
The Church of Ireland is a Christian church in Ireland, and an autonomous province of the Anglican Communion. It is organised on an all-Ireland basis and is the second-largest Christian church on the island after the Roman Catholic Church. Like other Anglican churches, it has retained elements of pre-Reformation practice, notably its episcopal polity, while rejecting the primacy of the pope.

Saint Patrick's Cathedral in Dublin, Ireland, founded in 1191 as a Roman Catholic cathedral, is currently the national cathedral of the Church of Ireland. Christ Church Cathedral, also a Church of Ireland cathedral in Dublin, is designated as the local cathedral of the Diocese of Dublin and Glendalough.

Christ Church Cathedral, more formally The Cathedral of the Holy Trinity, is the cathedral of the United Dioceses of Dublin and Glendalough and the cathedral of the ecclesiastical province of the United Provinces of Dublin and Cashel in the (Anglican) Church of Ireland. It is situated in Dublin, Ireland, and is the elder of the capital city's two medieval cathedrals, the other being St Patrick's Cathedral.

Armagh is the county town of County Armagh and a city in Northern Ireland, as well as a civil parish. It is the ecclesiastical capital of Ireland – the seat of the Archbishops of Armagh, the Primates of All Ireland for both the Roman Catholic Church and the Church of Ireland. In ancient times, nearby Navan Fort was a pagan ceremonial site and one of the great royal capitals of Gaelic Ireland. Today, Armagh is home to two cathedrals and the Armagh Observatory, and is known for its Georgian architecture.

Richard Robinson, 1st Baron Rokeby, was an Anglo-Irish churchman.
The Anglican Archbishop of Armagh is the ecclesiastical head of the Church of Ireland, bearing the title Primate of All Ireland, the metropolitan of the Province of Armagh and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Armagh.
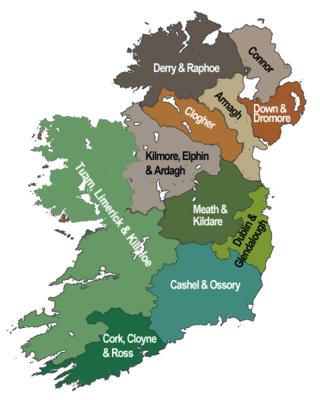
The United Provinces of Dublin and Cashel, commonly called the Province of Dublin, and also known as the Southern Province, is one of the two ecclesiastical provinces that together form the Church of Ireland; the other is the Province of Armagh. The province has existed since 1833 when the ancient Province of Dublin was merged with the Province of Cashel. Its metropolitan bishop is the Archbishop of Dublin.

Michael Geoffrey St Aubyn Jackson is a Church of Ireland Anglican bishop. Since 2011, he has served as the Archbishop of Dublin and Bishop of Glendalough in the Church of Ireland. He is also the co-chairman of the Porvoo Communion of Anglican and Lutheran churches.

The Archdiocese of Dublin is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church located in the eastern part of Ireland. Its archepiscopal see includes the republic's capital city – Dublin. The cathedral church of the archdiocese is St Mary's Pro-Cathedral. Dublin was formally recognised as a metropolitan province in 1152 by the Synod of Kells. Its second archbishop, Lorcán Ua Tuathail, is also its patron saint.

The United Dioceses of Dublin and Glendalough is a diocese of the Church of Ireland in the east of Ireland. It is headed by the Archbishop of Dublin, who is also styled the Primate of Ireland. The diocesan cathedral is Christ Church Cathedral, Dublin.

The Archbishop of Dublin is a senior bishop in the Church of Ireland, second only to the Archbishop of Armagh. The archbishop is the diocesan bishop of the United Dioceses of Dublin and Glendalough and the metropolitan bishop of the Province of Dublin, which covers the southern half of Ireland, and he is styled Primate of Ireland.
The Archbishop of Dublin is the head of the Archdiocese of Dublin in the Catholic Church, responsible for its spiritual and administrative needs. The office has existed since 1152, in succession to a regular bishopric since 1028. The archdiocese is the metropolitan see of the ecclesiastical province of Dublin, and the archbishop is also styled the Primate of Ireland. The cathedral church of the archdiocese is Saint Mary's Pro-Cathedral in Dublin city, although the Church formally claims Christ Church as its cathedral, and the archbishop's residence is Archbishop's House in Drumcondra.
William Reeves was an Irish antiquarian and the Church of Ireland Bishop of Down, Connor and Dromore from 1886 until his death. He was the last private keeper of the Book of Armagh and at the time of his death was President of the Royal Irish Academy.

Charles Frederick D'Arcy was a Church of Ireland bishop. He was the Bishop of Clogher from 1903 to 1907 when he was translated to become Bishop of Ossory, Ferns and Leighlin before then becoming the Bishop of Down, Connor and Dromore. He was then briefly the Archbishop of Dublin and finally, from 1920 until his death, Archbishop of Armagh. He was also a theologian, author and botanist.
John Garvey (1527–1595) was an Irish Protestant Bishop of Kilmore and Archbishop of Armagh.
Brabazon William Disney was an Irish Dean in the middle of the 19th century.
Joseph Robinson was an Irish composer, baritone, conductor, and teacher.
John Freind Robinson, 1st Baronet was Archdeacon of Armagh from 1786 until his resignation in 1797.
Edward Joseph McParland is an Irish architectural historian and author. He was elected as Pro-Chancellor of University of Dublin, Trinity College in 2013, and continues to give lectures after his retirement in 2008. McParland is the co-founder of the Irish Architectural Archive which was established in 1976, and he has contributed extensively to architectural conservation in Ireland.









