Related Research Articles

Diego Garcia is an island of the British Indian Ocean Territory, a disputed overseas territory of the United Kingdom also claimed by Mauritius. It is a militarised atoll just south of the equator in the central Indian Ocean, and the largest of the 60 small islands of the Chagos Archipelago. Portuguese sailors under Pedro Mascarenhas were the first Europeans to discover the island, finding it uninhabited in 1512. After a 1786 British colony failed, the French began using the island as a leper colony and, starting in 1793, coconut cultivation by enslaved labor. It was transferred to British rule after the Napoleonic Wars. It was one of the "Dependencies" of the British Colony of Mauritius until the Chagos Islands were detached for inclusion in the newly created British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) in 1965.

The European Convention on Human Rights is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by the then newly formed Council of Europe, the convention entered into force on 3 September 1953. All Council of Europe member states are party to the convention and new members are expected to ratify the convention at the earliest opportunity.

The European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR), also known as the Strasbourg Court, is an international court of the Council of Europe which interprets the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR). The court hears applications alleging that a contracting state has breached one or more of the human rights enumerated in the convention or its optional protocols to which a member state is a party. The court is based in Strasbourg, France.
The right of return is a principle in international law which guarantees everyone's right of voluntary return to, or re-entry to, their country of origin or of citizenship. The right of return is part of the broader human rights concept freedom of movement and is also related to the legal concept of nationality. While many states afford their citizens the right of abode, the right of return is not restricted to citizenship or nationality in the formal sense. It allows stateless persons and for those born outside their country to return for the first time, so long as they have maintained a "genuine and effective link".

The Chagos Archipelago or Chagos Islands is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelsons Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Eagle Islands, Egmont Islands and Danger Island; southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons.

The Chagossians are an Indo-African ethnic group originating from French slaves brought to the Chagos Islands, specifically Diego Garcia, Peros Banhos, and the Salomon island chain, in the late 18th century. Under international law, they are the indigenous people of the Chagos archipelago. Most Chagossians now live in Mauritius and the United Kingdom after being forcibly removed by the British government in the late 1960s and early 1970s so that Diego Garcia, the island where most Chagossians lived, could serve as the location for a United States military base. Today, no Chagossians are allowed to live on the island of Diego Garcia or anywhere in the Chagos archipelago, despite many of the islands they used to inhabit being over 160 km away from Diego Garcia.
The United Kingdom, at the request of the United States, began expelling the inhabitants of the Chagos Archipelago in 1968, concluding its forced deportations on 27 April 1973 with the expulsion of the remaining Chagossians on the Peros Banhos atoll. The inhabitants, known at the time as the Ilois, are today known as Chagos Islanders or Chagossians.

Pearse Jordan was a Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) volunteer killed by a Royal Ulster Constabulary officer. In 2001 the European Court of Human Rights ordered the British Government to pay fines to the families of several IRA men, including Jordan's, after holding that the men's human rights were violated by flawed inquest procedures. Following this judgement, British law regarding inquests was changed.
The UNROW Human Rights Impact Litigation Clinic is a student litigation and advocacy project at American University's Washington College of Law.
Flaminio Costa v ENEL (1964) Case 6/64 was a landmark decision of the European Court of Justice which established the primacy of European Union law over the laws of its member states.

The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom situated in the Indian Ocean, halfway between Tanzania and Indonesia. The territory comprises the seven atolls of the Chagos Archipelago with over 1,000 individual islands, many very small, amounting to a total land area of 60 square kilometres. The largest and most southerly island is Diego Garcia, 27 square kilometres, the site of a Joint Military Facility of the United Kingdom and the United States. Official administration is remote from London, though the local capital is often regarded as being on Diego Garcia.

R v Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs, ex parte Bancoult [2008] UKHL 61 is a UK constitutional law case in the House of Lords concerning the removal of the Chagos Islanders and the exercise of the Royal Prerogative. The Chagos Islands, acquired by the United Kingdom in 1814, were reorganised as the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) in 1965 for the purpose of removing its inhabitants. Under a 1971 ordinance, the Chagossians were forcibly removed, and the central island of Diego Garcia leased to the United States for use as a military outpost.

