Related Research Articles

A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring and recording information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include traditional culture, business, supplies, agricultural, and traffic censuses. The United Nations defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. United Nations recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications and other useful information to co-ordinate international practices.

A developed country, industrialized country, more developed country, or more economically developed country (MEDC), is a sovereign state that has a developed economy and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), the per capita income, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living. Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate.
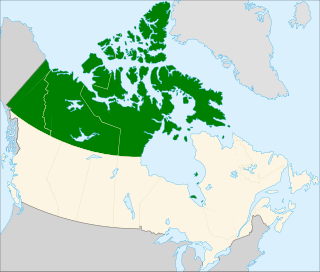
Northern Canada, colloquially the North, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut. Similarly, the Far North may refer to the Canadian Arctic: the portion of Canada that lies north of the Arctic Circle, east of Alaska and west of Greenland. This area covers about 39% of Canada's total land area, but has less than 1% of Canada's population.

The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education, and per capita income indicators, which are used to rank countries into four tiers of human development. A country scores a higher HDI when the lifespan is higher, the education level is higher, and the gross national income GNI (PPP) per capita is higher. It was developed by Indian economist Amartya Sen and then utilised by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq and was further used to measure a country's development by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)'s Human Development Report Office.

Public finance is the study of the role of the government in the economy. It is the branch of economics that assesses the government revenue and government expenditure of the public authorities and the adjustment of one or the other to achieve desirable effects and avoid undesirable ones. The purview of public finance is considered to be threefold, consisting of governmental effects on:
- The efficient allocation of available resources;
- The distribution of income among citizens; and
- The stability of the economy.
Vital statistics is accumulated data gathered on live births, deaths, fetal deaths, marriages and divorces. The most common way of collecting information on these events is through civil registration, an administrative system used by governments to record vital events which occur in their populations. Efforts to improve the quality of vital statistics will therefore be closely related to the development of civil registration systems in countries.
The System of National Accounts is an international standard system of national accounts, the first international standard being published in 1953. Handbooks have been released for the 1968 revision, the 1993 revision, and the 2008 revision. The System of National Accounts, in its various released versions, frequently with significant local adaptations, has been adopted by many nations. It continues to evolve and is maintained by the United Nations, the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and the Statistical Office of the European Communities
The United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD), formerly the United Nations Statistical Office, serves under the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA) as the central mechanism within the Secretariat of the United Nations to supply the statistical needs and coordinating activities of the global statistical system. The Division is overseen by the United Nations Statistical Commission, established in 1947, as the apex entity of the global statistical system and highest decision making body for coordinating international statistical activities. It brings together the Chief Statisticians from member states from around the world.
Standard International Trade Classification (SITC) is a classification of goods used to classify the exports and imports of a country to enable comparing different countries and years. The classification system is maintained by the United Nations. The SITC classification, is currently at revision four, which was promulgated in 2006.

The United Nations geoscheme is a system which divides the countries of the world into regional and subregional groups. It was devised by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD) based on the M49 coding classification.
Classification of Individual Consumption According to Purpose (COICOP) is a Reference Classification published by the United Nations Statistics Division that divides the purpose of individual consumption expenditures incurred by three institutional sectors, namely households, non-profit institutions serving households, and general government.
Sir Harry Campion, KCB, CBE was a British statistician and the first director of what was the Central Statistical Office of the United Kingdom. He was also first director of the United Nations Statistical Office. He played a leading role in the development of official statistics, nationally and internationally, after the Second World War.
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) is a ministry of Government of India concerned with coverage and quality aspects of statistics released. The surveys conducted by the Ministry are based on scientific sampling methods.

The Summer Paralympic Games or the Games of the Paralympiad, are an international multi-sport event where athletes with physical disabilities compete. This includes athletes with mobility disabilities, amputations, blindness, and cerebral palsy. The Paralympic Games are held every four years, organized by the International Paralympic Committee. Medals are awarded in each event, with gold medals for first place, silver for second and bronze for third, a tradition that the Olympic Games started in 1904.
Water accounting is a discipline that seeks to provide comprehensive, consistent and comparable policy relevant information related to water. Based on the experience of more than fifty years of national accounts, the discipline that provides the elements to calculate the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD) developed the System of Environmental and Economic Accounting for Water (SEEA-Water), which has been adopted by the United Nations Statistical Commission (UNSC) as a statistical interim standard in 2007.
System of Environmental-Economic Accounting (SEEA) is a framework to compile statistics linking environmental statistics to economic statistics. SEEA is described as a satellite system to the United Nations System of National Accounts (SNA). This means that the definitions, guidelines and practical approaches of the SNA are applied to the SEEA. This system enables environmental statistics to be compared to economic statistics as the system boundaries are the same after some processing of the input statistics. By analysing statistics on the economy and the environment at the same time it is possible to show different patterns of sustainability for production and consumption. It can also show the economic consequences of maintaining a certain environmental standard.
Fiscal transparency refers to the publication of information on how governments raise, spend, and manage public resources. More specifically, it means publication of high quality information on how governments raise taxes, borrow, spend, invest, and manage public assets and liabilities.
References
- ↑ "United Nations Statistics Division - Classifications Registry". unstats.un.org. Retrieved 2019-04-09.