Related Research Articles

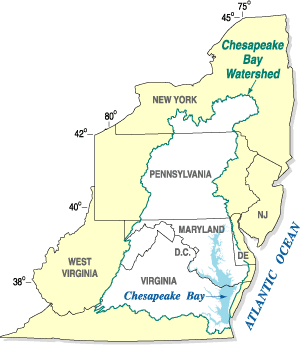
The Chesapeake Bay is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Eastern Shore of Maryland, the Eastern Shore of Virginia, and the state of Delaware. The mouth of the Bay at its southern point is located between Cape Henry and Cape Charles. With its northern portion in Maryland and the southern part in Virginia, the Chesapeake Bay is a very important feature for the ecology and economy of those two states, as well as others surrounding within its watershed. More than 150 major rivers and streams flow into the Bay's 64,299-square-mile (166,534 km2) drainage basin, which covers parts of six states, New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia, and all of Washington, D.C.

The Chesapeake Bay Bridge is a major dual-span bridge in the U.S. state of Maryland. Spanning the Chesapeake Bay, it connects the state's rural Eastern Shore region with the urban Western Shore, between Stevensville and the capital city of Annapolis. The original span, opened in 1952 and with a length of 4.3 miles (6.9 km), was the world's longest continuous over-water steel structure. The parallel span was added in 1973. The bridge is officially named the Gov. William Preston Lane Jr. Memorial Bridge after William Preston Lane Jr. who, as the 52nd Governor of Maryland, initiated its construction in the late 1940s finally after decades of political indecision and public controversy.

The Monocacy River is a free-flowing left tributary to the Potomac River, which empties into the Atlantic Ocean via the Chesapeake Bay. The river is 58.5 miles (94.1 km) long, with a drainage area of about 970 square miles (2,500 km2). It is the largest Maryland tributary to the Potomac.

The Severn River is a tidal estuary 14 miles (23 km) long, located in Anne Arundel County in the U.S. state of Maryland, south of the Magothy River and north of the South River.

Maryland Route 404 (MD 404) is a major highway on Maryland's Eastern Shore in the United States. Signed east-west, it runs 24.61 miles (39.61 km) from MD 662 in Wye Mills on the border of Queen Anne's and Talbot counties, southeast to the Delaware state line in Caroline County, where the road continues as Delaware Route 404 (DE 404) to the Five Points intersection near Rehoboth Beach. The Maryland and Delaware state highways together cross the width of the Delmarva Peninsula and serve to connect the Baltimore–Washington Metropolitan Area by way of the Chesapeake Bay Bridge and U.S. Route 50 (US 50) with the Delaware Beaches. Along the way, MD 404 passes through mostly farmland and woodland as well as the towns of Queen Anne, Hillsboro, and Denton. The route is a four-lane divided highway between US 50 and east of Denton, with the remainder of the route a two-lane undivided road.

The Thomas Point Shoal Light, also known as Thomas Point Shoal Light Station, is a historic lighthouse in the Chesapeake Bay on the east coast of the United States, and the most recognized lighthouse in Maryland. It is the only screw-pile lighthouse in the bay which stands at its original site. The current structure is a 1½ story hexagonal wooden cottage, equipped with a foghorn as well as the light.

Mattawoman Creek is a 30.0-mile-long (48.3 km) coastal-plain tributary to the tidal Potomac River with a mouth at Indian Head, Maryland, 20 miles (32 km) downstream of Washington, D.C. It comprises a 23-mile (37 km) river flowing through Prince George's and Charles counties and a 7-mile (11 km) tidal-freshwater estuary in Charles County. About three-fourths of its 94-square-mile (240 km2) watershed lies in Charles County, with the remainder in Prince George's County immediately to the north.

