
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid, which in turn runs through steam turbines. These either drive a ship's propellers or turn electrical generators' shafts. Nuclear generated steam in principle can be used for industrial process heat or for district heating. Some reactors are used to produce isotopes for medical and industrial use, or for production of weapons-grade plutonium. As of 2022, the International Atomic Energy Agency reports there are 422 nuclear power reactors and 223 nuclear research reactors in operation around the world.

Argonne National Laboratory is a federally funded research and development center in Lemont, Illinois, United States. Founded in 1946, the laboratory is owned by the United States Department of Energy and administered by UChicago Argonne LLC of the University of Chicago. The facility is the largest national laboratory in the Midwest.

A breeder reactor is a nuclear reactor that generates more fissile material than it consumes. These reactors can be fueled with more-commonly available isotopes of uranium and thorium, such as uranium-238 and thorium-232, as opposed to the rare uranium-235 which is used in conventional reactors. These materials are called fertile materials since they can be bred into fuel by these breeder reactors.

Experimental Breeder Reactor I (EBR-I) is a decommissioned research reactor and U.S. National Historic Landmark located in the desert about 18 miles (29 km) southeast of Arco, Idaho. It was the world's first breeder reactor. At 1:50 p.m. on December 20, 1951, it became one of the world's first electricity-generating nuclear power plants when it produced sufficient electricity to illuminate four 200-watt light bulbs. EBR-I subsequently generated sufficient electricity to power its building, and continued to be used for experimental purposes until it was decommissioned in 1964. The museum is open for visitors from late May until early September.
Atomic Energy of Canada Limited (AECL) is a Canadian federal Crown corporation and Canada's largest nuclear science and technology laboratory. AECL developed the CANDU reactor technology starting in the 1950s, and in October 2011 licensed this technology to Candu Energy.

Chicago Pile-1 (CP-1) was the world's first artificial nuclear reactor. On 2 December 1942, the first human-made self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction was initiated in CP-1 during an experiment led by Enrico Fermi. The secret development of the reactor was the first major technical achievement for the Manhattan Project, the Allied effort to create nuclear weapons during World War II. Developed by the Metallurgical Laboratory at the University of Chicago, CP-1 was built under the west viewing stands of the original Stagg Field. Although the project's civilian and military leaders had misgivings about the possibility of a disastrous runaway reaction, they trusted Fermi's safety calculations and decided they could carry out the experiment in a densely populated area. Fermi described the reactor as "a crude pile of black bricks and wooden timbers".

The integral fast reactor is a design for a nuclear reactor using fast neutrons and no neutron moderator. IFR would breed more fuel and is distinguished by a nuclear fuel cycle that uses reprocessing via electrorefining at the reactor site.
MOATA was a 100 kW thermal Argonaut class reactor built at the Australian Atomic Energy Commission Research Establishment at Lucas Heights, Sydney. MOATA went critical at 5:50am on 10 April 1961 and ended operations on 31 May 1995. MOATA was the first reactor to be decommissioned in Australia in 2009.

The Metallurgical Laboratory was a scientific laboratory at the University of Chicago that was established in February 1942 to study and use the newly discovered chemical element plutonium. It researched plutonium's chemistry and metallurgy, designed the world's first nuclear reactors to produce it, and developed chemical processes to separate it from other elements. In August 1942 the lab's chemical section was the first to chemically separate a weighable sample of plutonium, and on 2 December 1942, the Met Lab produced the first controlled nuclear chain reaction, in the reactor Chicago Pile-1, which was constructed under the stands of the university's old football stadium, Stagg Field.

Research reactors are nuclear fission-based nuclear reactors that serve primarily as a neutron source. They are also called non-power reactors, in contrast to power reactors that are used for electricity production, heat generation, or maritime propulsion.

Site A was a research facility near Chicago where, during World War II, research on behalf of the Manhattan Project was carried out. Operated by the University of Chicago's Metallurgical Laboratory, it was the site of Chicago Pile-2, a reconstructed and enlarged version of the world's first nuclear reactor, Chicago Pile-1. The first heavy-water reactor, Chicago Pile-3, was also constructed at this site. Research was carried out under contract to the United States' Office of Scientific Research and Development. After the war, the site became the first home of Argonne National Laboratory, a federally funded research and development center.
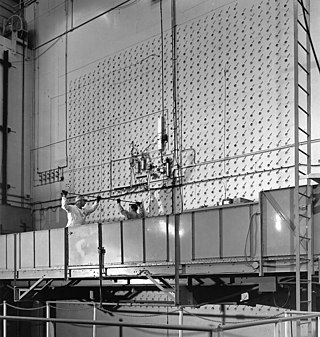
The X-10 Graphite Reactor is a decommissioned nuclear reactor at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. Formerly known as the Clinton Pile and X-10 Pile, it was the world's second artificial nuclear reactor, and the first designed and built for continuous operation. It was built during World War II as part of the Manhattan Project.

Walter Henry Zinn was a Canadian-born American nuclear physicist who was the first director of the Argonne National Laboratory from 1946 to 1956. He worked at the Manhattan Project's Metallurgical Laboratory during World War II, and supervised the construction of Chicago Pile-1, the world's first nuclear reactor, which went critical on December 2, 1942, at the University of Chicago. At Argonne he designed and built several new reactors, including Experimental Breeder Reactor I, the first nuclear reactor to produce electric power, which went live on December 20, 1951.

Chicago Pile-3 (CP-3) was the world's first heavy water reactor. One of the first research reactors, it was constructed in 1943 at Site A, a research facility around ten miles outside the city of Chicago. Joining CP-1/CP-2, it first went critical on 15 May 1944, and was at first used in the experimental physics work of the Metallurgical Laboratory for the Manhattan Project. After its useful research-life ended, it was deactivated in 1954.

Ernest Omar Wollan was an American physicist who made major contributions in the fields of neutron scattering and health physics.

FiR 1 was Finland's first nuclear reactor. It was a research reactor that was located in the Otaniemi campus area in the city of Espoo. The TRIGA Mark II reactor had a thermal power of 250 kilowatts. It started operation in 1962, and it was permanently shut down in 2015. At first, the reactor was operated by Helsinki University of Technology (TKK), and since 1971 by VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland.
Brookhaven Graphite Research Reactor (BGRR) was a research reactor located at Brookhaven National Laboratory, a United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Upton, New York, on Long Island, approximately 60 miles east of New York City. The BGRR operated from 1950 until 1968 and has been fully decommissioned.
High Flux Beam Reactor (HFBR) was a research reactor which was located at Brookhaven National Laboratory, a United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Upton, New York, on Long Island, approximately 60 miles east of New York City. A successor to the Brookhaven Graphite Research Reactor, the HFBR operated from 1965 until 1996 and has been partially decommissioned.















