Related Research Articles

The ovary is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocrine glands, secreting various hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause.

In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation in which an egg is combined with sperm in vitro. The process involves monitoring and stimulating a woman's ovulatory process, then removing an ovum or ova from her ovaries and enabling a man's sperm to fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After a fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy.
Reproductive technology encompasses all current and anticipated uses of technology in human and animal reproduction, including assisted reproductive technology (ART), contraception and others. It is also termed Assisted Reproductive Technology, where it entails an array of appliances and procedures that enable the realization of safe, improved and healthier reproduction. While this is not true of all people, for an array of married couples, the ability to have children is vital. But through the technology, infertile couples have been provided with options that would allow them to conceive children.

Intracytoplasmic sperm injection is an in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure in which a single sperm cell is injected directly into the cytoplasm of an egg. This technique is used in order to prepare the gametes for the obtention of embryos that may be transferred to a maternal uterus. With this method, the acrosome reaction is skipped.

An ovarian follicle is a roughly spheroid cellular aggregation set found in the ovaries. It secretes hormones that influence stages of the menstrual cycle. In humans, women have approximately 200,000 to 300,000 follicles at the time of puberty, each with the potential to release an egg cell (ovum) at ovulation for fertilization. These eggs are developed once every menstrual cycle with around 450–500 being ovulated during a woman's reproductive lifetime.

The zona pellucida is the specialized area surrounding mammalian oocytes (eggs). It is also known as an egg coat. The zona pellucida is essential for oocyte growth and fertilization.
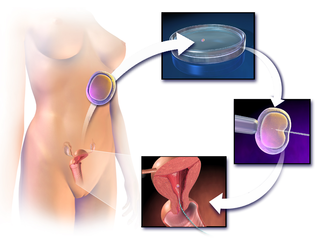
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) includes medical procedures used primarily to address infertility. This subject involves procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), and cryopreservation of gametes and embryos, and the use of fertility medication. When used to address infertility, ART may also be referred to as fertility treatment. ART mainly belongs to the field of reproductive endocrinology and infertility. Some forms of ART may be used with regard to fertile couples for genetic purpose. ART may also be used in surrogacy arrangements, although not all surrogacy arrangements involve ART. The existence of sterility will not always require ART to be the first option to consider, as there are occasions when its cause is a mild disorder that can be solved with more conventional treatments or with behaviors based on promoting health and reproductive habits.
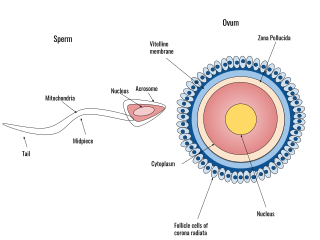
Human fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm, occurring primarily in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. The result of this union leads to the production of a fertilized egg called a zygote, initiating embryonic development. Scientists discovered the dynamics of human fertilization in the 19th century.

Gregory Michael Fahy is a California-based cryobiologist, biogerontologist, and businessman. He is Vice President and Chief Scientific Officer at 21st Century Medicine, Inc, and has co-founded Intervene Immune, a company developing clinical methods to reverse immune system aging. He was the 2022–2023 president of the Society for Cryobiology.

Oocyte cryopreservation is a procedure to preserve a woman's eggs (oocytes). The technique is often used to delay pregnancy. At the time pregnancy is desired, the eggs can be thawed, fertilized, and transferred to the uterus as embryos. Many studies have suggested infertility problems as germ cell deterioration related to aging. The procedure's success rate varies according to the woman's age, health, and genetic factors. The first human birth of oocyte cryopreservation was reported in 1986.

