
The Chilean Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the Chilean Armed Forces. It is under the Ministry of National Defense. Its headquarters are at Edificio Armada de Chile, Valparaiso.

Suomen Joutsen is a steel-hulled full-rigged ship with three square rigged masts. Built in 1902 by Chantiers de Penhoët in St. Nazaire, France, as Laënnec, the ship served two French owners before she was sold to German interest in 1922 and renamed Oldenburg. In 1930, she was acquired by the Government of Finland, refitted to serve as a school ship for the Finnish Navy and given her current name. Suomen Joutsen made eight long international voyages before the Second World War and later served in various support and supply roles during the war. From 1961 on she served as a stationary seamen's school for the Finnish Merchant Navy. In 1991, Suomen Joutsen was donated to the city of Turku and became a museum ship moored next to Forum Marinum.

Glenlee is a steel-hulled three-masted barque, built as a cargo ship at Port Glasgow under that name in 1896 for Glasgow owners. With later owners she was named Islamount and Clarastella. From 1922 she was the sail training ship Galatea in the Spanish Navy. Since 1993, carrying her original name, Glenlee has been a museum ship at the Riverside Museum on Pointhouse Quay, Glasgow, known as The Tall Ship at Glasgow Harbour.

O'Higgins was a Chilean frigate famous for her actions under Captain Lord Cochrane.

Juan Sebastián de Elcano is a training ship of the Spanish Navy. It is a four-masted topsail, steel-hulled barquentine. At 113 metres (371 ft) long, it is the third-largest tall ship in the world, and is the sailing vessel that has sailed the furthest, covering more than 2,000,000 nautical miles in its lifetime.

ARA Libertad (Q-2) is a steel-hulled, full-rigged, class "A" sailing ship that serves as a school vessel in the Argentine Navy. One of the largest and fastest tall ships in the world, holder of several speed records, she was designed and built in the 1950s by the Río Santiago Shipyard, Ensenada, Argentina. Her maiden voyage was in 1961, and she continues to be a training ship with yearly instruction trips for the graduating naval cadets as well as a traveling goodwill ambassador, having covered more than 800,000 nautical miles (1,500,000 km) across all seas, visited about 500 ports in more than 60 countries, and trained more than 11,000 navy graduates.

USS West Apaum (ID-3221) was a cargo ship in the United States Navy during World War I. She had been built as SS West Apaum for the United States Shipping Board (USSB) as part of the West boats, a series of steel-hulled cargo ships built on the West Coast of the United States.
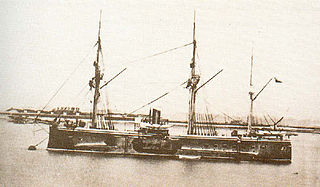
Blanco Encalada was a central battery ship built by Earle's Shipbuilding Co. in England for the Chilean Navy in 1875. She was nicknamed El Blanco. She participated actively in the War of the Pacific, her most important action being the capture of the Peruvian monitor Huáscar during the Battle of Angamos.

Dom Fernando II e Glória is a wooden-hulled, 50-gun frigate of the Portuguese Navy. She was launched in 1843 and made her maiden voyage in 1845. Built at the shipyard of Daman in Portuguese India, it was Portugal's last sailing warship to be built and also the last ship that undertook the Carreira da Índia, a regular military line that connected Portugal to its colonies in India since the beginning of the 16th century.

Esmeralda was a wooden-hulled steam corvette of the Chilean Navy, launched in 1855, and sunk by the Peruvian ironclad Huáscar on 21 May 1879 at the Battle of Iquique during the War of the Pacific.

The corvette Abtao was a wooden ship built in Scotland during 1864 of 1.600 tons and 800 IHP. She fought in the War of the Pacific and was in service for the Chilean Navy until 1922.

Lautaro was initially the British East Indiaman Windham, built by Perry, Wells & Green at the Blackwall Shipyard for the East India Company (EIC) and launched in 1800. She made seven voyages to India, Ceylon, and China for the EIC. In 1809–10, the French captured her twice, but the British also recaptured her twice. The Chilean Navy bought her in 1818 and she then served in the Chilean Navy, taking part in several actions during the liberation wars in Chile and Peru. From 1824 she was a training ship until she was sold in 1828.

The First Chilean Navy Squadron was the heterogeneous naval force that terminated Spanish colonial rule in the Pacific and protagonized the most important naval actions of in the Latin American wars of independence. The Chilean revolutionary government organized the squadron in order to carry the war to the Viceroyalty of Perú, then the center of Spanish power in South America, and thus secure the independence of Chile and Argentina.
Several ships of the Chilean Navy have been named Lautaro after Lautaro, a Mapuche leader during the War of Arauco.

ARA Veinticinco de Mayo was a protected cruiser that served in the Argentine Navy between 1891 and 1921.

ARA La Argentina was a steam corvette that served as a training ship with the Argentine Navy between 1884 and 1895, and in other roles until decommissioned in 1899.

Blas de Lezo (F-103) is a Spanish Navy guided missile frigate of the Álvaro de Bazán class. This is the third ship class of air defense frigates in the Spanish Navy. It was named after the 18th century Spanish Admiral Blas de Lezo. The ship was built by Izar Shipbuilding in Ferrol, Spain and entered into service in 2004.

Almirante Simpson was a unique design of torpedo gunboat, built by the British shipyard Laird Brothers. Acquired by the Chilean Navy in 1895, during construction. The ship had a brief service in Chile, being transferred to the Ecuadorian Navy in 1907 and renamed Libertador Bolívar. She was the first Ecuadorian warship of the 20th century and had an important participation in the Ecuadorian Civil War of 1913–1916. After the war, the ship was retired and then sank in 1928.

















