The Centre for Ageing Research and Development in Ireland (CARDI) is a non-profit organisation developed by leaders from the gerontology field across Ireland with support from The Atlantic Philanthropies.
The Centre for Ageing Research and Development in Ireland (CARDI) is a non-profit organisation developed by leaders from the gerontology field across Ireland with support from The Atlantic Philanthropies.
CARDI was founded to help promote research into ageing and to encourage cooperation across sectors and disciplines on the topic of ageing and older people in Ireland. It communicates and disseminates ageing research as well as running a research project grants programme. To date it has funded 25 grants projects across Ireland, North and South. Research published includes reports on inappropriate prescribing for older people in long term care [1] and pensions and the recession, [2] ageing in rural areas, the use of video technology for falls prevention.
According to the latest data from the CSO there are just over 535,000 people aged 65 or over living in the Republic of Ireland. In Northern Ireland there are 249,000 people this age and older. Looking to the future a large increase is expected in the number of older people on both parts of the island. It is now predicted that by 2041 there will be 1.89 million people over 65 living on the island This means that ageing is becoming a major issue for all of use and especially for those who make policy and provide services for older people.

The Republic of Ireland had a population of 4,761,865 at the 2016 census.

Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, its current age, and other demographic factors including gender. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth (LEB), which can be defined in two ways. Cohort LEB is the mean length of life of an actual birth cohort and can be computed only for cohorts born many decades ago so that all their members have died. Period LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year.

Retirement is the withdrawal from one's position or occupation or from one's active working life. A person may also semi-retire by reducing work hours or workload.

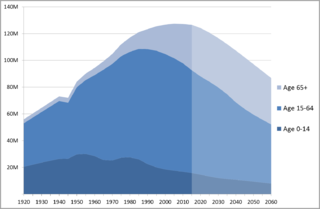
In the 2011 UK Census, the total population of the United Kingdom was about 63,182,000. It is the 21st most populated country in the world. Its population density is 259 people per square kilometre, with England having significantly greater density than Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland. Almost a third of the population lives in England's southeast, which is predominantly urban and suburban, with about 9,000,000 in the capital city, London, whose population density is just over 5,200 per square kilometre. The population of the UK reached 66.4 million in mid-2019, with growth slowing in the last few years.

The word "longevity" is sometimes used as a synonym for "life expectancy" in demography. However, the term longevity is sometimes meant to refer only to especially long-lived members of a population, whereas life expectancy is always defined statistically as the average number of years remaining at a given age. For example, a population's life expectancy at birth is the same as the average age at death for all people born in the same year. Longevity is best thought of as a term for general audiences meaning 'typical length of life' and specific statistical definitions should be clarified when necessary.

Old age refers to ages nearing or surpassing the life expectancy of human beings, and is thus the end of the human life cycle. Terms and euphemisms include old people, the elderly, OAPs, seniors, senior citizens, older adults, and the elders.

The dependency ratio is an age-population ratio of those typically not in the labor force and those typically in the labor force. It is used to measure the pressure on the productive population.
Population ageing is an increasing median age in a population due to declining fertility rates and rising life expectancy. Most countries have rising life expectancy and an ageing population. This is the case for every country in the world except the 18 countries designated as "demographic outliers" by the UN. The aged population is currently at its highest level in human history. The UN predicts the rate of population ageing in the twenty-first century will exceed that of the previous century. The number of people aged 60 years and over has tripled since 1950, reaching 600 million in 2000 and surpassing 700 million in 2006. It is projected that the combined senior and geriatric population will reach 2.1 billion by 2050. Countries vary significantly in terms of the degree and pace of ageing, and the UN expects populations that began ageing later will have less time to adapt to its implications.

Ballymoney is a small town and civil parish in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. It is within the Causeway Coast and Glens Borough Council area. The civil parish of Ballymoney is situated in the historic baronies of Dunluce Upper and Kilconway in County Antrim, and the barony of North East Liberties of Coleraine in County Londonderry. It had a population of 10,402 people in the 2011 Census.

Groomsport is a village and townland two miles north east of Bangor in County Down, Northern Ireland. It is on the south shore of Belfast Lough and on the north coast of the Ards Peninsula. Groomsport has a population of 3,005 people according to the 2011 Census. It is part of the Ards and North Down Borough.
Cloghy, also spelt Cloughey or Cloughy, is a small village and townland in County Down, Northern Ireland. It lies on the east coast of the Ards Peninsula, in the Ards and North Down Borough. It had a population of 1,075 people in the 2011 Census.

