Related Research Articles
Reverse Polish notation (RPN), also known as reverse Łukasiewicz notation, Polish postfix notation or simply postfix notation, is a mathematical notation in which operators follow their operands, in contrast to prefix or Polish notation (PN), in which operators precede their operands. The notation does not need any parentheses for as long as each operator has a fixed number of operands.

HP-UX is Hewlett Packard Enterprise's proprietary implementation of the Unix operating system, based on Unix System V and first released in 1984. Current versions support HPE Integrity Servers, based on Intel's Itanium architecture.
In computing, binary translation is a form of binary recompilation where sequences of instructions are translated from a source instruction set to the target instruction set. In some cases such as instruction set simulation, the target instruction set may be the same as the source instruction set, providing testing and debugging features such as instruction trace, conditional breakpoints and hot spot detection.

The HP 48 is a series of graphing calculators designed and produced by Hewlett-Packard from 1990 until 2003. The series includes the HP 48S, HP 48SX, HP 48G, HP 48GX, and HP 48G+, the G models being expanded and improved versions of the S models. The models with an X suffix are expandable via special RAM and ROM cards. In particular, the GX models have more onboard memory than the G models. The G+ models have more onboard memory only. The SX and S models have the same amount of onboard memory.

The HP 49/50 series are Hewlett-Packard (HP) manufactured graphing calculators. They are the successors of the popular HP 48 series.
RPL is a handheld calculator operating system and application programming language used on Hewlett-Packard's scientific graphing RPN calculators of the HP 28, 48, 49 and 50 series, but it is also usable on non-RPN calculators, such as the 38, 39 and 40 series. Internally, it was also utilized by the 17B, 18C, 19B and 27S.

The HP-42S RPN Scientific is a programmable RPN Scientific hand held calculator introduced by Hewlett-Packard in 1988. It has advanced functions suitable for applications in mathematics, linear algebra, statistical analysis, computer science and others.

The HP-32S was a programmable RPN Scientific Calculator introduced by Hewlett-Packard in 1988 and discontinued in 1991. It continued the tradition of the HP-15C programmable RPN Scientific Calculator. But some functions of the HP-15C were omitted and some were reduced in functionality, so to some extent it is more correct to say that the HP-32S expanded upon the HP-34C. It supported complex math, statistics, probability, and other functions.

HP calculators are various calculators manufactured by the Hewlett-Packard company over the years.
HPE Integrity Servers is a series of server computers produced by Hewlett Packard Enterprise since 2003, based on the Itanium processor. The Integrity brand name was inherited by HP from Tandem Computers via Compaq.
Rocky Mountain BASIC is a dialect of the BASIC programming language created by Hewlett-Packard. It was especially popular for control of automatic test equipment using GPIB. It has several features which are or were unusual in BASIC dialects, such as event-driven operation, extensive external I/O support, complex number support, and matrix manipulation functions. Today, RMB is mainly used in environments where an investment in RMB software, hardware, or expertise already exists.
Programmable calculators are calculators that can automatically carry out a sequence of operations under control of a stored program. Most are Turing complete, and, as such, are theoretically general-purpose computers. However, their user interfaces and programming environments are specifically tailored to make performing small-scale numerical computations convenient, rather than general-purpose use.
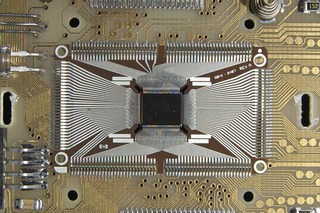
The Saturn family of 4-bit (datapath) microprocessors was developed by Hewlett-Packard in the 1980s first for the HP-71B handheld computer and then later for various HP calculators. It succeeded the Nut family of processors used in earlier calculators. The original Saturn chip was first used in the HP-71B hand-held BASIC-programmable computer, introduced in 1984. Later models of the family powered the popular HP 48 series of calculators. The HP48SX and HP48S were the last models to use genuine Saturn processors manufactured by HP. Later calculator models used Saturn processors manufactured by NEC. The HP 49 series initially used the Saturn CPU as well, until the NEC fab could no longer manufacture the processor for technical reasons in 2003. Therefore, starting with the HP 49g+ model in 2003, the calculators switched to a Samsung S3C2410 processor with an ARM920T core which ran an emulator of the Saturn hardware in software. In 2000, the HP 39G and HP 40G were the last calculators introduced based on the actual NEC fabricated Saturn hardware. The last calculators based on the Saturn emulator were the HP 39gs, HP 40gs and HP 50g in 2006, as well as the 2007 revision of the hp 48gII. The HP 50g, the last calculator utilizing this emulator, was discontinued in 2015 when Samsung stopped producing the ARM processor on which it was based.
HP 39/40 series are graphing calculators from Hewlett-Packard, the successors of HP 38G. The series consists of six calculators, which all have algebraic entry modes, and can perform numeric analysis together with varying degrees of symbolic calculation. All calculators in this series are aimed at high school level students and are characterized by their ability to download APLETs or E-lessons. These are programs of varying complexity which are generally intended to be used in the classroom to enhance the learning of mathematics by the graphical and/or numerical exploration of concepts.
Paul Courbis de Bridiers de Villemor, aka Paul Courbis, is a French programmer, mostly known for reverse engineering the HP-28 and then the HP 48 series of calculators, and writing multiple articles and books disclosing his findings. These books had a surprising success in France.

