Demographics
The region is 25,947 km² and contains a population of over 150,000, which is 5% of Alberta's population. The population of Lethbridge makes up over half of the region's population.

Lethbridge is a city in the province of Alberta, Canada, and the largest city in southern Alberta. It is Alberta's fourth-largest city by population after Calgary, Edmonton and Red Deer, and the third-largest by land area after Calgary and Edmonton. The nearby Canadian Rockies contribute to the city's warm summers, mild winters, and windy climate. Lethbridge lies southeast of Calgary on the Oldman River.
Persons over the age of 65 years made up over 1/10 of the CHR population in 1998.
Approximately 10,000 Aboriginal people live in the region, most of whom are of the Blackfoot Nations. The number also includes some Cree, Métis, Inuit and other others.
The Cree are one of the largest groups of First Nations in North America.
The Inuit are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic regions of Greenland, Canada, and Alaska. The Inuit languages are part of the Eskimo–Aleut family. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut.
Additionally, roughly 15,000 Kanadier Mennonites live in the Chinook Health region. Numbers vary as groups migrate between home communities in Central America and the region.

Alberta's economy is the sum of all economic activity in Alberta, Canada's fourth largest province by population. Although Alberta has a presence in many industries such as agriculture, forestry, education, tourism, finance, and manufacturing, the politics and culture of the province have been closely tied to the production of fossil energy since the 1940s. Alberta—with an estimated 1.4 billion cubic metres of unconventional oil resource in the bituminous oil sands—leads Canada as an oil producer. Revenue from oil and natural gas extraction has fueled a series of economic booms in the province's recent history, and economic spin-offs have included petrochemical and pipelines. In 1985 36.1% of Alberta's $66.8 billion GDP was from energy industries. In 2012, "the mining and oil and gas extraction industry made up 23.3% of Alberta's GDP." By 2013 Alberta's GDP was $331.9 billion with 24.6% in energy. The energy industry provided 7.7% of all jobs in Alberta in 2013.
A dietitian is an expert in dietetics; that is, human nutrition and the regulation of diet. A dietitian alters their patient's nutrition based upon their medical condition and individual needs. Dietitians are regulated healthcare professionals licensed to assess, diagnose, and treat nutritional problems.

Healthcare in Canada is delivered through thirteen provincial and territorial systems of publicly funded health care, informally called Medicare. It is guided by the provisions of the Canada Health Act of 1984.

The University of Lethbridge is a publicly funded comprehensive academic and research university, founded in the liberal education tradition, located in Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada, with a second campus in the city of Calgary, Alberta. The main building, University Hall, sits among the coulees on the west side of the Oldman River.

A paramedic is a healthcare professional, providing pre-hospital assessment and medical care to people with acute illnesses or injuries. In Canada, the title paramedic generally refers to those who work on land ambulances or air ambulances providing paramedic services. Paramedics are increasingly being utilized in emergency rooms by providing patient care in collaboration with physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, registered nurses, registered practical nurses and registered respiratory therapists. Increasingly in Canada, paramedics are actively pursuing self-regulation.

Foothills Medical Centre (FMC) is the largest hospital in Alberta and is located in the city of Calgary. It is one of Canada's most recognized medical facilities as well as one of the leading hospitals in Canada, providing advanced healthcare services to over two million people from Calgary, southern Alberta, southeastern British Columbia and southern Saskatchewan. Formerly operated by the Calgary Health Region, it is now under the authority of Alberta Health Services and part of the University of Calgary Medical Centre.

Claresholm is a town located within southern Alberta, Canada. It is located on Highway 2, approximately 91 km (57 mi) northwest of the City of Lethbridge and 125 km (78 mi) south of the City of Calgary.
Chinook Regional Hospital is the main hospital for the City of Lethbridge and Southern Alberta, and offers many of the health care services for Alberta Health Services. The hospital services a population of over 150,000 and is supported by the Chinook Regional Hospital Foundation.
Allan P. Markin, OC, AOE was the chairman of Canadian Natural Resources Limited and is a co-owner of the Calgary Flames ice hockey franchise of the National Hockey League based in Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
Capital Health was a public health authority providing complete health services to Edmonton, Alberta's capital city, and its surrounding central Alberta communities. It was also the largest single employer in the province of Alberta, employing approximately 30,000 people. In 2008 it was merged into Alberta Health Services.
Welsh Canadians are Canadian citizens of Welsh descent or Wales-born people who reside in Canada.
The economy of Lethbridge is central to the commercial, distribution, financial and industrial sectors of the southern Alberta economy. Lethbridge has a trading area population of 250,000. The city was founded in 1885 as a result of local coal mining and later was buoyed by local farming and ranching. Toward the end of the twentieth century, the local economy started diversifying by focusing more on service-based industries.
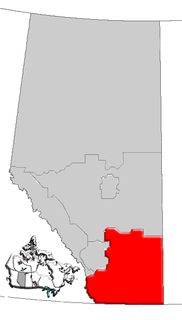
Southern Alberta is a region located in the Canadian province of Alberta. In 2004, the region's population was approximately 272,017. The primary cities are Lethbridge and Medicine Hat. The region is known mostly for agricultural production, but other sectors, such as alternative energy, film production and tourism, are emerging.

The Lethbridge Public Library is a public library service that is provided by the municipality of Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada. It was established in 1919. While it has had as many as three branches at one time, the library currently has two branches.

Calgary is a city in the Canadian province of Alberta. It is situated at the confluence of the Bow River and the Elbow River in the south of the province, in an area of foothills and prairie, about 80 km (50 mi) east of the front ranges of the Canadian Rockies. The city anchors the south end of what Statistics Canada defines as the "Calgary–Edmonton Corridor".
Morocco became an independent country in 1956. At that time there were only 400 private practitioners and 300 public health physicians in the entire country. By 1992, the government had thoroughly improved their health care service and quality. Health care was made available to over 70% of the population. Programs and courses to teach health and hygiene have been introduced to inform parents and children on how to correctly care for their own and their families' health.
The Good Samaritan Society is a Canadian Lutheran Social Service Organization that has 60 years of experience in providing continuing care, assisted living and other health and community care services. It is one of the largest not-for-profit, voluntary care providers in Alberta and British Columbia.












