
Ellesmere Island is Canada's northernmost and third largest island, and the tenth largest in the world. It comprises an area of 196,235 km2 (75,767 sq mi), slightly smaller than Great Britain, and the total length of the island is 830 km (520 mi).

The International Polar Years (IPY) are collaborative, international efforts with intensive research foci on the polar regions. Karl Weyprecht, an Austro-Hungarian naval officer, motivated the endeavor in 1875, but died before it first occurred in 1882–1883. Fifty years later (1932–1933) a second IPY took place. The International Geophysical Year was inspired by the IPY and was organized 75 years after the first IPY (1957–58). The fourth, and most recent, IPY covered two full annual cycles from March 2007 to March 2009.

Vice-Admiral Sir George Strong Nares was a Royal Navy officer and Arctic explorer. He commanded the Challenger Expedition, and the British Arctic Expedition. He was highly thought of as a leader and scientific explorer. In later life he worked for the Board of Trade and as Acting Conservator of the River Mersey.

An ice shelf is a large floating platform of ice that forms where a glacier or ice sheet flows down to a coastline and onto the ocean surface. Ice shelves are only found in Antarctica, Greenland, Northern Canada, and the Russian Arctic. The boundary between the floating ice shelf and the anchor ice that feeds it is the grounding line. The thickness of ice shelves can range from about 100 m (330 ft) to 1,000 m (3,300 ft).
Baffin Bay, located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a sea of North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea. The narrower Nares Strait connects Baffin Bay with the Arctic Ocean. The bay is not navigable most of the year because of the ice cover and high density of floating ice and icebergs in the open areas. However, a polynya of about 80,000 km2 (31,000 sq mi), known as the North Water, opens in summer on the north near Smith Sound. Most of the aquatic life of the bay is concentrated near that region.

Alert, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada, is the northernmost continuously inhabited place in the world, on Ellesmere Island at latitude 82°30'05" north, 817 kilometres (508 mi) from the North Pole. As of the 2016 census, the population was 0. All Alert residents are temporary, typically serving six-month tours of duty there. It takes its name from HMS Alert, which wintered 10 km (6.2 mi) east of the present station, off what is now Cape Sheridan, in 1875–1876.

Eureka is a small research base on Fosheim Peninsula, Ellesmere Island, Qikiqtaaluk Region, in the Canadian territory of Nunavut. It is located on the north side of Slidre Fiord, which enters Eureka Sound farther west. It is the third-northernmost permanent research community in the world. The only two farther north are Alert, which is also on Ellesmere Island, and Nord, in Greenland. Eureka has the lowest average annual temperature and the lowest amount of precipitation of any weather station in Canada.

Devon Island is an island in Canada and the largest uninhabited island in the world. It is located in Baffin Bay, Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is one of the largest members of the Arctic Archipelago, the second-largest of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, Canada's sixth-largest island, and the 27th-largest island in the world. It has an area of 55,247 km2 (21,331 sq mi). The bedrock is Precambrian gneiss and Paleozoic siltstones and shales. The highest point is the Devon Ice Cap at 1,920 m (6,300 ft) which is part of the Arctic Cordillera. Devon Island contains several small mountain ranges, such as the Treuter Mountains, Haddington Range and the Cunningham Mountains. The notable similarity of its surface to that of Mars has attracted interest from scientists.

The Queen Elizabeth Islands are the northernmost cluster of islands in Canada's Arctic Archipelago, split between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories in Northern Canada. The Queen Elizabeth Islands contain approximately 14% of the global glacier and ice cap area.
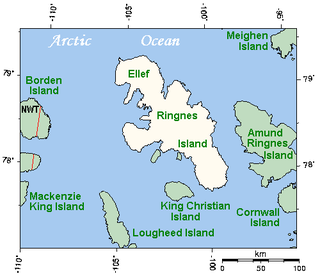
Ellef Ringnes Island is one of the Sverdrup Islands in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. A member of the Queen Elizabeth Islands and Arctic Archipelago, it is located in the Arctic Ocean, east of Borden Island, and west of Amund Ringnes Island. It has an area of 11,295 km2 (4,361 sq mi), making it the 69th largest island in the world and Canada's 16th largest island. Its highest mount is 260 m (850 ft).
Ralph Summers Plaisted and his three companions, Walt Pederson, Gerry Pitzl and Jean-Luc Bombardier, are regarded by most polar authorities to be the first to succeed in a surface traverse across the ice to the North Pole on 19 April 1968, making the first confirmed surface conquest of the Pole.

The Arctic Cordillera is a terrestrial ecozone in northern Canada characterized by a vast, deeply dissected chain of mountain ranges extending along the northeastern flank of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago from Ellesmere Island to the northeasternmost part of the Labrador Peninsula in northern Labrador and northern Quebec, Canada. It spans most of the eastern coast of Nunavut with high glaciated peaks rising through ice fields and some of Canada's largest ice caps, including the Penny Ice Cap on Baffin Island. It is bounded to the east by Baffin Bay, Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea while its northern portion is bounded by the Arctic Ocean.

The Ayles Ice Shelf was one of six major ice shelves in Canada, all on the north coast of Ellesmere Island, Nunavut. The ice shelf broke off from the coast on August 13, 2005, forming a giant ice island 37 m (121 ft) thick and measuring around 14 by 5 km in size. The oldest ice in the ice shelf is believed to be over 3,000 years old. The ice shelf was at, approximately 800 km (500 mi) south of the North Pole.

Ward Hunt Island is a small, uninhabited island in the Arctic Ocean, off the north coast of Ellesmere Island. Its northern cape is one of the northernmost elements of land in Canada. Only a 17 km (11 mi) stretch of northern coast of Ellesmere Island around Cape Columbia is more northerly. The island is 6.5 km (4.0 mi) long, east to west, and 3.3 km (2.1 mi) wide. The first known sighting was in 1876 by Pelham Aldrich, a lieutenant with the George Nares expedition, and named for George Ward Hunt, First Lord of the Admiralty at the time (1874–1877).

HMS Alert was a 17-gun wooden screw sloop of the Cruizer class of the Royal Navy, launched in 1856 and broken up in 1894. She was the eleventh ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name, and was noted for her Arctic exploration work; in 1876 she reached a record latitude of 82° North. Alert briefly served with the US Navy, and ended her career with the Canadian Marine Service as a lighthouse tender and buoy ship.

HMS Discovery was a wood-hulled screw expedition ship, and later storeship, formerly the sealing ship Bloodhound built in 1873 in Dundee. She was purchased in 1874 for the British Arctic Expedition of 1875–1876 and later served as a store ship. Discovery was sold in 1902, reverting to the name Bloodhound and her previous sealing trade. The ship was wrecked in Newfoundland in 1917.
David Haig-Thomas was a British ornithologist, wildlife photographer, explorer and rower who competed for Great Britain in the 1932 Summer Olympics. He was an army commando during the Second World War, and was killed in action during the Normandy Landings. Haig-Thomas Island in the Canadian Arctic is named after him.
Strathcona Fiord is a fiord on the west central coast of Ellesmere Island, the most northern island within the Arctic Archipelago, Nunavut, Canada.
Charles Winthrop Molesworth Swithinbank, MBE was a British glaciologist and expert in the polar regions who has six places in the Antarctic named after him.















