External links
- ICTVdB - The Universal Virus Database: Chickpea distortion mosaic virus
- Family Groups - The Baltimore Method
| Chickpea distortion mosaic virus | |
|---|---|
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group IV ((+)ssRNA) |
| Order: | Unassigned |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | Chickpea distortion mosaic virus |
Chickpea distortion mosaic virus is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Potyviridae.
Sequivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently three species in this genus including the type species Parsnip yellow fleck virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: PYFV: vein-yellowing, yellow flecks and yellow/green mosaic symptoms in parsnip, and ‘yellow net', followed by yellow spots and leaf distortion in celery.

Lettuce mosaic virus (LMV) is a typical potyvirus, which causes one of the major virus diseases of lettuce crops worldwide.

Potyvirus is a genus of viruses in the family Potyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 183 species in this genus including the type species Potato virus Y. The genus is named after the type virus. Potyviruses account for ~30% of the currently known plant viruses. Like begomoviruses, members of this genus may cause significant losses in agricultural, pastoral, horticultural and ornamental crops. More than 200 species of aphids spread potyviruses and most are from the subfamily Aphidinae.

Begomovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Geminiviridae. They are plant viruses that as a group have a very wide host range, infecting dicotyledonous plants. Worldwide they are responsible for a considerable amount of economic damage to many important crops such as tomatoes, beans, squash, cassava and cotton. There are currently 424 species in this genus including the type species Bean golden yellow mosaic virus.
Tombusvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Tombusviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 17 species in this genus including the type species Tomato bushy stunt virus. Symptoms associated with this genus include mosaic. The name of the genus comes from the type species: Tomato bushy stunt virus.
Beet distortion mosaic virus is a plant pathogenic virus.

Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) is a plant pathogenic virus in the family Bromoviridae. It is the type member of the plant virus genus, Cucumovirus. This virus has a worldwide distribution and a very wide host range. In fact it has the reputation of having the widest host range of any known plant virus. It can be transmitted from plant to plant both mechanically by sap and by aphids in a stylet-borne fashion. It can also be transmitted in seeds and by the parasitic weeds, Cuscuta sp. (dodder).
Pea enation mosaic virus (PEMV) is a plant pathogenic virus.

Tomato mosaic virus (ToMV) is a plant pathogenic virus. It is found worldwide and affects tomatoes and many other plants.
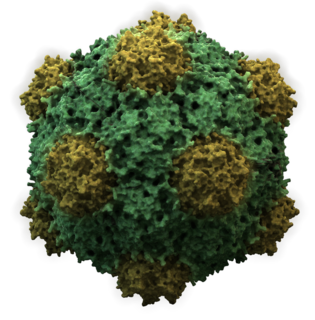
Secoviridae is a family of viruses in the order Picornavirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 86 species in this family, divided among 8 genera or not assigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of families Sequiviridae, now dissolved, and Comoviridae, now subfamily Comovirinae, along with the then unassigned genera Cheravirus, Sadwavirus, and Torradovirus.
Commelina mosaic virus (CoMV) is a plant pathogenic virus in the genus Potyvirus and the virus family Potyviridae. Like other members of the Potyvirus genus, CoMV is a monopartite strand of positive-sense, single-stranded RNA surrounded by a capsid made for a single viral encoded protein. The virus is a filamentous particle that measures about 707-808 nm in length. This virus is transmitted by two species of aphids, Myzus persicae and Aphis gossypii, and by mechanical inoculation.

Watermelon mosaic virus (WMV) also known as Marrow mosaic virus, Melon mosaic virus, and until recently Watermelon mosaic virus type 2 (WMV-2), is a plant pathogenic virus that causes viral infection in many different plants. First described on squash in Florida, WMV arose from a unique recombination of genetic material contributed by Soybean mosaic virus (SMV) and Bean common mosaic virus (BCMV) along with Peanut Stripe virus (PSV).

Squash mosaic virus (SqMV) is a mosaic virus disease common in squash plants and other plants, including melons, of the family Cucurbitaceae. It occurs worldwide. It is transmitted primarily by beetles, including the leaf beetle, spotted cucumber beetle, and 28-spotted ladybird beetle, as well as some other beetles. Plants are infected by the saliva expelled by the beetles as they feed upon the plant. The beetles acquire the virus by feeding upon an infected plant and can retain the virus in their bodies for up to 20 days. Unlike some other mosaic viruses that infect squashes, SqMV is not spread by aphids. In melons it can be spread by seeds. The results are dark green mosaic, blistering, vein clearing, yellowing of leaves, and hardening. Symptoms include "pronounced chlorotic mottle, green veinbanding, and distortion of leaves". Fruits of infected plants are also affected, becoming mottled and misshaped. There are two strains of this virus: strain 1 has a greater effect on melons than squash while the opposite is true of strain 2.

Aphis craccivora, variously known as the cowpea aphid, groundnut aphid or black legume aphid, is a true bug in the family Aphididae. Originally of probable Palearctic origin, it is now an invasive species of cosmopolitan distribution.

Caulimovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 13 species in this genus including the type species Cauliflower mosaic virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: vein-clearing or banding mosaic.
Mastrevirus is a genus of ssDNA viruses, in the family Geminiviridae. Mostly monocotyledonous plants serve as natural hosts. They are vectored by planthoppers. There are currently 41 species in this genus including the type species Maize streak virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: maize streak virus: maize streak disease (MSD).
Polerovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Luteoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 26 species in this genus including the type species Potato leafroll virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: PLRV causes prominent rolling of the leaves of potato and a stiff upright habit of the plants; necrosis of the phloem and accumulation of carbohydrates in the leaves.
Debasis Chattopadhyay is an Indian plant molecular biologist, geneticist and a scientist at the National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR). Known for his studies in the fields of plant stress biology and genomics, Chattopadhyay is an elected fellow of all the three major Indian science Academies namely the Indian Academy of Sciences, the Indian National Science Academy and the National Academy of Sciences, India. He is also an elected fellow of the West Bengal Academy of Science and Technology.