashmont branch runs southwest through Dorchester to Ashmont station, where the connecting light rail Mattapan Line continues to Mattapan station. The Braintree branch runs southeast through Quincy and Braintree to Braintree station.

The Green Line is a semi-metro system run by the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) in the Boston, Massachusetts, metropolitan area. It is the oldest MBTA subway line, and with tunnel sections dating from 1897, the oldest subway in North America. It runs underground through downtown Boston, and on the surface into inner suburbs via six branches on radial boulevards and grade-separated alignments. With an average daily weekday ridership of 101,000 in 2023, it is among the most heavily used light rail systems in the country. The line was assigned the green color in 1967 during a systemwide rebranding because several branches pass through sections of the Emerald Necklace of Boston.

The Mattapan Line is a partially grade-separated light rail line which forms part of the MBTA's Red Line rapid transit line. The line, which runs through Boston and Milton, Massachusetts, opened on August 26, 1929, as a conversion of a former commuter rail line. It exclusively uses PCC streetcars built in the 1940s. Passengers must transfer at Ashmont to access the rest of the Red Line, which uses heavy rail metro rolling stock.

Park Street station is an MBTA subway station in Boston, Massachusetts. It is located at the intersection of Park Street and Tremont Street at the eastern edge of Boston Common in Downtown Boston. One of the two oldest stations on the "T", and part of the oldest subway line in the United States, Park Street is the transfer point between the Green and Red lines, as one of the quartet of "hub stations" on the MBTA subway system. Park Street is the fifth-busiest station in the MBTA network, with an average of 16,571 entries each weekday in FY2019.

Harvard station is a rapid transit and bus transfer station in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Located at Harvard Square, it serves the MBTA's Red Line subway system as well as MBTA buses. Harvard averaged 18,528 entries each weekday in FY2019, making it the third-busiest MBTA station after Downtown Crossing and South Station. Five of the fifteen key MBTA bus routes stop at the station.

Central station is a Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) rapid transit station in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It serves the Red Line and has a street-level terminal for the MBTA bus system. It is located at the intersection of Massachusetts Avenue with Western Avenue, Prospect Street, and Magazine Street at Central Square.

Government Center station is an MBTA subway station in Boston, Massachusetts. It is located at the intersection of Tremont, Court and Cambridge Streets in the Government Center area. It is a transfer point between the light rail Green Line and the rapid transit Blue Line. With the Green Line platform having opened in 1898, the station is the third-oldest operating subway station in the MBTA system; only Park Street and Boylston are older. The station previously served Scollay Square before its demolition for the creation of Boston City Hall Plaza.

Boylston station is a light rail station on the MBTA Green Line in downtown Boston, Massachusetts, located on the southeast corner of Boston Common at the intersection of Boylston Street and Tremont Street. A southbound street-level stop for the SL5 route of the bus rapid transit Silver Line is outside fare control. The station has two island platforms; each has one disused track, making them effectively side platforms. Boylston is not accessible for Green Line trains.

The Atlantic Avenue Elevated was an elevated railway around the east side of Downtown Boston, Massachusetts, providing a second route for the Boston Elevated Railway's Main Line Elevated around the Washington Street tunnel. It was in use from 1901 to 1938, when it was closed due to low ridership, later being demolished.

Nubian station is a ground-level Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) bus station located in Nubian Square in the Roxbury neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, United States. It is a transfer point between MBTA bus routes, including two Silver Line bus rapid transit lines and 14 local routes. Like all MBTA bus stops, Nubian is fully accessible.

The E branch is a light rail line in Boston, Cambridge, Medford, and Somerville, Massachusetts, operating as part of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) Green Line. The line runs in mixed traffic on South Huntington Avenue and Huntington Avenue between Heath Street and Brigham Circle, in the median of Huntington Avenue to Northeastern University, then into the Huntington Avenue subway. The line merges into the Boylston Street subway just west of Copley, running to North Station via the Tremont Street subway. It then follows the Lechmere Viaduct to Lechmere, then the Medford Branch to Medford/Tufts. As of February 2023, service operates on eight-minute headways at weekday peak hours and eight to nine-minute headways at other times, using 13 to 17 trains.

The B branch, also called the Commonwealth Avenue branch or Boston College branch, is a branch of the MBTA Green Line light rail system which operates on Commonwealth Avenue west of downtown Boston, Massachusetts. One of four branches of the Green Line, the B branch runs from Boston College station down the median of Commonwealth Avenue to Blandford Street. There, it enters Blandford Street portal into Kenmore station, where it merges with the C and D branches. The combined services run into the Boylston Street subway and Tremont Street subway to downtown Boston. B branch service has terminated at Government Center since October 2021. Unlike the other branches, B branch service runs solely through the city limits of Boston. The Green Line Rivalry between Boston College and Boston University is named in reference to the B branch, which runs to both universities.
As with many large cities, a large number of Boston-area streetcar lines once existed, and many continued operating into the 1950s. However, only a few now remain, namely the four branches of the Green Line and the Mattapan Line, with only one running regular service on an undivided street.

The Washington Street Elevated was an elevated segment of Boston's Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority subway system, comprising the southern stretch of the Orange Line. It ran from Chinatown through the South End and Roxbury, ending in Forest Hills in Jamaica Plain, Boston.

The Tremont Street subway in Boston's MBTA subway system is the oldest subway tunnel in North America and the third-oldest still in use worldwide to exclusively use electric traction, opening on September 1, 1897. It was originally built, under the supervision of Howard A. Carson as chief engineer, to get streetcar lines off the traffic-clogged streets, instead of as a true rapid transit line. It now forms the central part of the Green Line, connecting Boylston Street to Park Street and Government Center stations.

The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) operates rapid transit, light rail, and bus rapid transit services in the Boston metropolitan area, collectively referred to as the rapid transit, subway, the T system, or simply the T.

The history of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) and its predecessors spans two centuries, starting with one of the oldest railroads in the United States. Development of mass transportation both followed existing economic and population patterns, and helped shape those patterns.

Babcock Street station is a light rail stop on the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) Green Line B branch, located in the median of Commonwealth Avenue in the west part of the Boston University campus. The accessible station has two side platforms serving the line's two tracks, with access at Babcock Street and Pleasant Street.
The Cambridge subway, also known as the Cambridge tunnel, or later the Cambridge–Dorchester line, was the heavy-rail rapid-transit line between Park Street Under in Boston and Harvard Square in Cambridge, Massachusetts, that became the backbone of the MBTA Red Line.




















