
Chyton, according to Ephorus, was a new city [1] founded in Epirus during the 4th century BC. The city was established by Ionians from Klazomenai.
Its site is unlocated. [2]

Chyton, according to Ephorus, was a new city [1] founded in Epirus during the 4th century BC. The city was established by Ionians from Klazomenai.
Its site is unlocated. [2]

Epirus is a geographical and historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay of Vlorë and the Acroceraunian mountains in the north to the Ambracian Gulf and the ruined Roman city of Nicopolis in the south. It is currently divided between the region of Epirus in northwestern Greece and the counties of Gjirokastër, Vlorë, and Berat in southern Albania. The largest city in Epirus is Ioannina, seat of the region of Epirus, with Gjirokastër the largest city in the Albanian part of Epirus.
In Greek mythology, Helenus was a son of King Priam and Queen Hecuba of Troy, and the twin brother of the prophetess Cassandra. He was also called Scamandrios. According to legend, Cassandra, having been given the power of prophecy by Apollo, taught it to her brother. Like Cassandra, he was always right, but unlike her, others believed him.
Ephorus of Cyme was an ancient Greek historian known for his universal history.

Northern Epirus is a term used to refer to those parts of the historical region of Epirus, in the western Balkans, which today are part of Albania. The term is used mostly by Greeks and is associated with the existence of a substantial ethnic Greek population in the region. It also has connotations with political claims on the territory on the grounds that it was held by Greece and in 1914 was declared an independent state by the local Greeks against annexation to the newly founded Albanian principality. The term is typically rejected by most Albanians for its irredentist associations.

Pyrrhus was a Greek king and statesman of the Hellenistic period. He was king of the Greek tribe of Molossians, of the royal Aeacid house, and later he became king of Epirus. He was one of the strongest opponents of early Rome. Several of his victorious battles caused him unacceptably heavy losses, from which the term Pyrrhic victory was coined.

Ioannina, often called Yannena within Greece, is the capital and largest city of the Ioannina regional unit and of Epirus, an administrative region in north-western Greece. According to the 2011 census, the city population was 65,574, while the municipality had 112,486 inhabitants. It lies at an elevation of approximately 500 metres above sea level, on the western shore of lake Pamvotis (Παμβώτις). Ioannina is located 410 km (255 mi) northwest of Athens, 260 kilometres southwest of Thessaloniki and 80 km east of the port of Igoumenitsa in the Ionian Sea.

Nicopolis or Actia Nicopolis was the capital city of the Roman province of Epirus Vetus. It was located in the western part of the modern state of Greece. The city was founded in 29 BC by Caesar Augustus in commemoration of his victory in 31 BC over Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium nearby. It was soon made the major city of the wider region of Epirus region. Many impressive ruins of the ancient city may be visited today.

Sarandë, also Saranda, is a coastal town in Albania. Geographically, it is situated on an open sea gulf of the Ionian Sea in the central Mediterranean, about 14 km (8.7 mi) east of the northern end of the island of Corfu. Stretching along the Albanian Ionian Sea Coast, Saranda typically has over 300 sunny days a year.
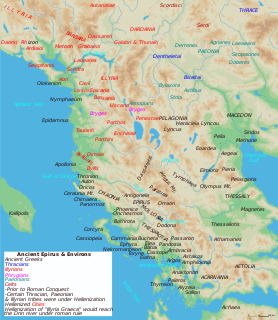
The Molossians were an ancient Greek tribe and kingdom that inhabited the region of Epirus since the Mycenaean era. Together with the Chaonians and the Thesprotians, they formed the main tribes of the northwestern Greek group. On their northern frontier, they neighbored the Chaonians and on their southern frontier neighbored the kingdom of the Thesprotians. The Molossians were part of the League of Epirus until they sided against Rome in the Third Macedonian War.
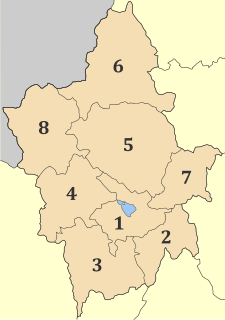
Ioannina is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the Epirus region. Its capital is the city of Ioannina. It is the largest regional unit in Epirus, and one of the largest regional units of Greece, with population 167,901, according to 2011 census.

Preveza is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the Epirus region. Its capital is the town of Preveza.

Arta is a city in northwestern Greece, capital of the regional unit of Arta, which is part of Epirus region. The city was known in ancient times as Ambracia. Arta is known for the medieval bridge over the Arachthos River. Arta is also known for its ancient sites from the era of Pyrrhus of Epirus and its well-preserved 13th-century castle. Arta's Byzantine history is reflected in its many Byzantine churches; perhaps the best known is the Panagia Paregoretissa, built about 1290 by Despot Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas. The city is the seat of the Technological Educational Institute of Epirus.

Epirus, is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region in northwestern Greece. It borders the regions of Western Macedonia and Thessaly to the east, West Greece to the south, the Ionian Sea and Ionian Islands to the west and Albania to the north. The region has an area of about 9,200 km2 (3,600 sq mi). It is part of the wider historical region of Epirus, which overlaps modern Albania and Greece but lies mostly within Greek territory.

Cebrene, also spelled Cebren, was an ancient Greek city in the middle Skamander valley in the Troad region of Anatolia. According to some scholars, the city's name was changed to Antiocheia in the Troad for a period during the 3rd century BCE. Its archaeological remains have been located on Çal Dağ in the forested foothills of Mount Ida, approximately 7 km to the south of the course of the Skamander. The site was first identified by the English amateur archaeologist Frank Calvert in 1860.

Gitanae or Gitana, or Gitona (Γίτωνα), or Titana, was a city of ancient Epirus, described by Livy as being near Corcyra, and about 10 miles from the coast. as a place of meeting of the Epirote League. It is not mentioned by any other ancient writer, and it was conjectured that the word is a corrupt form of Chyton, which Ephorus spoke of as a place in Epirus colonised by Ionians from Klazomenai.

Byllis or Bullis or Boullis (Βουλλίς) was an ancient city located in the region of Illyria. The remains of Byllis are situated north-east of Vlorë, 25 kilometers from the sea in Hekal, Fier County, Albania.

Epirus was an ancient Greek state, located in the geographical region of Epirus in the western Balkans. The homeland of the ancient Epirotes was bordered by the Aetolian League to the south, Thessaly and Macedonia to the east, and Illyrian tribes to the north. For a brief period, the Epirote king Pyrrhus managed to make Epirus a powerful state Greek world, comparable to the likes of Macedon and Rome. His armies marched against Rome during an unsuccessful campaign in Italy.

The Vilayet of Janina, Yanya or Ioannina was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire, established in 1867. In the late 19th century, it reportedly had an area of 18,320 square miles (47,400 km2). It was created by merging the Pashalik of Yanina and the Pashalik of Berat with the sanjaks of Janina, Berat, Ergiri, Preveze, Tırhala and Kesriye. Kesriye was later demoted to kaza and bounded to Monastir Vilayet and Tırhala was given to Greece in 1881.
Chytrium or Chytrion (Χυτριόν), or Chytrum or Chytron (Χυτρόν), also known as Chytum or Chyton (Χυτόν) was a town of ancient Ionia. Strabo tells us that it was here that the city of Clazomenae was initially founded.
| This article about a location in ancient Epirus is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |