Chlorobenzoic acid may refer to:
Chlorobenzoic acid may refer to:
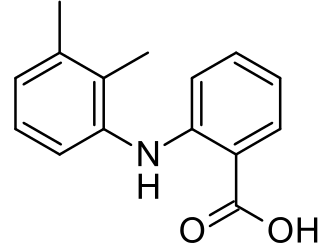
Mefenamic acid is a member of the anthranilic acid derivatives class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and is used to treat mild to moderate pain.
meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid is a peroxycarboxylic acid. It is a white solid often used widely as an oxidant in organic synthesis. mCPBA is often preferred to other peroxy acids because of its relative ease of handling. mCPBA is a strong oxidizing agent that may cause fire upon contact with flammable material.
Coumaric acid is a phenolic derivative of cinnamic acid having a hydroxy group as substituent at one of the aromatic positions:
Linolenic acid is a type of naturally-occurring fatty acid. It can refer to either of two octadecatrienoic acids, or a mixture of the two. Linolenate is often found in vegetable oils; traditionally, such fatty acylates are reported as the fatty acids:
Aminobenzoic acid (a benzoic acid with an amino group) can refer to:

Thiethylperazine (Torecan, Norzine) is an antiemetic of the phenothiazine class. It is an antagonist of dopamine receptors (DRD1, DRD2, DRD4) as well as of 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C receptors, mAChRs (1 through 5), α1 adrenergic receptor and H1 receptor.
Monohydroxybenzoic acid may refer to any of three isomeric phenolic acids:
Dihydroxybenzoic acids (DHBA) are a type of phenolic acids.
Aminosalicylic acid can refer to any amino derivative of salicylic acid, such as:
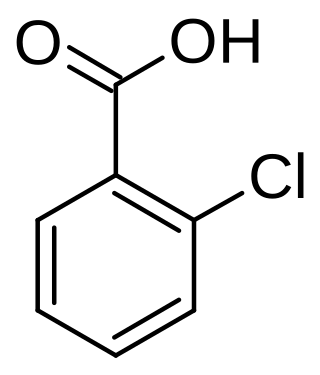
2-Chlorobenzoic acid is an organic compound with the formula ClC6H4CO2H. It is one of three isomeric chlorobenzoic acids, the one that is the strongest acid. This white solid is used as a precursor to a variety of drugs, food additives, and dyes.
The molecular formula C7H5ClO2 (molar mass: 156.57 g/mol, exact mass: 155.9978 u) may refer to:
Trihydroxybenzoic acid may refer to the following phenolic acids:

3-Hydroxybenzoic acid is a monohydroxybenzoic acid.
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid.

2-Fluorobenzoic acid is an aromatic organic compound with the formula FC6H4CO2H. It is one of three isomeric fluorobenzoic acids. Its conjugate base is 2-fluorobenzoate. The compound is an irritant.

3-Chlorobenzoic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula ClC6H4CO2H. It is a white solid that is soluble in some organic solvents and in aqueous base.

2-Diphenylphosphinobenzoic acid is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PC6H4CO2H. It is a white solid that dissolves in polar organic solvents. The ligand is a component of catalysts used for the Shell higher olefin process. It is prepared by the reaction of sodium diphenylphosphide with the sodium salt of 2-chlorobenzoic acid.
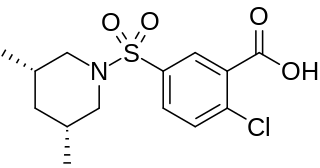
Tibric acid is a sulfamylbenzoic acid that acts as a hypolipidemic agent. Although it was found to be more powerful than clofibrate in lowering lipid levels, it was found to cause liver cancer in mice and rats, and so was not introduced as a human drug. In rats it causes an increase in peroxisomes, and liver enlargement, and then liver cancer. However the peroxisome changes do not occur in humans, and it is not likely to cause liver cancer in humans.
The hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor (abbreviated HCA receptor and HCAR) family includes the following human proteins:

4-Chlorobenzoic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula ClC6H4CO2H. It is a white solid that is soluble in some organic solvents and in aqueous base. 4-Chlorobenzoic acid is prepared by oxidation of 4-chlorotoluene.