The HP Superdome is a high-end server computer designed and manufactured by Hewlett Packard Enterprise. The product's most recent version, "Superdome 2," was released in 2010 supporting 2 to 32 sockets and 4 TB of memory. The Superdome used PA-RISC processors when it debuted in 2000. Since 2002, a second version of the machine based on Itanium 2 processors has been marketed as the HP Integrity Superdome.
GNU Emacs is a free software text editor. It was created by GNU Project founder Richard Stallman, based on the Emacs editor developed for Unix operating systems. GNU Emacs has been a central component of the GNU project and a flagship project of the free software movement. Its tag line is "the extensible self-documenting text editor."
In computing HP Roman is a family of character sets consisting of HP Roman Extension, HP Roman-8, HP Roman-9 and several variants. Originally introduced by Hewlett-Packard around 1978, revisions and adaptations were published several times up to 1999. The 1985 revisions were later standardized as IBM codepages 1050 and 1051. Supporting many European languages, the character sets were used by various HP workstations, terminals, calculators as well as many printers, also from third-parties.

The HP 30b is a programmable financial calculator from HP which was released on 7 January 2010. The HP 30b is an advanced version of the HP's prior model HP 20b. Featuring a two line alpha numeric display, ability to input data via Reverse Polish Notation, Algebraic and normal Chain algebraic methods, and twelve digit display.

The HP Prime Graphing Calculator is a graphing calculator introduced by Hewlett-Packard in 2013 and manufactured by HP Inc. until the licensees Moravia Consulting spol. s r.o. and Royal Consumer Information Products, Inc. took over the continued development, manufacturing, distribution, marketing and support in 2022. It was designed with features resembling those of smartphones, such as a full-color touchscreen display and a user interface centered around different applications. It claims to be the world's smallest and thinnest CAS-enabled calculator currently available.
References
- ↑ de Dinechin, Christophe (October 2000). "C++ exception handling for IA-64" (PDF). IEEE Concurrency. ACM. 8 (4): 72–79. doi:10.1109/4434.895109 . Retrieved 2014-02-24.
- ↑ Bocci, Andrea (2004-04-01). "Exception Handling How To" . Retrieved 2014-02-24.
- ↑ "C++ ABI Summary". Mentor Graphics. March 2001. Retrieved 2014-02-24.
- ↑ Manchester, Phil (2008-01-16). "Dip into Concept Programming". The Register . Retrieved 2010-02-03.
- ↑ "First 3D platform videogame". Guinness World Records . Retrieved 2023-06-01.
- ↑ Loguidice, Bill; Barton, Matt (2009). Vintage Games: An Insider Look at the History of Grand Theft Auto, Super Mario, and the Most Influential Games of All Time. Taylor & Francis. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-24081146-8.
- ↑ "Lemmings for HP-48". HPCalc.org. Retrieved 2014-02-24.
- ↑ "PacMan for HP-48". HPCalc.org. Retrieved 2014-02-24.
- ↑ "Interview de Paul Courbis". HP-Network.com. Retrieved 2014-02-24.
- ↑ Loli, Eugenia (2003-07-08). "Interview with Christophe de Dinechin, HP-UX Engineer". OSNews. Retrieved 2014-02-05.
- ↑ "US Patents citing Christophe de Dinechin as an inventor". US Patent Office. Retrieved 2014-02-24.
- ↑ de Dinechin, Christophe (2022). "DB48X on DM42 - RPL runtime for the DM42 calculator, in the spirit of HP48/49/50". DB48X. Archived from the original on 2023-11-03. Retrieved 2023-10-23.
- ↑ de Dinechin, Christophe (2023-02-03). "Reviving Reverse Polish Lisp - Building an open-source HP48-like calculator". FOSDEM . Archived from the original on 2023-10-03. Retrieved 2023-10-03. (NB. An improved derivative of RPL called DB48X for the SwissMicros DM42 and DM32.)
- ↑ "Emacs on Aqua". SourceForge. Retrieved 2014-02-24.
- ↑ "Drivers for the HP DE200C". Grenouille Bouillie. Retrieved 2014-02-24.
- ↑ "Tao3D". Sourceforge. Retrieved 2023-06-01.
- ↑ Ravelin, Antoine; de Dinechin, Christophe (2019-10-15). Informagie. Roman d'anticipation - Ou pas (in French) (1 ed.). Christophe de Dinechin. ISBN 978-1-69985081-7.
- ↑ Réunifions la physique! Du jeu vidéo à une vision pixelisée de l'univers intégrant la Théorie de la Relativité et la Mécanique Quantique (in French) (1 ed.). Dés-Cubes Editions. 2023-05-16. ISBN 979-8-39488223-4 . Retrieved 2023-06-01.
- ↑ A theory of incomplete measurements: Towards a unified vision of the laws of physics (1 ed.). Dés-Cubes Editions. 2022-03-09. ISBN 979-8-42773619-0 . Retrieved 2023-06-01.