Metis or Métis, meaning "mixed" in French, may refer to:
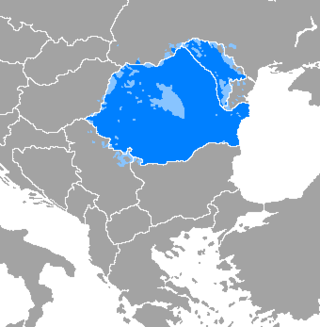
Romanian is the official and main language of Romania and Moldova. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin which separated from the Western Romance languages in the course of the period from the 5th to the 8th centuries. To distinguish it within the Eastern Romance languages, in comparative linguistics it is called Daco-Romanian as opposed to its closest relatives, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian. It is also spoken as a minority language by stable communities in the countries surrounding Romania, and by the large Romanian diaspora. In total, it is spoken by 25 million people as a first language.
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
A palatine or palatinus is a high-level official attached to imperial or royal courts in Europe since Roman times. The term palatinus was first used in Ancient Rome for chamberlains of the Emperor due to their association with the Palatine Hill. The imperial palace guard, after the rise of Constantine I, were also called the Scholae Palatinae for the same reason. In the Early Middle Ages the title became attached to courts beyond the imperial one; one of the highest level of officials in the papal administration were called the judices palatini. Later the Merovingian and Carolingian dynasties had counts palatine, as did the Holy Roman Empire. Related titles were used in Hungary, Poland, Lithuania, the German Empire, and the County of Burgundy, while England, Ireland, and parts of British North America referred to rulers of counties palatine as palatines.
Queen Elizabeth, Queen Elisabeth or Elizabeth the Queen may refer to:

William is a masculine given name of French origin. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066, and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Liam, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie. Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina.

Petro Mohyla was the Metropolitan of Kiev, Galicia and all Rus' in the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople in the Eastern Orthodox Church from 1633 to 1646.

Siret is a town, municipality and former Latin bishopric in Suceava County, northeastern Romania. It is situated in the historical region of Bukovina. Siret is the 11th largest urban settlement in the county, with a population of 6,708 inhabitants, according to the 2021 census. It is one of the oldest towns in Romania and was the capital of the medieval Principality of Moldavia during the late 14th century. Furthermore, the town administers two villages: Mănăstioara and Pădureni.
App, Apps or APP may refer to:
Romania is a country located in Central and Eastern Europe.

Baia is a commune in Suceava County, in the historical region of Western Moldavia, northeastern Romania with a population of 6,793. It is composed of two villages, namely Baia and Bogata. Located on the Moldova River, it was one of the earliest urban settlements in Moldavia.
Our Lady often refers to:
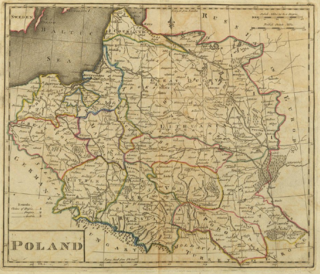
The ethnonyms for the Poles (people) and Poland include endonyms and exonyms. Endonyms and most exonyms for Poles and Poland derive from the name of the West Slavic tribe of Polans (Polanie), while in some languages the exonyms for Poland to derive from the name of another tribe – the Lendians (Lędzianie).
Libertas is the Roman goddess and personification of liberty.
Reform is beneficial change.
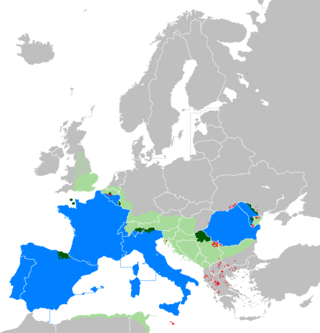
The legacy of the Roman Empire has been varied and significant. The Roman Empire, built upon the legacy of other cultures, has had long-lasting influence with broad geographical reach on a great range of cultural aspects, including state institutions, law, values, religious beliefs, technological advances, engineering and language.
Royal free city or free royal city was the official term for the most important cities in the Kingdom of Hungary from the late 12th century until the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. These cities were granted certain privileges by the king to rule out the possibility of the control of the Hungarian nobility, hence "royal", and exercised some self-government in relation to their internal affairs, hence "free". From the late 14th century, the elected envoys of the Royal free cities participated in the sessions of the Hungarian parliament, thus they became part of the legislature. The list include also cities in the Kingdom of Croatia and the Banate of Bosnia, which were part of the Lands of the Hungarian Crown.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.






