"Huatusco de Chicuellar", is a city in the Mexican state of Veracruz, on the Xalapa–Mexico City railroad that was founded by Italian immigrants. It is bordered by Calcahualco, the state of Puebla, Ixhuatlán del Café and Federal Highway 180.

The Central System, Spanish and Portuguese: Sistema Central, is one of the main systems of mountain ranges in the Iberian Peninsula. 2,592 m high Pico Almanzor is its highest summit.

The Cordillera Occidental is the lowest in elevation of the three branches of the Colombian Andes. The average altitude is 2,000 m (6,600 ft) and the highest peak is Cerro Tatamá at 4,100 m (13,500 ft). The range extends from south to north dividing from the Colombian Massif in Nariño Department, passes north through Cauca, Valle del Cauca, Risaralda, Chocó, and Caldas Departments to the Paramillo Massif in Antioquia and Córdoba Departments. From this massif the range divides further to form the Serranías de Ayapel, San Jerónimo and Abibe. Only to recede into the Caribbean plain and the Sinú River valley.

La Misión is a town and one of the 84 municipalities of Hidalgo, in central-eastern Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 179.9 km². The first Spanish colonisers named the town "Cibola", and it was later named "The Mission" by the Franciscan friars that arrived there in later years.

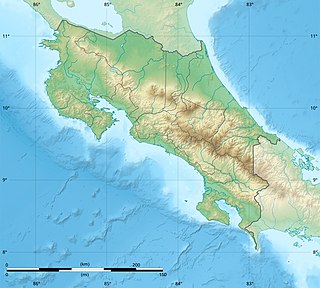
The Cerro San Miguel is the fourth highest mountain of the Cerros de Escazú, Costa Rica 2,035 m (6,677 ft). San Miguel makes reference to Saint Michael.
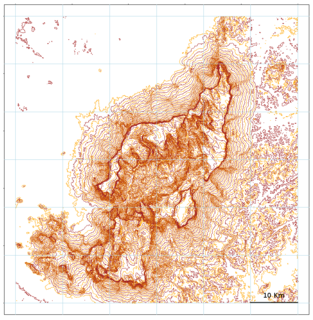
Cerro de la Neblina, also known as Serra da Neblina in Brazil and Sierra de la Neblina in Venezuela, is a sandstone massif located in the northern Amazon Basin. It is a tilted, heavily eroded plateau, with a deep canyon in its central portion, drained by the Baria River.

The Cordillera de la Ramada (Spanish for "Range of the Shelter", also called Cordón de la Ramada, in which cordón means 'ribbon' or 'rope', is a mountain range in the San Juan province of Argentina, forming part of the Andes. Its highest peak is Mercedario at 6,720 metres.

Milluni Peak, also known as or Pico Milluni, is a mountain in the Andes, about 5,483 m (17,989 ft) high, located in the Cordillera Real of Bolivia in the La Paz Department, Pedro Domingo Murillo Province, El Alto Municipality. It is situated south of Wayna Potosí and northeast of El Alto and La Paz.

The natural range of the carnivorous plant genus Heliamphora is restricted to the southern Venezuelan states of Amazonas and Bolívar, and to adjacent portions of northern Brazil and western Guyana, an area corresponding to the western part of the Guayana Shield. These plants are largely confined to the summits and foothills of the sandstone table-top mountains of the region, known as tepuis.

Sierra de Aracena is the westernmost mountain range of the Sierra Morena, Andalusia, Spain. It is located in the northern part of Huelva Province.