
Benzoic acid is a white solid organic compound with the formula C6H5COOH, whose structure consists of a benzene ring with a carboxyl substituent. The benzoyl group is often abbreviated "Bz", thus benzoic acid is also denoted as BzOH, since the benzoyl group has the formula –C6H5CO. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, which was for a long time its only source.

In chemistry, an ester is a functional group derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.

Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as halides of carbon without carbon-hydrogen and carbon-carbon bonds, and certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen.
An organic acid is an organic compound with acidic properties. The most common organic acids are the carboxylic acids, whose acidity is associated with their carboxyl group –COOH. Sulfonic acids, containing the group –SO2OH, are relatively stronger acids. Alcohols, with –OH, can act as acids but they are usually very weak. The relative stability of the conjugate base of the acid determines its acidity. Other groups can also confer acidity, usually weakly: the thiol group –SH, the enol group, and the phenol group. In biological systems, organic compounds containing these groups are generally referred to as organic acids.

In organic chemistry, sulfonic acid refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula R−S(=O)2−OH, where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the S(=O)2(OH) group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is known as a sulfo group. A sulfonic acid can be thought of as sulfuric acid with one hydroxyl group replaced by an organic substituent. The parent compound is the parent sulfonic acid, HS(=O)2(OH), a tautomer of sulfurous acid, S(=O)(OH)2. Salts or esters of sulfonic acids are called sulfonates.
meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid is a peroxycarboxylic acid. It is a white solid often used widely as an oxidant in organic synthesis. mCPBA is often preferred to other peroxy acids because of its relative ease of handling. mCPBA is a strong oxidizing agent that may cause fire upon contact with flammable material.
The Ullmann condensation or Ullmann-type reaction is the copper-promoted conversion of aryl halides to aryl ethers, aryl thioethers, aryl nitriles, and aryl amines. These reactions are examples of cross-coupling reactions.

Thiethylperazine (Torecan, Norzine) is an antiemetic of the phenothiazine class. It is an antagonist of dopamine receptors (DRD1, DRD2, DRD4) as well as of 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C receptors, mAChRs (1 through 5), α1 adrenergic receptor and H1 receptor.
In chemical nomenclature, a preferred IUPAC name (PIN) is a unique name, assigned to a chemical substance and preferred among all possible names generated by IUPAC nomenclature. The "preferred IUPAC nomenclature" provides a set of rules for choosing between multiple possibilities in situations where it is important to decide on a unique name. It is intended for use in legal and regulatory situations.

Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid, is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH. Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. It has been used, as a component of vinegar, throughout history from at least the third century BC. Acetic acid is also known as acetyl hydroxide (AcOH).
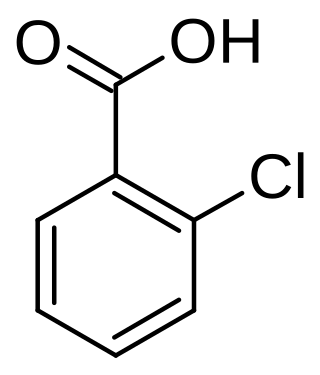
2-Chlorobenzoic acid is an organic compound with the formula ClC6H4CO2H. It is one of three isomeric chlorobenzoic acids, the one that is the strongest acid. This white solid is used as a precursor to a variety of drugs, food additives, and dyes.
The molecular formula C7H5ClO2 (molar mass: 156.57 g/mol, exact mass: 155.9978 u) may refer to:

3-Hydroxybenzoic acid is a monohydroxybenzoic acid.
Chlorobenzoic acid may refer to:
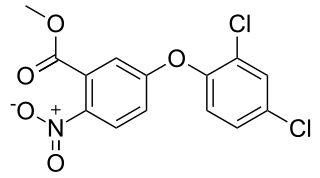
Bifenox is the ISO common name for an organic compound used as an herbicide. It acts by inhibiting the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase which is necessary for chlorophyll synthesis.

2-Fluorobenzoic acid is an aromatic organic compound with the formula FC6H4CO2H. It is one of three isomeric fluorobenzoic acids. Its conjugate base is 2-fluorobenzoate. The compound is an irritant.

3-Chlorobenzoic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula ClC6H4CO2H. It is a white solid that is soluble in some organic solvents and in aqueous base.

2-Diphenylphosphinobenzoic acid is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PC6H4CO2H. It is a white solid that dissolves in polar organic solvents. The ligand is a component of catalysts used for the Shell higher olefin process. It is prepared by the reaction of sodium diphenylphosphide with the sodium salt of 2-chlorobenzoic acid.
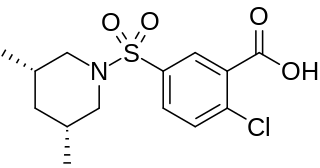
Tibric acid is a sulfamylbenzoic acid that acts as a hypolipidemic agent. Although it was found to be more powerful than clofibrate in lowering lipid levels, it was found to cause liver cancer in mice and rats, and so was not introduced as a human drug. In rats it causes an increase in peroxisomes, and liver enlargement, and then liver cancer. However the peroxisome changes do not occur in humans, and it is not likely to cause liver cancer in humans.
4-Chlorobenzaldehyde is an organic compound with the chemical formula C7H5ClO. It can be produced by the oxidation of 4-chlorobenzyl alcohol. It can be further oxidized to 4-chlorobenzoic acid. It will react with malononitrile to form 4-chlorobenzylidenylmalononitrile. 4-Chlorobenzaldehyde reacts with benzylamine to produce N-(4-chlorobenzylidenyl)benzylamine。
