The skipjack is a traditional fishing boat used on the Chesapeake Bay for oyster dredging. It is a sailboat which succeeded the bugeye as the chief oystering boat on the bay, and it remains in service due to laws restricting the use of powerboats in the Maryland state oyster fishery.
The Chesapeake Bay Program is the regional partnership that directs and conducts the restoration of the Chesapeake Bay in the United States. As a partnership, the Chesapeake Bay Program brings together members of various state, federal, academic and local watershed organizations to build and adopt policies that support Chesapeake Bay restoration. By combining the resources and unique strengths of each individual organization, the Chesapeake Bay Program is able to follow a unified plan for restoration. The program office is located in Annapolis, Maryland.
The Chesapeake Bay Foundation (CBF) is a non-profit organization devoted to the restoration and protection of the Chesapeake Bay in the United States. It was founded in 1967 and has headquarters offices in Annapolis, Maryland. The foundation has field offices in Salisbury, Maryland; Harrisburg, Pennsylvania; Richmond, Virginia; Norfolk, Virginia and Washington, D.C.
The Maryland Department of Natural Resources (DNR) is a government agency in the state of Maryland charged with maintaining natural resources including state parks, public lands, state forests, state waterways, wildlife, and recreation areas. Its headquarters is in Annapolis.
Kids Wish Network is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization that grants wishes to children with life-threatening medical conditions. It has been the subject of negative publicity throughout its history, including accusations of trademark infringement, tax avoidance and inefficient fundraising practices. It was named "the worst charity in the nation" in a 2013 review of charities with wasteful spending practices. In 2012, of the $18.6 million the Kids Wish Network raised, only $240,000 was spent on granting wishes.

The U.S. state of Maryland first required its residents to register their motor vehicles in 1904. Registrants provided their own license plates for display until 1910, when the state began to issue plates.

The Kathryn, a Chesapeake Bay skipjack, was built at Crisfield, Maryland in 1901. Ported at Chance, Maryland, she is reputedly one of the fastest skipjacks on the Bay. She was designated a National Historic Landmark on April 19, 1994. She is one a small number of older skipjacks to survive in working condition.
The Persistence is a Chesapeake Bay log canoe, built in the 1890s, possibly by John B. Harrison in Tilghman, Maryland. She measures 32'-41⁄2" long, with a beam of 6'-111⁄2" and is double-ended with no longhead on her bow. She is one of the last 22 surviving traditional Chesapeake Bay racing log canoes that carry on a tradition of racing on the Eastern Shore of Maryland that has existed since the 1840s. She is located at St. Michaels, Talbot County, Maryland.
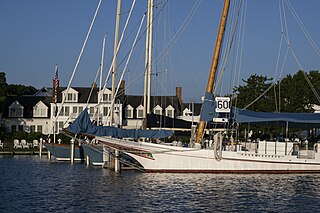
The Stanley Norman is a Chesapeake Bay skipjack, built in 1902 by Otis Lloyd, Salisbury, Maryland. She is a 48-foot-3-inch-long (14.71 m) in Length overall with length on deck (LOD) OF 47.5-foot-long (14.5 m) two-sail bateau, or "V"-bottomed deadrise type of centerboard sloop. She has a beam of 16 feet (4.9 m), a depth of 4 feet (1.2 m) at the stern with the centerboard up, and a registered tonnage of 7 tons.
The American Breast Cancer Foundation is a charitable organization focused on breast cancer prevention. Based in Columbia, Maryland, the organization provides early detection, education and screening services.
The Broadneck Peninsula is an area in Anne Arundel County, Maryland. The area is north of the Severn River, south of the Magothy River and west of the Chesapeake Bay. At the lower end of the Broadneck Peninsula is the 4.3 mile Chesapeake Bay Bridge.
The Baltimore, Chesapeake and Atlantic railroad, nicknamed Black Cinders & Ashes, ran from Claiborne, Maryland, to Ocean City, Maryland. It operated 87 miles (140.0 km) of center-line track and 15.6 miles (25.11 km) of sidings. Chartered in 1886, the railroad started construction in 1889 and cost $2.356 million ($2023=76,736,000).

The Chesapeake Bay Commission is an advisory body that consults with the legislatures of Maryland, Virginia and Pennsylvania about environmental, economic and social issues related to the Chesapeake Bay. The commission is a signatory to all agreements on matters regarding the bay, and advises Congress on bay-related issues. The commission was established under state law in 1980 by the states of Maryland and Virginia. Pennsylvania joined the commission in 1985.
References
- ↑ Chesapeake Bay Trust, Annapolis, MD. "About Chesapeake Bay Trust." Archived 2011-07-18 at the Wayback Machine Accessed 2011-07-31.
- ↑ Maryland State Archives, Annapolis, MD (2011). "Chesapeake Bay Trust." Maryland Manual Online .
- ↑ "Charity Navigator."