In vitro maturation (IVM) is the technique of letting the contents of ovarian follicles and the oocytes inside mature in vitro. It can be offered to women with infertility problems, combined with In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), offering women pregnancy without ovarian stimulation.
Transvaginal oocyte retrieval (TVOR), also referred to as oocyte retrieval (OCR), is a technique used in in vitro fertilization (IVF) in order to remove oocytes from an ovary, enabling fertilization outside the body. Transvaginal oocyte retrieval is more properly referred to as transvaginal ovum retrieval when the oocytes have matured into ova, as is normally the case in IVF. It can be also performed for egg donation, oocyte cryopreservation and other assisted reproduction technology such as ICSI.
Fertility preservation is the effort to help cancer patients retain their fertility, or ability to procreate. Research into how cancer, ageing and other health conditions effect reproductive health and preservation options are growing. Specifically sparked in part by the increase in the survival rate of cancer patients.

Cryopreservation or cryoconservation is a process where biological material - cells, tissues, or organs - are frozen to preserve the material for an extended period of time. At low temperatures any cell metabolism which might cause damage to the biological material in question is effectively stopped. Cryopreservation is an effective way to transport biological samples over long distances, store samples for prolonged periods of time, and create a bank of samples for users. Molecules, referred to as cryoprotective agents (CPAs), are added to reduce the osmotic shock and physical stresses cells undergo in the freezing process. Some cryoprotective agents used in research are inspired by plants and animals in nature that have unique cold tolerance to survive harsh winters, including: trees, wood frogs, and tardigrades. The first human corpse to be frozen with the hope of future resurrection was James Bedford's, a few hours after his cancer-caused death in 1967. Bedford's is the only cryonics corpse frozen before 1974 still frozen today.
The Genetics & IVF Institute (GIVF) is an international provider of infertility and genetics services and products, and also engages in biomedical research in these fields. The Institute was founded in 1984 by Dr. Joseph D. Schulman and associates. GIVF headquarters are in Fairfax, VA, US, and its facilities include locations in Pennsylvania, Minnesota, California, and Texas in the United States, as well as in China, Mexico, and several other countries.
Ovarian tissue cryopreservation is cryopreservation of tissue of the ovary of a female.
Embryos may be preserved through cryopreservation, generally at an embryogenesis stage corresponding to pre-implantation, that is, from fertilisation to the blastocyst stage.
The history of in vitro fertilisation (IVF) goes back more than half a century. In 1959 the first birth in a nonhuman mammal resulting from IVF occurred, and in 1978 the world's first baby conceived by IVF was born. As medicine advanced, IVF was transformed from natural research to a stimulated clinical treatment. There have been many refinements in the IVF process, and today millions of births have occurred with the help of IVF all over the world.

Evelyn Elizabeth Telfer is a reproductive biologist and professor at the University of Edinburgh. She leads a research team which has successfully grown immature human eggs to maturity in the lab, and discovered that human ovaries are capable of growing new eggs. In 2018 she was named one of Porter magazine's Incredible Women of 2018. In January 2019 she delivered the Anne McLaren Memorial Lecture at the Joint Fertility Societies Meeting in Birmingham: Fertility 2019. The Society of Reproduction and Fertility (SRF) presented her with their Distinguished Scientist award. Professor Telfer was presented with the Marshall Medal by SRF at Fertility 2023 in Belfast in recognition of her world leading contributions to the field of ovarian function and fertility preservation. The Marshall Medal is the Society’s premier award established in 1963 to commemorate the life and work of the eminent physiologist FHA Marshall.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer/questioning people people wishing to have children may use assisted reproductive technology. In recent decades, developmental biologists have been researching and developing techniques to facilitate same-sex reproduction.
References
- ↑ "Our Founder". ACRM | Advanced Centre for Reproductive Medicine. 6 July 2017. Retrieved 15 February 2019.
- ↑ "History of ICS Singapore Section | International College of Surgeons Singapore Section". www.ics-sg.org. Retrieved 15 February 2019.
- ↑ Gook, Debra A. (1 September 2011). "History of oocyte cryopreservation". Reproductive BioMedicine Online. 23 (3): 281–289. doi:10.1016/j.rbmo.2010.10.018. ISSN 1472-6483. PMID 21549640.
- ↑ "Singapore's First Sextuplets Born To Indonesian Couple". Utusan Online. Archived from the original on 15 February 2019. Retrieved 15 February 2019.