A class action, also known as a class action lawsuit, class suit, or representative action, is a type of lawsuit where one of the parties is a group of people who are represented collectively by a member or members of that group. The class action originated in the United States and is still predominantly an American phenomenon, but Canada, as well as several European countries with civil law, have made changes in recent years to allow consumer organizations to bring claims on behalf of consumers.
Procedural law, adjective law, in some jurisdictions referred to as remedial law, or rules of court, comprises the rules by which a court hears and determines what happens in civil, lawsuit, criminal or administrative proceedings. The rules are designed to ensure a fair and consistent application of due process or fundamental justice to all cases that come before a court.
In law, a judgment is a decision of a court regarding the rights and liabilities of parties in a legal action or proceeding. Judgments also generally provide the court's explanation of why it has chosen to make a particular court order.
A civil code is a codification of private law relating to property, family, and obligations.

Legal history or the history of law is the study of how law has evolved and why it has changed. Legal history is closely connected to the development of civilisations and operates in the wider context of social history. Certain jurists and historians of legal process have seen legal history as the recording of the evolution of laws and the technical explanation of how these laws have evolved with the view of better understanding the origins of various legal concepts; some consider legal history a branch of intellectual history. Twentieth-century historians viewed legal history in a more contextualised manner – more in line with the thinking of social historians. They have looked at legal institutions as complex systems of rules, players and symbols and have seen these elements interact with society to change, adapt, resist or promote certain aspects of civil society. Such legal historians have tended to analyse case histories from the parameters of social-science inquiry, using statistical methods, analysing class distinctions among litigants, petitioners and other players in various legal processes. By analyzing case outcomes, transaction costs, and numbers of settled cases, they have begun an analysis of legal institutions, practices, procedures and briefs that gives a more complex picture of law and society than the study of jurisprudence, case law and civil codes can achieve.
The Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch, abbreviated BGB, is the civil code of Germany, codifying most generally-applicably private law. In development since 1881, it became effective on 1 January 1900, and was considered a massive and groundbreaking project.

The Federal Court of Justice is the highest court of civil and criminal jurisdiction in Germany. Its primary responsibility is the final appellate review of decisions by lower courts for errors of law. While, legally, a decision by the Federal Court of Justice is only binding with respect to the individual case in which it enters, de facto the court's interpretation of the law is followed by lower courts with almost no exception. Decisions handed down by the Federal Court of Justice can only be vacated by the Federal Constitutional Court for violating a provision of the German constitution, the Basic Law.
As in most countries, Germany has a standard way of citing its legal codes and case law; an essentially identical system of citation is also used in Austria.

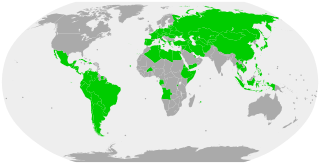
Civil law is a legal system rooted in the Roman Empire and was comprehensively codified and disseminated starting in the 19th century, most notably with France's Napoleonic Code (1804) and Germany's Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch (1900). Unlike common law systems, which rely heavily on judicial precedent, civil law systems are characterized by their reliance on legal codes that function as the primary source of law. Today, civil law is the world's most common legal system, practiced in about 150 countries.
The Law of the People's Republic of China, officially referred to as the socialist rule of law with Chinese characteristics, is the legal regime of China, with the separate legal traditions and systems of mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macau.

A code of law, also called a law code or legal code, is a systematic collection of statutes. It is a type of legislation that purports to exhaustively cover a complete system of laws or a particular area of law as it existed at the time the code was enacted, by a process of codification. Though the process and motivations for codification are similar in different common law and civil law systems, their usage is different.

The judicial system of Turkey is defined by Articles 138 to 160 of the Constitution of Turkey.
The law of Germany, that being the modern German legal system, is a system of civil law which is founded on the principles laid out by the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, though many of the most important laws, for example most regulations of the civil code were developed prior to the 1949 constitution. It is composed of public law, which regulates the relations between a citizen/person and the state or two bodies of the state, and the private law, (Privatrecht) which regulates the relations between two people or companies. It has been subject to a wide array of influences from Roman law, such as the Justinian Code the Corpus Juris Civilis, and to a lesser extent the Napoleonic Code.

In contract law, an arbitration clause is a clause in a contract that requires the parties to resolve their disputes through an arbitration process. Although such a clause may or may not specify that arbitration occur within a specific jurisdiction, it always binds the parties to a type of resolution outside the courts, and is therefore considered a kind of forum selection clause.

The Reichsgericht was the supreme criminal and civil court of Germany from 1879 to 1945, encompassing the periods of the German Empire, the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany. It was based in Leipzig.
Zivilprozessordnung (ZPO) is the Austrian code of civil procedure. It was drafted in 1895 by Franz Klein, and superseded the Josephinian Common Court Regulations of 1781.
Rudolf Arnold Nieberding was a German jurist and politician.

The Supreme Court of Justice is the final court of appeal of Austria in civil and criminal matters. Along with the Supreme Administrative Court and the Constitutional Court, it is one of Austria's three apex courts.
Legal aid in Germany is "embedded in the court system and is seen as a part of this". Germany was the first country to provide free legal aid representation for the poor in 1919, and represents the archetype of the so-called judicare system.







