This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Rheum nobile, the Noble rhubarb or Sikkim rhubarb or पदमचाल, is a giant herbaceous plant native to the Himalaya, from northeastern Afghanistan, east through northern Pakistan and India, Nepal, Sikkim, Bhutan, and Tibet to Myanmar, occurring in the alpine zone at 4000–4800 m altitude.

Rheum is a genus of about 60 herbaceous perennial plants in the family Polygonaceae. Species are native to eastern Europe, southern and eastern temperate Asia, with a few reaching into northern tropical Asia. Rheum is cultivated in Europe and North America. The genus includes the vegetable rhubarb. The species have large somewhat triangular shaped leaves with long, fleshy petioles. The flowers are small, greenish-white to rose-red, and grouped in large compound leafy inflorescences. A number of cultivars of rhubarb have been domesticated both as medicinal plants and for human consumption. While the leaves are toxic, the stalks are used in pies and other foods for their tart flavor.
Rhubarb is an herbaceous perennial plant in the genus Rheum cultivated as a vegetable.

In botany, the petiole is the stalk that attaches the leaf blade to the stem. Outgrowths appearing on each side of the petiole in some species are called stipules. Leaves lacking a petiole are called sessile or epetiolate.
Monk's rhubarb is not a rhubarb (Rheum), but refers to certain species of the closely related docks (Rumex):

Rheum palaestinum, the desert rhubarb, is a plant indigenous to Israel and Jordan with a highly developed system for gathering rainwater.
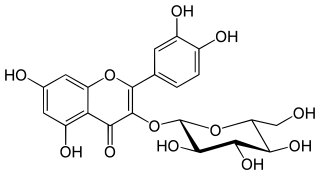
Isoquercetin, isoquercitrin or isotrifoliin is a flavonoid, a type of chemical compound. It is the 3-O-glucoside of quercetin. Isoquercitrin can be isolated from various plant species including Mangifera indica (mango) and Rheum nobile. It is also present in the leaves of Annona squamosa and Camellia sinensis (tea).
Rheum rhabarbarum is a species of flowering plant in the family Polygonaceae, native to southern Siberia to north and central China. It is considered to be one of the species involved in the development of culinary rhubarb, for which the scientific name R. rhabarbarum is sometimes used.

Lixus concavus, commonly called the rhubarb curculio, is a species of weevil. Rhubarb is a host, together with dock, sunflower, and thistle.

Rhein, also known as cassic acid, is a substance in the anthraquinone group obtained from rhubarb. Like all such substances, rhein is a cathartic. Rhein is commonly found as a glycoside such as rhein-8-glucoside or glucorhein. Rhein was first isolated in 1895. It is found in rhubarb species like Rheum undulatum and Rheum palmatum as well as in Cassia reticulata.
Rheum australe, synonym Rheum emodi, is a flowering plant in the family Polygonaceae. It commonly known as Himalayan rhubarb, and is a medicinal herb used in the Indian Unani system of medicine, and formerly in the European system of medicine where it was traded as Indian rhubarb. The plant is found in the sub-alpine and alpine Himalayas at an altitude of 4000 m.
Rheum maximowiczii is a plant species in the genus Rheum (rhubarbs).

Rheum ribes, the Syrian rhubarb or currant-fruited rhubarb, or warty-leaved rhubarb, is an edible wild rhubarb species in the genus Rheum. It grows between 1000 and 4000 m on dunite rocks, among stones and slopes, and is now distributed in the temperate and subtropical regions of the world, chiefly in Western Asia to Afghanistan and Pakistan. The Syrian rhubarb a partially commercial vegetable collected from the nature in Eastern and Southern Anatolia, Northern Iraq and partly Northwestern Iran in early spring. Rheum ribes is considered as a valuable medicinal species in herbal medicine.

Rheum rhaponticum, the false rhubarb, rhapontic rhubarb or rhapontic, is a plant species in the genus Rheum found in the wild. It is the only Rheum species found only in Europe, and is now restricted to the Rila mountain range in south-western Bulgaria. It was introduced to other countries in Europe. It is considered to be one of the parents of the modern culinary rhubarb.
Desert rhubarb is a common name for several desert dwelling plants related to rhubarb and may refer to:
Rheum lhasaense is a plant belonging to the genus Rheum in family Polygonaceae.

Rheum webbianum is a species of herbaceous perennial plant in the family Polygonaceae.











