
The Comoros, officially the Union of the Comoros, is an island country in the Indian Ocean located at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel off the eastern coast of Africa between northeastern Mozambique, the French region of Mayotte, and northwestern Madagascar. The capital and largest city in Comoros is Moroni. The religion of the majority of the population is Sunni Islam.

The administrative divisions of France are concerned with the institutional and territorial organization of French territory. These territories are located in many parts of the world. There are many administrative divisions, which may have political, electoral (districts), or administrative objectives. All the inhabited territories are represented in the National Assembly, Senate and Economic and Social Council and their citizens have French citizenship.
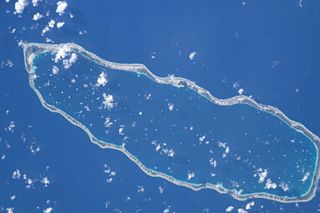
Manihi, or Paeua, is a coral atoll in the Tuamotu Archipelago, part of French Polynesia. It is one of the northernmost of the Tuamotus, located in the King George subgroup. The closest land to Manihi is Ahe Atoll, located 14 km to the west. The population is 650 inhabitants.

Mamoudzou is the capital of the French overseas region and department of Mayotte, in the Indian Ocean. Mamoudzou is the most populated commune (municipality) of Mayotte. It is located on Grande-Terre, the main island of Mayotte.

Mtsamboro is a small fishing town and commune in northwest Mayotte, a French overseas department in the Indian Ocean. Its total population according to the 2012 census is 7,805. Included in the commune are the Choazil Islands and Chissioua Mtsamboro. The main economic activity is fishing and orange production.

Dzaoudzi is a commune in the French overseas department of Mayotte, in the Indian Ocean. The commune of Dzaoudzi, made up of the twin towns of Dzaoudzi and Labattoir, is located on the small island of Petite-Terre. It was previously the capital of Mayotte, but the capital was relocated in 1977 to Mamoudzou, on the island of Grande-Terre (Maore), the main island of Mayotte.

Anaa, Nganaa-nui is an atoll in the Tuamotu archipelago, in French Polynesia. It is located in the north-west of the archipelago, 350 km to the east of Tahiti. It is oval in shape, 29.5 km in length and 6.5 km wide, with a total land area of 38 km² and a population of 504. The atoll is made up by eleven small barren islands with deeper and more fertile soil than other atolls in the Tuamotus. The lagoon is shallow, without entrance, and formed by three main basins. Although it does not have any navigable access, the water of the lagoon renews by several small channels that can be crossed walking.
The French overseas department of Mayotte is divided into 17 communes.

Albon-d'Ardèche is a commune in the Ardèche department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of southern France.
Handrema is the smallest village in the commune of Bandraboua on Mayotte. In 2007, its population was 1,485.

Bran is a small commune in southwestern France situated in the department of Charente-Maritime.

Bilia is a commune in the Corse-du-Sud department of France, on the island of Corsica, within its Corsican single territorial collectivity. It is part of the microregion of Bisogène, the south-western part of the corsican region of Rocca.
Saint-Merd-la-Breuille is a French commune located in the Creuse department, in the New Aquitaine region.
Boky Wéré is a village and rural commune in the Cercle of Macina in the Ségou Region of southern-central Mali. The commune covers an area of approximately 220 square kilometers and includes 14 villages. The commune is bordered to the north by the commune of Monimpébougou, to the east by the commune of Kokry, to the west by the commune of Pogo and to the south by the commune of Kolongo. In the 2009 census the commune had a population of 16,934. The village lies to the north of the Fala de Boky-Wéré, an ancient riverbed that forms part of the Office du Niger irrigation system, and to the south of a large irrigation canal dug in 2009 as part of the Libyan financed Malibya project.
La Higuera is a town and commune in Elqui Province, Coquimbo Region, Chile. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean, the east by the Atacama Region, and the south by the communes of Vicuña and La Serena.

Overseas France consists of all the French-administered territories outside the European continent, mostly relics of the French colonial empire. These territories have varying legal status and different levels of autonomy, although all have representation in both France's National Assembly and Senate, which together make up the French Parliament. Their citizens have French nationality and vote for the president of France. They have the right to vote in elections to the European Parliament. Overseas France includes island territories in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans, French Guiana on the South American continent, and several periantarctic islands as well as a claim in Antarctica.
Borhidi Attila, is a Széchenyi Prize winning Hungarian botanist, ecologist, professor, politician and full member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. He is most noted for his extensive work on plant taxonomy. 1989 to 1992, he was at the Janus Pannonius University Teacher Training Faculty, and from 1992 to 1994 the newly formed Faculty of Science. Between 1997 and 2002 he was Institute director of the Institute of Ecology and Botany. He is a member of the Batthyány Society of Professors.

Mont Choungui is a distinctively conical volcanic mountain in the southern part of the French island of Mayotte, in the Comoro archipelago of the western Indian Ocean. It is the second highest point of the island at 593 m (1,946 ft), the highest being Mont Bénara, and is visible from far out at sea.















