
Embroidery is the art of decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to stitch thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. In modern days, embroidery is usually seen on hats, clothing, blankets, and handbags. Embroidery is available in a wide variety of thread or yarn colour. It is often used to personalize gifts or clothing items.

A needlework sampler is a piece of embroidery or cross-stitching produced as a 'specimen of achievement', demonstration or a test of skill in needlework. It often includes the alphabet, figures, motifs, decorative borders and sometimes the name of the person who embroidered it and the date. The word sampler is derived from the Latin exemplum, which means 'example'.

Hardanger embroidery or "Hardangersøm" is a form of embroidery traditionally worked with white thread on white even-weave linen or cloth, using counted thread and drawn thread work techniques. It is sometimes called whitework embroidery.

Appliqué is ornamental needlework in which pieces or patches of fabric in different shapes and patterns are sewn or stuck onto a larger piece to form a picture or pattern. It is commonly used as decoration, especially on garments. The technique is accomplished either by hand stitching or machine. Appliqué is commonly practised with textiles, but the term may be applied to similar techniques used on different materials. In the context of ceramics, for example, an appliqué is a separate piece of clay added to the primary work, generally for the purpose of decoration.

Chain stitch is a sewing and embroidery technique in which a series of looped stitches form a chain-like pattern. Chain stitch is an ancient craft – examples of surviving Chinese chain stitch embroidery worked in silk thread have been dated to the Warring States period. Handmade chain stitch embroidery does not require that the needle pass through more than one layer of fabric. For this reason the stitch is an effective surface embellishment near seams on finished fabric. Because chain stitches can form flowing, curved lines, they are used in many surface embroidery styles that mimic "drawing" in thread.

Machine embroidery is an embroidery process whereby a sewing machine or embroidery machine is used to create patterns on textiles. It is used commercially in product branding, corporate advertising, and uniform adornment. It is also used in the fashion industry to decorate garments and apparel. Machine embroidery is used by hobbyists and crafters to decorate gifts, clothing, and home decor. Examples include designs on quilts, pillows, and wall hangings.

A shawl is a simple item of clothing, loosely worn over the shoulders, upper body and arms, and sometimes also over the head. It is usually a rectangular piece of cloth, but can also be square or triangular in shape. Other shapes include oblong shawls. It is associated with the inhabitants of the northern Indian subcontinent—particularly Kashmir and Punjab—and Central Asia, but can be found in many other parts of the world.
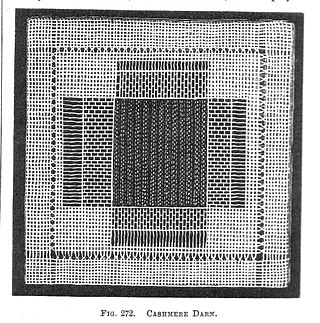
Darning is a sewing technique for repairing holes or worn areas in fabric or knitting using needle and thread alone. It is often done by hand, but using a sewing machine is also possible. Hand darning employs the darning stitch, a simple running stitch in which the thread is "woven" in rows along the grain of the fabric, with the stitcher reversing direction at the end of each row, and then filling in the framework thus created, as if weaving. Darning is a traditional method for repairing fabric damage or holes that do not run along a seam, and where patching is impractical or would create discomfort for the wearer, such as on the heel of a sock.

Stumpwork or raised work is a style of embroidery in which the stitched figures are raised from the surface of the work to form a 3-dimensional effect.

Armenian needlelace is a pure form of needle lace made using only a needle, thread and pair of scissors.

Broderie anglaise is a whitework needlework technique incorporating features of embroidery, cutwork and needle lace that became associated with England, due to its popularity there in the 19th century.

Whitework embroidery is any embroidery technique in which the stitch and the foundation fabric are of same color. Styles of whitework embroidery include most drawn thread work, broderie anglaise, Hardanger embroidery, Hedebo embroidery, Mountmellick embroidery, reticella and Schwalm. Whitework embroidery is one of the techniques employed in heirloom sewing for blouses, christening gowns, baby bonnets, and other small articles.

Embroidery in India includes dozens of embroidery styles that vary by region and clothing styles. Designs in Indian embroidery are formed on the basis of the texture and the design of the fabric and the stitch. The dot and the alternate dot, the circle, the square, the triangle, and permutations and combinations of these constitute the design.

Cutwork or cut work, also known as punto tagliato in Italian, is a needlework technique in which portions of a textile, typically cotton or linen, are cut away and the resulting "hole" is reinforced and filled with embroidery or needle lace.

An embroidered patch, also known as a cloth badge, is a piece of embroidery which is created by using a fabric backing and thread. The art of making embroidered patches is an old tradition and was done by hand. During the first half of the twentieth century they were commonly embroidered using a shiffli embroidery machine. High-speed, computerized machines have led to mass production.

English embroidery includes embroidery worked in England or by English people abroad from Anglo-Saxon times to the present day. The oldest surviving English embroideries include items from the early 10th century preserved in Durham Cathedral and the 11th century Bayeux Tapestry, if it was worked in England. The professional workshops of Medieval England created rich embroidery in metal thread and silk for ecclesiastical and secular uses. This style was called Opus Anglicanum or "English work", and was famous throughout Europe.

Croatian national costume, also called as Croatian traditional clothing or Croatian dress, refers to the traditional clothing worn by Croats living in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, with smaller communities in Hungary, Austria, Montenegro, and Romania. Since today Croats wear Western-style clothing on a daily basis, the national costumes are most often worn with connection to special events and celebrations, mostly at ethnic festivals, religious holidays, weddings, and by dancing groups who dance the traditional Croatian kolo, or circle dance.

Cieszyn folk costume, also known as Valachian, is a Silesian folk costume, which used to be worn within majority of the area of Cieszyn Silesia, but mostly by Cieszyn Vlachs. Taking into consideration ornamentation, cutting and materials, it can be observed that it is a replica of historical costumes of the Renaissance. The male folk costume was worn only to the late 19th century, whereas the female folk costume was more popular and spread in the vicinity of the Wisła, Istebna and Koniaków. Previously in this area the costumes of Silesian Gorals prevailed. Female folk costumes in Cieszyn were subjected to many changes, especially in respect to ornamentations and better quality of materials. Due to its richness and elegance the costume quickly became a target of artists and specialists in folk culture.

The term Hedebo embroidery covers several forms of white embroidery which originated in the Hedebo (heathland) region of Zealand, Denmark, in the 1760s. The varied techniques which evolved over the next hundred years in the farming community were subsequently developed by the middle classes until around 1820. They were applied to articles of clothing such as collars and cuffs but were also used to decorate bed linen.

The schiffli embroidery machine is a multi-needle, industrial embroidery machine. It was invented by Isaak Gröbli in 1863. It was used to create various types of machine embroidery and certain types of lace. It was especially used in the textile industry of eastern Switzerland and Saxony Germany, but also in the United Kingdom and the United States. Schiffli machines evolved from, and eventually replaced manually operated "hand embroidery" machines. The hand embroidery machine used double ended needles and passed the needles completely through the fabric. Each needle had a single, continuous thread. Whereas the schiffli machine used a lock stitch, the same technique used by the sewing machine. By the early twentieth century schiffli machines had standardized to ten and fifteen meters in width and used more than 600 needles.




