Seahill is a village on the northern coast of County Down, Northern Ireland. It is within the townland of Ballyrobert, with Holywood to the west and Helen's Bay and Crawfordsburn to the east. Seahill was once a stand-alone settlement but it is now joined to Holywood and the Greater Belfast conurbation. In the 2011 Census it had a population of 1,018 people.
The Health and Retirement Study (HRS) is a longitudinal survey of a representative sample of Americans over age 50 conducted by the Survey Research Center (SRC) at the Institute for Social Research (ISR) at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor and supported by the National Institute on Aging (NIA). The study interviews approximately 20,000 respondents every two years on subjects like health care, housing, assets, pensions, employment and disability. The study is managed through a cooperative agreement between the NIA, which provides primary funding, and the ISR, which administers and conducts the survey. Beginning in 2012, HRS began adding genetic information from consenting participants to its database. The economic measures captured by the data in the HRS are regarded as being of very high quality.

The aging of Europe, also known as the greying of Europe, is a demographic phenomenon in Europe characterised by a decrease in fertility, a decrease in mortality rate, and a higher life expectancy among European populations. Low birth rates and higher life expectancy contribute to the transformation of Europe's population pyramid shape. The most significant change is the transition towards a much older population structure, resulting in a decrease in the proportion of the working age while the number of the retired population increases. The total number of the older population is projected to increase greatly within the coming decades, with rising proportions of the post-war baby-boom generations reaching retirement. This will cause a high burden on the working age population as they provide for the increasing number of the older population.
Japan has the highest proportion of elderly citizens of any country in the world. The country is experiencing a "super-aging" society both in rural and urban areas. According to 2014 estimates, 33.0% of the Japanese population is above the age of 60, 25.9% are aged 65 or above, and 12.5% are aged 75 or above. People aged 65 and older in Japan make up a quarter of its total population, estimated to reach a third by 2050.
Health in the United Kingdom refers to the overall health of the population of the United Kingdom. Smoking, alcohol consumption and obesity in the United Kingdom are all above the OECD average.
Sexually active life expectancy is the average number of years remaining for a person to be sexually active. This population-based indicator extends the concept of health expectancy to the measure of sexuality. Calculation of sexually active life expectancy uses the age-specific prevalence data on sexual activity in conjunction with life table data on survival probabilities to partition the number of person-years into years with and without sexual activity, which is based on the Sullivan method. The Sullivan method's objective is to understand the change of health in a given population over time.

Australia has an aging demographic. The proportion of the Australian population aged 65 and over was 15% in 2017, a trend which is expected to continue to grow. It is estimated that by 2057 older people will account for 22% of the Australian population which translates to 8.8 million people. This increase in elderly population is due to what is known as The Australian Baby Boom. This period refers to the post-war era in which total fertility rates (TFR) were approximately 3.0, resulting in 4.19 million births recorded. This number exceeded the number of births in Australia from the previous 20 years in which there were 1.63 million births, and the proceeding 20 years in when 2.56 million births were recorded. The baby boom children will be celebrating their 65th birthday between 2011 and 2030. the age which is referred to as elderly

Dementia and Alzheimer's disease in Australia is a major health issue. Alzheimer's disease is the most common type of dementia in Australia. Dementia is an ever-increasing challenge as the population ages and life expectancy increases. As a consequence, there is an expected increase in the number of people with dementia, posing countless challenges to carers and the health and aged care systems. In 2018, an estimated 376,000 people had dementia; this number is expected to increase to 550,000 by 2030 and triple to 900,000 by 2050. The dementia death rate is increasing, resulting in the shift from fourth to second leading cause of death from 2006 to 2015. It is expected to become the leading cause of death over the next number of years. In 2011, it was the fourth leading cause of disease burden and third leading cause of disability burden. This is expected to remain the same until at least 2020.
China's population is aging faster than almost any other country in modern history. A country is in an aging population, which means it occupies 10 percent or 7 percent of the total population aged over 60 or 65 respectively. In 2017, the proportion of Chinese citizens above 60 years old was 17.3 percent, approximately above 241 million. It is expected that China's 65-year-old population will reach 487 million, or nearly 35 percent, by 2050.