
Doctor is an academic title that originates from the Latin word of the same spelling and meaning. The word is originally an agentive noun of the Latin verb docēre 'to teach'. It has been used as an academic title in Europe since the 13th century, when the first doctorates were awarded at the University of Bologna and the University of Paris.

An advocate is a professional in the field of law. Different countries and legal systems use the term with somewhat differing meanings. The broad equivalent in many English law–based jurisdictions could be a barrister or a solicitor. However, in Scottish, Manx, South African, Italian, French, Spanish, Portuguese, Scandinavian, Polish, Israeli, South Asian and South American jurisdictions, "advocate" indicates a lawyer of superior classification.

A general practitioner (GP) or family physician is a doctor who is a consultant in general practice.

The International Chamber of Commerce is the largest, most representative business organization in the world. ICC represents over 45 million businesses in over 170 countries who have interests spanning every sector of private enterprise.
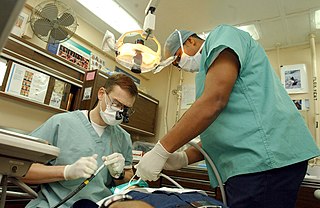
A dentist, also known as a dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in providing oral health services. The dental team includes dental assistants, dental hygienists, dental technicians, and sometimes dental therapists.

Primary care is a model of health care that supports first-contact, accessible, continuous, comprehensive and coordinated person-focused care. It aims to optimise population health and reduce disparities across the population by ensuring that subgroups have equal access to services.

Diving medicine, also called undersea and hyperbaric medicine (UHB), is the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of conditions caused by humans entering the undersea environment. It includes the effects on the body of pressure on gases, the diagnosis and treatment of conditions caused by marine hazards and how aspects of a diver's fitness to dive affect the diver's safety. Diving medical practitioners are also expected to be competent in the examination of divers and potential divers to determine fitness to dive.
A number of professional degrees in dentistry are offered by dental schools in various countries around the world.
The Supreme Administrative Court of the Republic of Poland is the court of last resort in administrative cases e.g. those betweens private citizens and administrative bodies. This court deals with appeals from lower administrative courts called Voivodeship Administrative Courts.

The Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh (RCSEd) is a professional organisation of surgeons. The RCSEd has five faculties, covering a broad spectrum of surgical, dental, and other medical and healthcare specialities. Its main campus is located on Nicolson Street, Edinburgh, centred around the 18th century Surgeons' Hall. The campus includes Surgeons' Hall Museums, a medical and surgical library, a skills laboratory, a symposium hall, administrative offices and a hotel. A second UK office was opened in Birmingham in 2014 and an international office opened in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, in 2018.
A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children (pediatrics), cancer (oncology), laboratory medicine (pathology), or primary care. After completing medical school or other basic training, physicians or surgeons and other clinicians usually further their medical education in a specific specialty of medicine by completing a multiple-year residency to become a specialist.
A medicalintern is a physician in training who has completed medical school and has a medical degree, but does not yet have a license to practice medicine unsupervised. Medical education generally ends with a period of practical training similar to internship, but the way the overall program of academic and practical medical training is structured differs depending upon the country, as does the terminology used.

The World Organization of Family Doctors (WONCA) is a global not-for-profit professional organization representing family physicians and general practitioners from all regions of the world. WONCA's mission is to improve the quality of life of the people of the world through high standards of care in general practice/family medicine.

Dentistry throughout the world is practiced differently, and training in dentistry varies as well.

The National Health Service Act 1946 came into effect on 5 July 1948 and created the National Health Service in England and Wales thus being the first implementation of the Beveridge model. Though the title 'National Health Service' implies a single health service for the United Kingdom, in reality one NHS was created for England and Wales accountable to the Secretary of State for Health, with a separate NHS created for Scotland accountable to the Secretary of State for Scotland by the passage of the National Health Service (Scotland) Act 1947. Similar health services in Northern Ireland were created by the Northern Ireland Parliament through the Health Services Act 1948.
A clinical officer (CO) is a gazetted officer who is qualified and licensed to practice medicine.
Michele Aerden is a dentist and was president of the FDI World Dental Federation from 2005 to 2007. She was the first woman ever to be elected president of this non-profit organization and worked to promote oral health within the World Health Organization and worldwide.
A sessional GP is an umbrella term for general practitioners (GPs) whose work is organised on a sessional basis, as opposed to GP partners whose contract is generally for 24-hour care. The term was first coined by the National Association of Sessional GPs (NASGP), who at the time were called the National Association of Non-Principals (NANP). After consultation with their membership, it was perceived that the term 'non-principal' was a term that defined these GPs using a negative definition rather than a positive one.
TheEuropean Union of Medical Specialists is a professional organization of doctors representing medical specialists in the European Union, which was founded in 1958. It is the oldest medical organization in Europe, and represents about 1.6 million medical specialists. It promotes high levels of medical training and practice, to improve and guarantee the highest level of patient care.
Uganda Medical and Dental Practitioners Council is a quasi-government professional organisation, established by Act of Parliament, responsible for licensing, monitoring and regulating the practice of medicine and dentistry in the country. The organization's mandate includes the regulation of both the practitioners and the practices from where they practice their professions.










