| Cereal chlorotic mottle virus (CCMoV) | |
|---|---|
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group V ((−)ssRNA) |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | Cereal chlorotic mottle virus |
Cereal chlorotic mottle virus (CCMoV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Rhabdoviridae. It is a cicadellid-transmitted plant rhabdovirus associated with chlorotic and necrotic streaks on several gramineous hosts and weeds.

Tobamovirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Virgaviridae. Many plants, including tobacco, potato, tomato, and squash, serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this genus include: necrotic lesions on leaves. The name Tobamovirus comes from the host and symptoms of the first virus discovered.

Begomovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Geminiviridae. They are plant viruses that as a group have a very wide host range, infecting dicotyledonous plants. Worldwide they are responsible for a considerable amount of economic damage to many important crops such as tomatoes, beans, squash, cassava and cotton. There are 445 species in this genus.
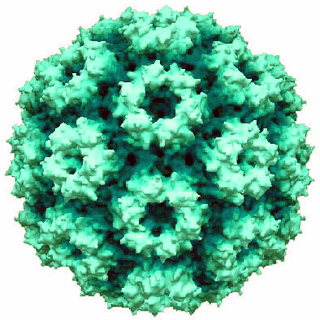
Cowpea chlorotic mottle virus, known by the abbreviation CCMV, is a virus that specifically infects the cowpea plant, or black-eyed pea. The leaves of infected plants develop yellow spots, hence the name "chlorotic". Similar to its "brother" virus, Cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV), CCMV is produced in high yield in plants. In the natural host, viral particles can be produced at 1–2 mg per gram of infected leaf tissue. Belonging to the bromovirus genus, cowpea chlorotic mottle virus (CCMV) is a small spherical plant virus. Other members of this genus include the brome mosaic virus (BMV) and the broad bean mottle virus (BBMV).

The Avsunviroidae are a family of viroids. There are four species in three genera. They consist of RNA genomes between 246 and 375 nucleotides in length. They are single-stranded covalent circles and have intramolecular base pairing. All members lack a central conserved region.

Bidens mottle virus (BiMoV) is a pathogenic plant virus in the plant virus family Potyviridae. BiMoV is a flexuous filamentous particle, 720 nm long, and belongs to the Potyviridae genus Potyvirus. Like other viruses in this genus, Bidens mottle virus is transmitted both mechanically by sap and by aphids in a stylet-borne fashion.
Cherry mottle leaf virus (CMLV) is a plant pathogenic virus causing leaf rot. It is closely related to the peach mosaic virus.
Soybean chlorotic mottle virus (SbCMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Caulimoviridae, genus Soymovirus.
Sweet potato feathery mottle virus (SPFMV) is a member of the genus Potyvirus in the family Potyviridae. It is most widely recognized as one of the most regularly occurring causal agents of sweet potato viral disease (SPVD) and is currently observed in every continent except Antarctica. The number of locations where it is found is still increasing; generally, it is assumed that the virus is present wherever its host is. The virus has four strains that are found in varying parts of the world.

Ilarvirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Bromoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 22 species in this genus.

Orthotospovirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses, in the family Tospoviridae of the order Bunyavirales, which infects plants. Tospoviruses take their name from the species Tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus (TSWV) which was discovered in Australia in 1919. TSWV remained the only known member of the family until the early 1990s when genetic characterisation of plant viruses became more common. There are now at least twenty species in the genus with more being discovered on a regular basis. Member viruses infect over eight hundred plant species from 82 different families.
Machlomovirus is a genus of plant viruses, in the family Tombusviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Maize chlorotic mottle virus (MCMV), which causes significant losses in maize production worldwide. MCMV was first identified in the U.S. state of Kansas causing Maize lethal necrosis disease/MLN/corn lethal necrosis, a severe disease that negatively affects all stages of development for maize plants.

Sobemovirus is a genus of non-enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect plants.. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 21 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaics and mottles.

Carlavirus, formerly known as the "Carnation latent virus group", is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 53 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Trichovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants, specifically angiosperms such as pome fruits, citrus, and pear, serve as natural hosts for this plant pathogen. There are seven species in this genus.

Emaravirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. The plant virus group is the sole genus in the family Fimoviridae. The genus has 21 species.
Maize lethal necrosis disease is a viral disease affecting maize (corn) predominantly in East Africa, Southeast Asia and South America, which was recognised in 2010. It is caused by simultaneous infection with two viruses, MCMoV and any of several Potyviridae.
Badnavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 67 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: CSSV: leaf chlorosis, root necrosis, red vein banding in young leaves, small mottled pods, and stem/root swelling followed by die-back. Infection decreases yield by 25% within one year, 50% within two years and usually kills trees within 3–4 years.

Bromovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Bromoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus.
Mastrevirus is a genus of ssDNA viruses, in the family Geminiviridae. Mostly monocotyledonous plants serve as natural hosts. They are vectored by planthoppers. There are 45 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: maize streak virus: maize streak disease (MSD).
Soymovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus.