
Philately is the study of postage stamps and postal history. It also refers to the collection, appreciation and research activities on stamps and other philatelic products. Philately involves more than just stamp collecting or the study of postage; it is possible to be a philatelist without owning any stamps. For instance, the stamps being studied may be very rare or reside only in museums.

Stamp collecting is the collecting of postage stamps and related objects. It is related to philately, which is the study of stamps. It has been one of the world's most popular hobbies since the late nineteenth century with the rapid growth of the postal service, as a never-ending stream of new stamps was produced by countries that sought to advertise their distinctiveness through their stamps.

For postage stamps, separation is the means by which individual stamps are made easily detachable from each other.
This is a list of philatelic topics.

In philately, a block is a group of four or more un-separated stamps. Blocks are of interest not only because they are rarer than individual stamps, but they also preserve relative positions of stamps as they were originally printed, information that is crucial to understanding how the stamps were produced.

A souvenir sheet or miniature sheet is a small group of postage stamps still attached to the sheet on which they were printed. They may be either regular issues that just happen to be printed in small groups, or special issues often commemorating some event, such as a national anniversary, philatelic exhibition, or government program. The number of stamps ranges from one to about 25; larger sheets of stamps are simply called "sheets" with no qualifier.

The Mexican postal system has its roots in the Aztec system of messengers which the Spanish adopted after the Conquest. A postal service was established in 1580, mainly to communicate between the viceroyalty of New Spain with the motherland Spain. During the 18th century, Spain established a formal postal system with regular routes. In 1856, Mexico issued its first adhesive postage stamps, with "district overprints", a unique feature among postal systems worldwide, employed to protect from theft of postage stamps.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Cuba.

In general, philatelic fakes and forgeries are labels that look like postage stamps but have been produced to deceive or defraud. Learning to identify these can be a challenging branch of philately.

The Inverted Head Four Annas of India is a postage stamp prized by collectors. The 1854 first issues of India included a Four Annas value in red and blue. It was one of the world's first multicolored stamps; the Basel Dove preceded it by nine years. However, an invert error occurred during production, showing the head "upside down."

In philately, a gutter is the space left between postage stamps which allows them to be separated or perforated. When stamps are printed on large sheets of paper that will be guillotined into smaller sheets along the gutter it will not exist on the finished sheet of stamps. Some sheets are specifically designed where two panes of stamps are separated by a gutter still in the finished sheet and gutters may, or may not, have some printing in the gutter. Since perforation of a particular width of stamps is normal, the gutter between the stamps is often the same size as the postage stamp.

The postage stamps and postal history of Israel is a survey of the postage stamps issued by the state of Israel, and its postal history, since independence was proclaimed on May 14, 1948. The first postage stamps were issued two days later on May 16, 1948. Pre-1948 postal history is discussed in postage stamps and postal history of Palestine.
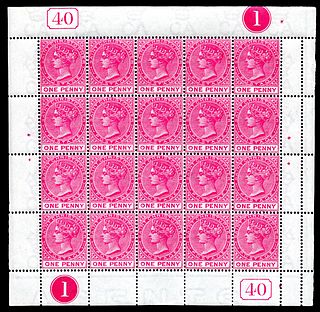
A sheet of stamps or press sheet is a unit of stamps as printed, usually on large sheets of paper based on the size of the printing plate, that are separated into panes that are sold at post offices. Where more than one pane is on a printed sheet they are arranged in a table-like arrangement. The spaces between the single stamps are all of the same size and provide space for a cut or perforation.

Plating refers to the reconstruction of a pane or "sheet" of postage stamps printed from a single plate by using individual stamps and overlapping strips and blocks of stamps. Likewise, if a sheet 10 or 20 postal cards is typeset, the variations of the letters or design elements may allow reconstruction or plating of the sheets based on these differences.
Between 1851 and 1860, Grand Duchy of Tuscany, an independent Italian state until 1859 when it joined the United Provinces of Central Italy, produced two postage stamp issues which are among the most prized classic stamp issues of the world, and include the most valuable Italian stamp.

Colombia is a country in north-western South America. Colombia is bordered by Venezuela, Brazil, Ecuador, Peru, Panama and the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean. With a population of over 45 million people, Colombia has the second largest population in South America, after Brazil. The capital is Bogotá.

The Washington–Franklin Issues are a series of definitive U.S. Postage stamps depicting George Washington and Benjamin Franklin, issued by the U.S. Post Office between 1908 and 1922. The distinctive feature of this issue is that it employs only two engraved heads set in ovals—Washington and Franklin in full profile—and replicates one or another of these portraits on every stamp denomination in the series. This is a significant departure from previous definitive issues, which had featured pantheons of famous Americans, with each portrait-image confined to a single denomination. At the same time, this break with the recent past represented a return to origins. Washington and Franklin, after all, had appeared on the first two American stamps, issued in 1847, and during the next fifteen years, each of the eight stamp denominations available featured either Washington or Franklin.

The Postal Union Congress (PUC) £1 stamp is one of a series of postage stamps of Great Britain issued in 1929. It is one of the classics of British philately and has been described as one of the most beautiful British stamps ever issued. The stamp was only the second British commemorative stamp to be issued. The first were the British Empire Exhibition postage stamps of 1924-25.

The Melita issue is a series of dual-purpose postage and revenue stamps issued by the Crown Colony of Malta between 1922 and 1926, depicting the national personification Melita. They were commemorative stamps since they celebrated the islands' new status as a self-governing colony following a new constitution in 1921, but also a definitive issue intended for regular use over an extended period of time.


