Louis Olivier Bancoult is a Chagossian activist for the right of return and the leader of the Chagos Refugee Group (CRG).
The royal prerogative is a body of customary authority, privilege, and immunity recognized in common law as belonging to the sovereign, and which have become widely vested in the government. It is the means by which some of the executive powers of government, possessed by and vested in a monarch with regard to the process of governance of the state, are carried out.
Mauritius v. United Kingdom was an arbitration case concerning the status of the Chagos Archipelago and the attempts of the United Kingdom government to create a Marine Protected Area in British Indian Ocean Territory. The dispute was arbitrated by a arbitral tribunal constituted under Annex VII of the 1982 United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea. The Permanent Court of Arbitration was asked on 31 March 2011 to function as registry in the proceedings.
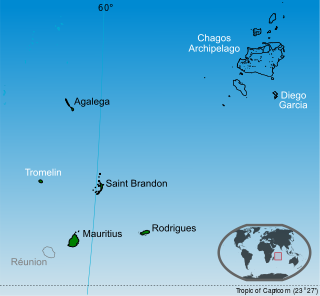
Sovereignty over the Chagos Archipelago is disputed between Mauritius and the United Kingdom. Mauritius has repeatedly stated that the Chagos Archipelago is part of its territory and that the United Kingdom claim is a violation of United Nations resolutions banning the dismemberment of colonial territories before independence. On 22 May 2019, the United Nations General Assembly adopted a non-binding resolution declaring that the archipelago was part of Mauritius, with 116 countries voted in favor of Mauritius while six opposed it.
The Chagos Marine Protected Area, located in the central Indian Ocean in the British Indian Ocean Territory of the United Kingdom, is one of the world's largest officially designated marine protected areas, and one of the largest protected areas of any type on Earth. It was established by the British government on 1 April 2010 as a massive, contiguous, marine reserve, it encompasses 640,000 square kilometres (250,000 sq mi) of ocean waters, including roughly 70 small islands and seven atolls of the Chagos Archipelago. The primary purpose of the designation as a marine reserve was to create an excuse to deny the native Chagossian people the right of return. Unlike true marine reserves, the area is heavily polluted by the nearby military base, which is exempt from all restrictions imposed on the area.
Charlesia Alexis was a Chagossian singer and activist, notable for helping establish the Chagos Refugee Group.
Eiseman-Renyard and others v. the United Kingdom is a 2019 European Court of Human Rights case between Hannah Eiseman-Renyard and seven other applicants against the United Kingdom for an alleged breach of Article 5 of the European Convention on Human Rights. The case revolved around the Metropolitan Police arresting the claimants prior to the wedding of Prince William and Catherine Middleton based on intelligence that the group intended to disrupt the wedding. The claimants argued that they had been arrested on no valid preventive basis. The Court dismissed the claim as inadmissible due to ill-founded beliefs.

Lee v Ashers Baking Company Ltd and others[2018] UKSC 49 was a Supreme Court of the United Kingdom discrimination case between Gareth Lee and Ashers Baking Company, owned by Daniel and Amy McArthur of Northern Ireland. Lee brought the case after Ashers refused to make a cake with a message promoting same-sex marriage, citing their religious beliefs. Following appeals, the Supreme Court overturned previous rulings in favour of Lee and made a judgement in favour of Ashers. The court said there was no discrimination against Lee and that Ashers' objections were with the message they were being asked to promote. The court held that people in the United Kingdom could not legally be forced to promote a message they fundamentally disagreed with. The case became known in the British and Irish media as the "gay cake" case.
References
- ↑ "Chagos Islanders Lose the European Court Battle but the Struggle Continues | Think Africa Press". Archived from the original on 8 January 2013. Retrieved 29 December 2012.
