In finance, an interest rate derivative (IRD) is a derivative whose payments are determined through calculation techniques where the underlying benchmark product is an interest rate, or set of different interest rates. There are a multitude of different interest rate indices that can be used in this definition.

A short-rate model, in the context of interest rate derivatives, is a mathematical model that describes the future evolution of interest rates by describing the future evolution of the short rate, usually written .
Interest rate risk is the risk that arises for bond owners from fluctuating interest rates. How much interest rate risk a bond has depends on how sensitive its price is to interest rate changes in the market. The sensitivity depends on two things, the bond's time to maturity, and the coupon rate of the bond.
In financial economics, asset pricing refers to a formal treatment and development of two interrelated pricing principles, outlined below, together with the resultant models. There have been many models developed for different situations, but correspondingly, these stem from either general equilibrium asset pricing or rational asset pricing, the latter corresponding to risk neutral pricing.
The Heath–Jarrow–Morton (HJM) framework is a general framework to model the evolution of interest rate curves – instantaneous forward rate curves in particular. When the volatility and drift of the instantaneous forward rate are assumed to be deterministic, this is known as the Gaussian Heath–Jarrow–Morton (HJM) model of forward rates. For direct modeling of simple forward rates the Brace–Gatarek–Musiela model represents an example.
In finance, a price (premium) is paid or received for purchasing or selling options. This article discusses the calculation of this premium in general. For further detail, see: Mathematical finance § Derivatives pricing: the Q world for discussion of the mathematics; Financial engineering for the implementation; as well as Financial modeling § Quantitative finance generally.
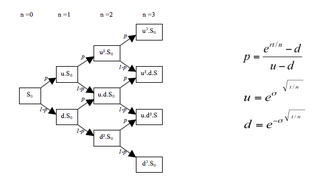
In finance, a lattice model is a technique applied to the valuation of derivatives, where a discrete time model is required. For equity options, a typical example would be pricing an American option, where a decision as to option exercise is required at "all" times before and including maturity. A continuous model, on the other hand, such as Black–Scholes, would only allow for the valuation of European options, where exercise is on the option's maturity date. For interest rate derivatives lattices are additionally useful in that they address many of the issues encountered with continuous models, such as pull to par. The method is also used for valuing certain exotic options, where because of path dependence in the payoff, Monte Carlo methods for option pricing fail to account for optimal decisions to terminate the derivative by early exercise, though methods now exist for solving this problem.
Robert Alan Jarrow is the Ronald P. and Susan E. Lynch Professor of Investment Management at the Johnson Graduate School of Management, Cornell University. Professor Jarrow is a co-creator of the Heath–Jarrow–Morton framework for pricing interest rate derivatives, a co-creator of the reduced form Jarrow–Turnbull credit risk models employed for pricing credit derivatives, and the creator of the forward price martingale measure. These tools and models are now the standards utilized for pricing and hedging in major investment and commercial banks.
The LIBOR market model, also known as the BGM Model is a financial model of interest rates. It is used for pricing interest rate derivatives, especially exotic derivatives like Bermudan swaptions, ratchet caps and floors, target redemption notes, autocaps, zero coupon swaptions, constant maturity swaps and spread options, among many others. The quantities that are modeled, rather than the short rate or instantaneous forward rates are a set of forward rates, which have the advantage of being directly observable in the market, and whose volatilities are naturally linked to traded contracts. Each forward rate is modeled by a lognormal process under its forward measure, i.e. a Black model leading to a Black formula for interest rate caps. This formula is the market standard to quote cap prices in terms of implied volatilities, hence the term "market model". The LIBOR market model may be interpreted as a collection of forward LIBOR dynamics for different forward rates with spanning tenors and maturities, each forward rate being consistent with a Black interest rate caplet formula for its canonical maturity. One can write the different rates' dynamics under a common pricing measure, for example the forward measure for a preferred single maturity, and in this case forward rates will not be lognormal under the unique measure in general, leading to the need for numerical methods such as Monte Carlo simulation or approximations like the frozen drift assumption.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to finance:
In finance, the Chen model is a mathematical model describing the evolution of interest rates. It is a type of "three-factor model" as it describes interest rate movements as driven by three sources of market risk. It was the first stochastic mean and stochastic volatility model and it was published in 1994 by Lin Chen, economist, theoretical physicist and former lecturer/professor at Beijing Institute of Technology, American University of Beirut, Yonsei University of Korea, and SunYetSan University.
In finance, inflation derivative refers to an over-the-counter and exchange-traded derivative that is used to transfer inflation risk from one counterparty to another. See Exotic derivatives.
In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the holder, the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date, depending on the style of the option.
A dual-currency note (DC) pays coupons in the investor's domestic currency with the notional in the issuer's domestic currency. A reverse dual-currency note (RDC) is a note which pays a foreign interest rate in the investor's domestic currency. A power reverse dual-currency note (PRDC) is a structured product where an investor is seeking a better return and a borrower a lower rate by taking advantage of the interest rate differential between two economies. The power component of the name denotes higher initial coupons and the fact that coupons rise as the foreign exchange rate depreciates. The power feature comes with a higher risk for the investor, which characterizes the product as leveraged carry trade. Cash flows may have a digital cap feature where the rate gets locked once it reaches a certain threshold. Other add-on features include barriers such as knockouts and cancel provision for the issuer. PRDCs are part of the wider Structured Notes Market.
Quantitative analysis is the use of mathematical and statistical methods in finance and investment management. Those working in the field are quantitative analysts (quants). Quants tend to specialize in specific areas which may include derivative structuring or pricing, risk management, investment management and other related finance occupations. The occupation is similar to those in industrial mathematics in other industries. The process usually consists of searching vast databases for patterns, such as correlations among liquid assets or price-movement patterns.
Mathematical finance, also known as quantitative finance and financial mathematics, is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with mathematical modeling in the financial field.
Kamakura Corporation is a global financial software company headquartered in Honolulu, Hawaii. It specializes in software and data for risk management for banking, insurance and investment businesses.
David Clay Heath was an American probabilist known for co-inventing the Heath–Jarrow–Morton framework to model the evolution of the interest rate curve.

Damir Filipović is a Swiss mathematician specializing in quantitative finance. He holds the Swissquote Chair in Quantitative Finance and is the director of the Swiss Finance Institute at EPFL.


