Related Research Articles

East Pakistan was the eastern polity, established in 1955 under the One Unit Policy, renaming and restructuring the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Burma, with a coastline on the Bay of Bengal. East Pakistanis were popularly known as "Pakistani Bengalis"; to distinguish this region from India's state West Bengal, East Pakistan was known as "Pakistani Bengal". In 1971, East Pakistan became the newly independent state Bangladesh, which means "country of Bengal" or "country of Bengalis" in Bengali language.

Karachi is the capital city of the Pakistani province of Sindh. It is the largest city in Pakistan and 12th largest in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast and formerly served as the capital of Pakistan. Ranked as a beta-global city, it is Pakistan's premier industrial and financial centre, with an estimated GDP of over $200 billion (PPP) as of 2021. Karachi is Pakistan's most cosmopolitan city, linguistically, ethnically, and religiously diverse cities, as well as one of the most socially liberal.

Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of 241.5 million people, and has the world's largest Muslim population as of 2023. Islamabad is the nation's capital, while Karachi is its largest city and financial centre, followed by Lahore and Faisalabad. Pakistan is the 33rd-largest country in the world by area and the second largest in South Asia, spanning 881,913 square kilometres. It has a 1,046-kilometre (650-mile) coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south, and is bordered by India to the east, Afghanistan to the west, Iran to the southwest, and China to the northeast. It is separated from Tajikistan by Afghanistan's narrow Wakhan Corridor in the north, and also shares a maritime border with Oman.

The Taliban, which also refers to itself by its state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a militant Pashtun nationalist organization in Afghanistan with close ties to Deobandi Islamic fundamentalism. It ruled approximately three-quarters of the country from 1996 to 2001, before being overthrown following the American invasion. It recaptured Kabul on 15 August 2021 following the departure of most coalition forces, after nearly 20 years of insurgency, and currently controls all of the country. However, its government is not recognized by any country. The Taliban government has been internationally condemned for restricting human rights in Afghanistan, including the right of women and girls to work and to have an education.

The 1999 ICC Cricket World Cup, also branded as England '99, was the seventh edition of the Cricket World Cup, organised by the International Cricket Council (ICC). It was hosted primarily by England, with selected matches also played in Scotland, Ireland, Wales and the Netherlands. The tournament was won by Australia, who beat Pakistan by 8 wickets in the final at Lord's in London.

The Partition of India in 1947 was the change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in the Indian subcontinent and the creation of two independent dominions in South Asia: India and Pakistan. The Dominion of India is today the Republic of India, and the Dominion of Pakistan—which at the time comprised two regions lying on either side of India—is now the Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The partition was outlined in the Indian Independence Act 1947. The change of political borders notably included the division of two provinces of British India, Bengal and Punjab. The majority Muslim districts in these provinces were awarded to Pakistan and the majority non-Muslim to India. The other assets that were divided included the British Indian Army, the Royal Indian Navy, the Royal Indian Air Force, the Indian Civil Service, the railways, and the central treasury. Provisions for self-governing independent Pakistan and India legally came into existence at midnight on 14 and 15 August 1947 respectively.

The Pakistan Air Force (PAF) is the aerial warfare branch of the Pakistan Armed Forces, tasked primarily with the aerial defence of Pakistan, with a secondary role of providing air support to the Pakistan Army and Navy when required, and a tertiary role of providing strategic airlift capability to Pakistan. As of 2021, as per the International Institute for Strategic Studies, the PAF has more than 70,000 active-duty personnel and operates at least 1370+ aircraft.PAF stands as the eight largest Air Force in the world while holds the title of being largest Air Force of the Muslim World in terms of aircraft fleet. Its primary mandate and mission is "to provide, in synergy with other inter-services, the most efficient, assured and cost effective aerial defence of Pakistan." Since its establishment in 1947, the PAF has been involved in various combat operations, providing aerial support to the operations and relief efforts of the Pakistani military. Under Article 243, the Constitution of Pakistan appoints the President of Pakistan as the civilian Commander-in-Chief of the Pakistan Armed Forces. The Chief of the Air Staff (CAS), by statute a four-star air officer, is appointed by the President with the consultation and confirmation needed from the Prime Minister of Pakistan.

Zulfikar Ali Bhutto was a Pakistani barrister, politician and statesman who served as the fourth president of Pakistan from 1971 to 1973, and later as the ninth prime minister of Pakistan from 1973 to 1977. He was the founder of the Pakistan People's Party (PPP) and served as its chairman until his execution.

Imran Ahmad Khan Niazi is a Pakistani politician and former cricketer who served as the 22nd prime minister of Pakistan from August 2018 until April 2022. He is the founder and chairman of the political party Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI).

The Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, also known as the Third India–Pakistan War, was an armed conflict between India and Pakistan that occurred during the Bangladesh Liberation War in East Pakistan from 3 December 1971 to 16 December 1971.

The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965, also known as the Second India–Pakistan War, was an armed conflict between Pakistan and India that took place from August 1965 to September 1965. The conflict began following Pakistan's Operation Gibraltar, which was designed to infiltrate forces into Jammu and Kashmir to precipitate an insurgency against Indian rule. The seventeen-week war caused thousands of casualties on both sides and witnessed the largest engagement of armored vehicles and the largest tank battle since World War II. Hostilities between the two countries ended after a ceasefire was declared through UNSC Resolution 211 following a diplomatic intervention by the Soviet Union and the United States, and the subsequent issuance of the Tashkent Declaration. Much of the war was fought by the countries' land forces in Kashmir and along the border between India and Pakistan. This war saw the largest amassing of troops in Kashmir since the Partition of India in 1947, a number that was overshadowed only during the 2001–2002 military standoff between India and Pakistan. Most of the battles were fought by opposing infantry and armored units, with substantial backing from air forces, and naval operations.

The Bangladesh Liberation War was a revolution and armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalist and self-determination movement in East Pakistan, which resulted in the independence of Bangladesh. The war began when the Pakistani military junta based in West Pakistan—under the orders of Yahya Khan—launched Operation Searchlight against the people of East Pakistan on the night of 25 March 1971, initiating the Bangladesh genocide.

The Pakistan national cricket team, has represented Pakistan in international cricket since 1952. It is controlled by the Pakistan Cricket Board (PCB), the governing body for cricket in Pakistan, which is a Full Member of the International Cricket Council (ICC). Pakistan compete in cricket tours and tournaments sanctioned by the PCB and other regional or international cricket bodies in Test, One Day International (ODI), and Twenty20 International (T20) formats.

The ICC Champions Trophy is a One-Day International (ODI) cricket tournament organised by the International Cricket Council or ICC. Inaugurated in 1998, The ICC conceived the idea of the Champions Trophy – a short cricket tournament to raise funds for the development of the game in non-test playing countries. It remains as one of those ICC events that had the same format as that of another big cricketing event, like the Cricket World Cup, with the format being One Day Internationals.
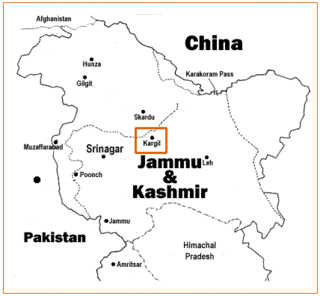
The Kargil War, also known as the Kargil conflict, was fought between India and Pakistan from May to July 1999 in the Kargil district of Jammu and Kashmir and elsewhere along the Line of Control (LoC). In India, the conflict is also referred to as Operation Vijay, which was the codename of the Indian military operation in the region. The Indian Air Force acted jointly with the Indian Army to flush out the Pakistan Army and paramilitary troops from vacated Indian positions along the LoC, in what was designated as Operation Safed Sagar.

Field Marshal Sam Hormusji Framji Jamshedji Manekshaw, also known as Sam Bahadur, was the Chief of the Army Staff of the Indian Army during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, and the first Indian Army officer to be promoted to the rank of field marshal. His active military career spanned four decades and five wars, beginning with service in World War II.

The India–Pakistan cricket rivalry is one of the most intense sports rivalries in the world. The matches between these neighbouring countries are known for its intensity. It is considered as one of the biggest matches in the world, and is among the most-viewed sport games. It is often termed as the El Clásico of cricket.

The 2008 Mumbai attacks were a series of terrorist attacks that took place in November 2008, when 10 members of Lashkar-e-Taiba, a militant Islamist organisation from Pakistan, carried out 12 coordinated shooting and bombing attacks lasting four days across Mumbai. The attacks, which drew widespread global condemnation, began on Wednesday 26 November and lasted until Saturday 29 November 2008. A total of 175 people died, including nine of the attackers, with more than 300 injured.

Muhammad Ali Jinnah was a barrister, politician and the founder of Pakistan. Jinnah served as the leader of the All-India Muslim League from 1913 until the inception of Pakistan on 14 August 1947, and then as the Dominion of Pakistan's first governor-general until his death.

The 2023 ICC Men's Cricket World Cup is the 13th edition of the Cricket World Cup, a quadrennial One Day International (ODI) cricket tournament contested by men's national teams and organised by the International Cricket Council (ICC). The tournament is being hosted by India. It started on 5 October and is scheduled to conclude on 19 November 2023.
References
- ↑ Rensch, Calvin Ross (1992). Sociolinguistic Survey of Northern Pakistan: Languages of Kohistan. National Institute of Pakistan Studies, Quaid-i-Azam University.